
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
Listed in the data table are IQ scores for a random sample of subjects with medium lead levels in their blood. Also listed are statistics from a study done of IQ scores for a random sample of subjects with high lead levels. Assume that the two samples are independent simple random samples selected from normally distributed populations. Do not assume that the population standard deviation’s are equal.
Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that the mean IQ scores for subjects with medium lead levels is higher than the mean for subjects with high lead levels.
What is the test statistic
What is the P value
Construct a confidence interval
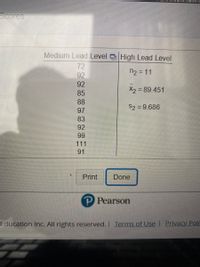
Transcribed Image Text:Scores
Medium Lead Level High Lead Level
72
n2 = 11
92
92
X2 = 89.451
85
88
S2 = 9.686
97
83
92
99
111
91
Print
Done
P Pearson
Education Inc. All rights reserved. I Terms of Use Privacy Poli
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 8 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A professor believes that, for the introductory art history classes at his university, the mean test score of students in the evening classes is lower than the mean test score of students in the morning classes. He collects data from a random sample of 250 students in evening classes and finds that they have a mean test score of 76.8. He knows the population standard deviation for the evening classes to be 7.2 points. A random sample of 200 students from morning classes results in a mean test score of 77.8. He knows the population standard deviation for the morning classes to be 1.9 points. Test his claim with a 90% level of confidence. Let students in the evening classes be Population 1 and let students in the morning classes be Population 2. Step 1 of 3 : State the null and alternative hypotheses for the test. Fill in the blank below. H0: μ1=μ2 Ha: μ1__μ2arrow_forwardAverage adult Americans are about one inch taller but nearly a whopping 25 pounds heavier than they were in 1960, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). City A is considered one of America's healthiest cities. Is the weight gain since 1960 similar in city A? A sample of n=25 adults suggested a mean increase of 22 pounds with a standard deviation of 9.4 pounds. Is City A significantly different in terms of weight gain since 1960? Complete and interpret 5 step hypothesis testing by hand at a 5% level of significance using a Z-test. Show each step and your work.arrow_forwardPlease help me with this question.arrow_forward
- Fran is training for her first marathon, and she wants to know if there is a significant difference between the mean number of miles run each week by group runners and individual runners who are training for marathons. She interviews 42 randomly selected people who train in groups and finds that they run a mean of 47.1 miles per week. Assume that the population standard deviation for group runners is known to be 4.4 miles per week. She also interviews a random sample of 47 people who train on their own and finds that they run a mean of 48.5 miles per week. Assume that the population standard deviation for people who run by themselves is 1.8 miles per week. Test the claim at the 0.01 level of significance. Let group runners training for marathons be Population 1 and let individual runners training for marathons be Population 2. Step 2 of 3 : Compute the value of the test statistic. Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardUse z scores to compare the given values. The tallest living man at one time had a height of 238 cm. The shortest living man at that time had a height of 142.4 cm. Heights of men at that time had a mean of 175.45 cm and a standard deviation of 5.59 cm. Which of these two men had the height that was more extreme? ... Since the z score for the tallest man is z = 0 and the z score for the shortest man is z = the man had the height that was Im- more extreme. (Round to two decimal places.) shortest tallestarrow_forwardwhat statistical test should be used, what are the null and alternative hypotheses, what are the critical values, what is the test statistic, effect size, upper and lower 95% CI, and a conclusion statement?arrow_forward
- A professor believes that, for the introductory art history classes at his university, the mean test score of students in the evening classes is lower than the mean test score of students in the morning classes. He collects data from a random sample of 250 students in evening classes and finds that they have a mean test score of 85.6. He knows the population standard deviation for the evening classes to be 4.6 points. A random sample of 150 students from morning classes results in a mean test score of 86.7. He knows the population standard deviation for the morning classes to be 8.3 points. Test his claim with a 99 % level of confidence. Let students in the evening classes be Population 1 and let students in the morning classes be Population 2. Step 3 of 3: Draw a conclusion and interpret the decision. Answer 围 Tables E Keypad Keyboard Shortcuts We fail to reject the null hypothesis and conclude that there is sufficient evidence at a 0.01 level of significance to support the…arrow_forwardLow-density lipoprotein, or LDL, is the main source of cholesterol buildup and blockage in the arteries. This is why LDL is known as "bad cholesterol." LDL is measured in milligrams per deciliter of blood, or mg/dL. In a population of adults at risk for cardiovascular problems, the distribution of LDL levels is normal, with a mean of 123 mg/dL and a standard deviation of 41 mg/dL. If an individual's LDL is at least 1 standard deviation or more above the mean, he or she will be monitored carefully by a doctor. What percentage of individuals from this population will have LDL levels 1 or more standard deviations above the mean? Use the 68–95–99.7 rule. (Enter your exact answer as a whole number.) percentage %arrow_forwardThe salaries of professional baseball players are heavily skewed right with a mean of $3.2 million and a standard deviation of $2 million. The salaries of professional football players are also heavily skewed right with a mean of $1.9 million and a standard deviation of $1.5 million. A random sample of 40 baseball players’ salaries and 35 football players’ salaries is selected. The mean salary is determined for both samples. Let represent the difference in the mean salaries for baseball and football players. Which of the following represents the shape of the sampling distribution for ? skewed right since the populations are both right skewed skewed right since the differences in salaries cannot be negative approximately Normal since both sample sizes are greater than 30 approximately Normal since the sum of the sample sizes is greater than 30arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman