
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781337106665
Author: Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Engineering Econ HW8 Q3
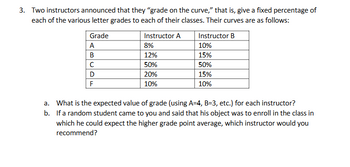
Transcribed Image Text:3. Two instructors announced that they "grade on the curve," that is, give a fixed percentage of
each of the various letter grades to each of their classes. Their curves are as follows:
Grade
A
Instructor A
8%
Instructor B
10%
B
12%
15%
C
50%
50%
D
20%
15%
F
10%
10%
a. What is the expected value of grade (using A-4, B=3, etc.) for each instructor?
b. If a random student came to you and said that his object was to enroll in the class in
which he could expect the higher grade point average, which instructor would you
recommend?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The economic analysis division of Mapco Enterprises has estimated the demand function for its line of weed trimmers as QD=18,000+0.4N350PM+90Ps where N=numberofnewhomescompletedintheprimarymarketarea PM=priceoftheMapcotrimmerPS=priceofitscompetitorsSurefiretrimmer In 2010, 15,000 new homes are expected to be completed in the primary market area. Mapco plans to charge $50 for its trimmer. The Surefire trimmer is expected to sell for $55. What sales are forecasted for 2010 under these conditions? If its competitor cuts the price of the Surefire trimmer to $50, what effect will this have on Mapcos sales? What effect would a 30 percent reduction in the number of new homes completed have on Mapcos sales (ignore the impact of the price cut of the Surefire trimmer)?arrow_forwardYou are considering entry into a market in which there is currently only one producer (incumbent). If you enter, the incumbent can take one of two strategies, price low or price high. If he prices high, then you expect a $60K profit per year. If he prices low, then you expect $20K loss per year. You should enter if you believe demand is inelastic. you believe the probability that the incumbent will price low is greater than 0.75. you believe the probability that the incumbent will price low is less than 0.75. you believe the market size is growing.arrow_forwardFurniture Forecasting Futura Furniture Products manufactures upscale office furniture for the Office of the Future. The sales division comprises regionally based sales offices made up of sales representatives and regional managers. Sales representativeswho report to the regional managersconduct direct sales efforts with customers in their regions. As part of the sales process, representatives gather information about likely future orders and convey that information back to the regional managers. Regional managers use that information to create sales forecasts, which are then used as the basis for manufacturing schedules. Sales representatives and regional managers are both compensated on a salary plus commission (percentage of revenue as pricing is centrally controlled). However, a regional managers commission is adjusted based on regional sales that exceed the forecasted budget. Corporate managers are concerned with one of Futuras key products, the DeskPod. They worry that DeskPod forecasts are inaccurate, causing extreme havoc in the manufacturing process. How are the forecasts likely to be inaccurate? What do you think is driving this inaccuracy? How might this problem be solved?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning


Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...
Economics
ISBN:9781305506381
Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. Harris
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning

