
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
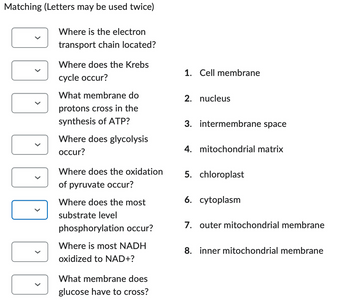
Transcribed Image Text:Matching (Letters may be used twice)
DD DDD DD
Where is the electron
transport chain located?
Where does the Krebs
cycle occur?
What membrane do
protons cross in the
synthesis of ATP?
Where does glycolysis
occur?
Where does the oxidation
of pyruvate occur?
Where does the most
substrate level
phosphorylation occur?
Where is most NADH
oxidized to NAD+?
What membrane does
glucose have to cross?
1. Cell membrane
2. nucleus
3. intermembrane space
4. mitochondrial matrix
5. chloroplast
6. cytoplasm
7. outer mitochondrial membrane
8. inner mitochondrial membrane
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
numbers may only be used twice. I see 8 3 times
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
numbers may only be used twice. I see 8 3 times
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Hold Cycle continued) Complete the summaries below by filling in the blanks. 1. Pyruvate oxidation atom is removed via atoms, creating 2. Citric acid cycle enters the mitochondrion from the cytoplasm. One and becomes attached to the remaining six-carbon compound enters the cycle and then combines with which then enters the citric acid cycle. is removed using undergoes a number of reactions, releasing is eventually converted into During the eight steps of the citric cycle, and number of steps. can be used again during the citric acid cycle. to make t in a SOarrow_forwardDuring glycolysis, transition, and the citric acid cycle: How many ATP (or GTP) is made in each step? Why is CO2 made in some steps? (Hint: this is NOT from O2) Which steps make activated carrier molecules? What are they “carrying”?arrow_forwardONLY Answer #4arrow_forward
- Referring to the diagram above, where does pathway "A" occur? Where does pathway "B" occur? Remember to include BOTH prokaryotes and eukaryotes in your answer.arrow_forward2 ATP + HCO₂ + NH₂ 140 CPS-1 H₂N OPO,2 H₂N 2 ADP, P CH₂ HỘ NHỎ coo 1 0=UN NH₂ P OTC ARG1 H₂O NH₂ H₂H Coo NH CHI CH₂ Coo CH₂ 7 CH₂ HỘ NHĨ coo 4 5 Which of the following is a carbon input to this pathway? (Numbers refer to the above key) 1 2 3 4 None of these is a carbon input NH CH₂ CH₂ CH₂ HỒ NH coo ASL -8---8 CH₂ HỘ NHĨ coo CH ASS ATP PP L-Asp AMP 1 L-ornithine 2 carbamoyl phosphate 3 L-citrulline 4 argininosuccinate 5 fumarate 6 L-arginine 7 urea L-Asp L-aspartate CPS-1 carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I OTC Ornithine transcarbamoylase ASS argininosuccinate synthetase ASL argininosuccinate lyase ARG1 arginase 1 OH OH NH₂arrow_forward333arrow_forward
- answers below are somewhat right but not alll are correct.arrow_forward4) What are the different components of the electron transport chain, where are they situated in cells? Write down the ultimate electron donor and acceptor for each component. How is the released free energy immediately stored during each of these oxidation-reduction reactions (as the reactions are executed)?arrow_forward1.provide a solution using a table, listing all the specific individual reactions that will generate ATP either by substrate level phosphorylation (SLP) or by oxidative phosphorylation (OP). 2. Shall the given question require a shuttle system, please use both and indicate the net ATP for each. 3. Get the net ATP for each question given you Specific reaction Number of ATP (+ or -) Question 1: fructose 6-phosphate to 2acetyl coa Question 2: fructose 6-phosphate to 6C02 Question 3: fructose 6-phosphate to 2succinyl coaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education