
Exploring Economics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781544336329
Author: Robert L. Sexton
Publisher: SAGE Publications, Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Microeconomics
Unit 4 Practice Sheet
Riya
Price
Part 1: Monopoly- Use the graph of a
non-price discriminating monopoly to
answer the following questions. Show
your work when asked to calculate.
$160
$140
1. Identify the profit maximizing price and
quantity.
$120
MC
2. Calculate the total revenue at the profit $100
maximizing price and quantity.
ATC
$80
3. Calculate the total cost at the profit
maximizing price and quantity.
$60
4. Calculate the profit or loss at the profit
maximizing price and quantity.
$40
5. Calculate the area of deadweight loss.
$20
6. Identify the socially optimal
(allocatively efficient) price and
quantity.
7. Identify the price and quantity where
the total revenue is maximized.
MR
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
Quantity
8. At the price of $120, is the demand relatively elastic, relatively inelastic, or unit elastic? Why?
9. Identify the price and quantity if this monopoly's fixed costs increase by $140.
10. Identify the profit maximizing price and quantity if the government levies a $30 per unit tax on
this monopoly.
11. Identify the profit maximizing price and quantity if this monopoly figures out a way to perfectly price
discriminate.
12. Assume instead that the costs of production changed for this monopoly so that the marginal cost
(MC) and average total cost (ATC) for every unit was $80. Under these new circumstances, identify
the profit maximizing price and quantity.
13. Calculate the new total revenue at the profit maximizing price and quantity.
14. Calculate the new total cost at the profit maximizing price and quantity.
15. Calculate the new profit or loss at the profit maximizing price and quantity.
Copyright Jacob Clifford 2020. Ultimate Review Packet
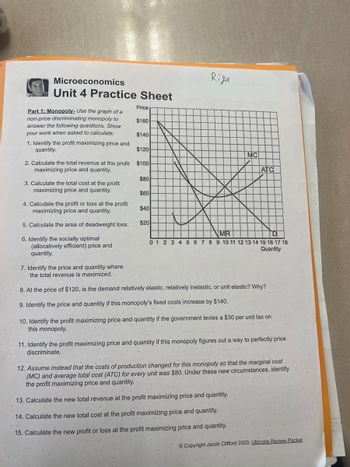
Transcribed Image Text:Microeconomics
Unit 4 Practice Sheet
Riya
Price
Part 1: Monopoly- Use the graph of a
non-price discriminating monopoly to
answer the following questions. Show
your work when asked to calculate.
$160
$140
1. Identify the profit maximizing price and
quantity.
$120
MC
2. Calculate the total revenue at the profit $100
maximizing price and quantity.
ATC
$80
3. Calculate the total cost at the profit
maximizing price and quantity.
$60
4. Calculate the profit or loss at the profit
maximizing price and quantity.
$40
5. Calculate the area of deadweight loss.
$20
6. Identify the socially optimal
MR
D
(allocatively efficient) price and
quantity.
7. Identify the price and quantity where
the total revenue is maximized.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
Quantity
8. At the price of $120, is the demand relatively elastic, relatively inelastic, or unit elastic? Why?
9. Identify the price and quantity if this monopoly's fixed costs increase by $140.
10. Identify the profit maximizing price and quantity if the government levies a $30 per unit tax on
this monopoly.
11. Identify the profit maximizing price and quantity if this monopoly figures out a way to perfectly price
discriminate.
12. Assume instead that the costs of production changed for this monopoly so that the marginal cost
(MC) and average total cost (ATC) for every unit was $80. Under these new circumstances, identify
the profit maximizing price and quantity.
13. Calculate the new total revenue at the profit maximizing price and quantity.
14. Calculate the new total cost at the profit maximizing price and quantity.
15. Calculate the new profit or loss at the profit maximizing price and quantity.
Copyright Jacob Clifford 2020. Ultimate Review Packet
W
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Imagine a monopolist could charge a different price to every customer based on how much he or she were willing to pay. How would this affect monopoly profits?arrow_forwardIs a monopolistically competitive firm productively efficient? Is it allocatively efficient? Why or why not?arrow_forwardFrom the graph you drew to answer Exercise 11.6, would you say this transit system is a natural monopoly? Justify. Use the following information to answer the next three questions. In the years before wireless phones, when telephone technology requited having a wile matting to every home, it seemed plausible that telephone service had diminishing average costs and might require regulation like a natural monopoly. For most of the twentieth century, the national U.S. phone company was AT&T, and the company functioned as a regulated monopoly. Think about the deregulation of the U.S. telecommunications industry that has occurred over the last few decades. (This is not a research assignment, but a thought assignment based on what you have learned in this chapter.)arrow_forward
- Imagine that you ale managing a small firm and thinking about entering the market of a monopolist. The monopolist is currently charging a high price, and you have calculated that you can make a nice profit charging 10 less than the monopolist. Before you go ahead and challenge the monopolist, what possibility should you consider for how the monopolist might react?arrow_forwardDraw a monopolists demand curve, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves. Identify the monopolists profit-maximizing output level. Now, think about a slightly higher level of output (sayQ0+1). According to the graph, is there any consumer willing to pay more than the marginal cost of that new level of output? If so, what does this mean?arrow_forwardHow can a monopolist identify the profit-maximizing level of output if it knows its total revenue and total cost curves?arrow_forward
- Why are urban areas willing to subsidize urban transit systems? Does the argument for subsidies make sense to you?arrow_forwardIn the middle of the twentieth century, major U.S. cities had multiple competing city bus companies. Today, there is usually only one and it runs as a subsidized, regulated monopoly. What do you suppose caused the change?arrow_forwardCan you think of any examples of successful predatory pricing in the real world?arrow_forward
- Some years ago. two intercity bus companies, Greyhound Lines, Inc. and Trailways Transportation System, wanted to merge. One possible definition of the market for this case was the market for intercity bus service. Another possible definition was the market for intercity transportation, including personal cars, car rentals, passenger trains, and commuter air flights.' Which definition do you think the bus companies preferred, and why?arrow_forwardSuppose demand for a monopolys product falls 50 that its profit-maximizing price is below average variable cost. How much output should the film supply? Hint: Draw the graph.arrow_forwardIs a monopolist a price taker? Explain briefly.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax

 Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc

Principles of Economics 2e
Economics
ISBN:9781947172364
Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher:OpenStax



Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning