
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase, such as edrophonium, are used to treat Alzheimer’s disease. The substrate for acetylcholinesterase is acetylcholine. Structures are attached.
- What kind of inhibitor is edrophonium? Explain.
- Can inhibition by edrophonium be overcome in vitro by increasing the substrate concentration? Explain.
- Does this inhibitor bind reversibly or irreversibly to the enzyme? Explain.
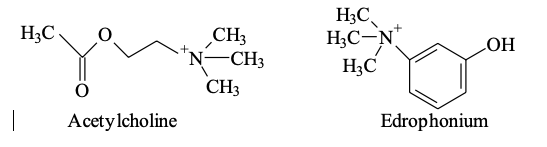
Transcribed Image Text:НС.
Нас -N
НС
Н,С.
CH3
-CHз
НО
CH3
Acetylcholine
Edrophonium
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A.What is the Result of the sodium potassium ATPase activity in the cell? B.What mechanism does the sodium potassium ATPase use to achieve this result? C. Why is the above-mentioned change in affinity critical for the sodium potassium ATPase to perform its function?arrow_forwardVitamin K questionsa) What transformation of glutamate side chains is Vitamin K (as its reduced form, VitaminKH2) involved in, and what is the relevance of this reaction to blood clotting?b) How does the blood thinner Coumadin (warfarin) prevent clotting?c) How can the dietary intake of large amounts of green vegetables, such as broccoli or kaleinterfere with the action of Coumadin?arrow_forwardDescribe the general function and structural features of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Be sure to include an explanation of GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) and GDP exchange factors (GEFs) in the context of the GTPase cycle. How are different classes of heterotrimeric G-proteins defined?arrow_forward
- In pure noncompetitive inhibition: a. Where on the enzyme does the inhibitor bind? b. Does the inhibitor bind to E, ES or both? c. What is the effect of I on Vmax? d. What is the effect of I on Km?arrow_forwardFor each of the following examples, indicate whether the drug is acting on physical process, chemical process or enzymatic system (your answer should be only; Physical, Chemical or Enzymatic). A. A drug is used as an antidote in lead poisoning and acts by binding to lead particles in body (chelation therapy). B. A drug acts to reduce flatulence and acts by reducing the surface tension of intestinal gas bubbles in the GI tract (e.g. Simethicone). C. A drug competes with alpha-glucosidase in intestine to reduce glucose conversion from disaccharides (e.g. Acarbose).arrow_forwardWhat step ends the first-half of the chymotrypsin mechanism? Attack of water on the acyl-enzyme intermediate. Selected Collapse of the first tetrahedral intermediate, releasing of the C-terminal peptide fragment and formation of the acyl-enzyme intermediate. Deprotonation of serine by the histidine. Collapse of the second tetrahedral intermediate leading to the final products. REVIEW QUESTION 1/1 CONTINUE MacBook Pro https://virginiacommonwealth.instructure.com/courses/42082/assignments/271397 esc OTarrow_forward
- How can you decrease (or stop) the rate of binding for a noncompetitive inhibitor? Could you change the receptor allosteric sites to prevent noncompetitive binding?arrow_forwardExplain the differences and similarities in the three kinds of reversible inhibition. Include what is physically happening, how inhibition affects KM and Vmax and if the inhibition can be overcome.arrow_forwardThe physiological effects of epinephrine should in principle be mimicked by addition of cAMP to the target cells. In practice, addition of cAMP to intact target cells elicits only a minimal physiological response. Why? When the structurally related derivative dibutyryl cAMP (shown below) is added to intact cells, the expected physiological response is readily apparent. Explain the basis for the difference in cellular response to these two substances. Dibutyryl cAMP is widely used in studies of cAMP function.arrow_forward
- The Graph below shows the binding curves of two proteins (A and B) for the same ligand (L). Use this Graph and determine the dissociation constant, K, for both proteins. Which protein (A or B) has a greater affinity for ligand L? Which of the two proteins would be more easily inhibited by an antagonist? 1.0 Y 0.5 2 A 4 6 B 8 [L] (μM) 10 12 14 16arrow_forwardTetrodotoxin identify the species which releases the toxin (if it is man-made then this will be all that is required for this part) identify the step disrupted in the neuromuscular junction pathway Provide any consequences of this disruption. Does the toxin have any applications in biomedicine as a painkiller, disease treatment or analgesic? Provide your source in APA format for each. If this is missing no credit will be awarded.arrow_forwardDescribe the categories of enzyme control: (image provided) Allosteric control with example Covalent modification with examplearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education