
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
In this aggregate demand model, which one of the following statements correctly describes the economy if it is at point Y on the diagram?
1 - The economy is at the full employment equilibrium
2- There are forces that are tending to make income (output) fall.
3-There are forces that are tending to make income (output) rise.
4-The economy is in equilibrium at less than full employment.
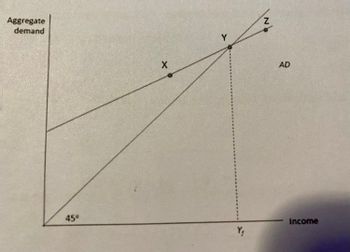
Transcribed Image Text:Aggregate
demand
45°
X
Y₁
Z
AD
Income
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. The theory of liquidity preference and the downward-slopingaggregate demand curve Suppose the money market for some hypothetical economy is given by the following graph, which plots the money demand and money supply curves. Assume the central bank in this economy (the Fed) fixes the quantity of money supplied. Suppose the price level increases from 90 to 105. Shift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of an increase in the overall price level on the market for money. INTEREST RATE (Percent) 18 15 12 8 3 0 0 20 Money Supply Money Demand 40 60 80 MONEY (Billions of dollars) 100 120 Money Demand Money Supply Following the price level increase, the quantity of money demanded at the initial interest rate of 9% will be supplied by the Fed at this interest rate. As a result, individuals will attempt to bonds and other interest-bearing assets, and bond issuers will realize that they restored in the money market at an interest rate of % than the quantity of money their money…arrow_forwardAggregate demand and aggregate supply, based on a problem from “Principles of Economics” by N. Gregory Mankiw a) List the components of country’s GDP in an open economy. For each component, provide an example of an event that would cause a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right.b) What will be the effect of such events on the level of prices and the real outcome in the short run? Provide a graph.c) What will be the effect of such events on the level of prices and the real outcome in the longrun? Update your grapharrow_forwardAggregate Supply, and a New Equilibrium How will each of the following likely change the aggregate supply curve? Drag and drop options on the right-hand side and submit. For keyboard navigation... SHOW MORE ✓ Increase in the labor force. Increase in capital. Increase in the cost of raw materials. 7/20 answered Decrease in costs created by regulations. Increase in unemployment. = E = = = The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the right. The aggregate supply curve does not move but there is movement along the curve. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the left. The aggregate supply curve shifts to the left. The aggregate supply curve does not move but there is movement along the curve.arrow_forward
- Question: The attached picture shows the aggregate demand/aggregate supply situation in the U.S. What is the value of actual GDP? What is the value of the GDP deflator? Assume that people and businesses become pessimistic about the future of the economy; how will this affect the graph above in the short run? (i.e., which curve(s) will shift, and in which direction?) After the short-run event in part b, what will happen to actual GDP? What will happen to the price level? After the short-run event in part b, describe how the economy is doing in terms of the business cycle (i.e., recession, full employment, expansion). What long-run adjustments will be made in this economy as a result of the short-run changes in part c? How will the curve(s) shift in response to these long-run adjustments? After the long-run adjustments in part e, describe how the economy is doing in terms of the business cycle (i.e., recession, full employment, expansion).arrow_forwardSuppose that firms become very pessimistic about future business conditions and cut heavily on investment in capital equipment. [Label A, B, C for the initial, new short-run and new long-run equilibrium respectively] a)Use an aggregate-demand/aggregate-supply model to show the short-run effect of this pessimism on the economy. Label the new levels of prices and real output. Explain in words why the aggregate quantity of output supplied changes. (Use the sticky wage theory in your explanation)arrow_forwardAssume the Canadian economy is currently at equilibrium. a. Using a correctly labeled aggregate demand and supply graph, show Full employment output (yf) Current price level (PL1) b. World War III breaks out and Canada has to get involved. The Prime Minister chooses to increase the military budget by 40%. On your graph from part A, show what will happen in the economy, labeling the new equilibrium as Q2, PL2. c. Using a correctly labeled graph of the loanable funds market, show how the Prime Minister’s decision will affect the economy.arrow_forward
- Answer both questions that need to be answered and the second question has a graph that’s needs to be answered as well.arrow_forwardAggregate demand and aggregate supply, based on a problem from “Principles of Economics” by N. Gregory Mankiw a) List the components of country’s GDP in an open economy. For each component, provide an example of an event that would cause a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right.b) What will be the effect of such events on the level of prices and the real outcome in the short run? Provide a graph.c) What will be the effect of such events on the level of prices and the real outcome in the longrun? Update your grapharrow_forward1) Define aggregate demand and aggregate supply. 2) Give three reasons why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward. 3) Give three reasons why the aggregate supply curve slopes upwards.arrow_forward
- Answer the given question with a proper explanation and step-by-step solution.arrow_forwardIn March 2020, as the Covid-19 recession hit the world, consumers became pessimistic about their future incomes. How did this increased pessimism affect the aggregate demand curve in the year 2020? Group of answer choices This will shift the aggregate demand curve to the right. This will move the economy down along a stationary aggregate demand curve. This will move the economy up along a stationary aggregate demand curve. This will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.arrow_forwardWhich of the following would increase aggregate demand? A) Increase in taxation. B) Increase in savings. C) Decrease in consumption spending. D) Increase in government spending.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education