
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
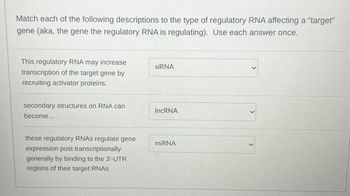
Transcribed Image Text:Match each of the following descriptions to the type of regulatory RNA affecting a "target"
gene (aka, the gene the regulatory RNA is regulating). Use each answer once.
This regulatory RNA may increase
siRNA
transcription of the target gene by
recruiting activator proteins.
secondary structures on RNA can
become...
IncRNA
these regulatory RNAs regulate gene
miRNA
expression post transcriptionally
generally by binding to the 3'-UTR
regions of their target RNAs
>
>
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You are studying how gene expression is regulated in the cell. For gene z, you find that while there are high levels of mRNA in the cell, there are low levels of the protein encoded by gene z. Describe a regulatory mechanism that could explain this finding that occurs after translation.arrow_forwarda. How do bacteria increase the efficiency of gene expression? Is this possible in eukaryotes? b. A mutation in the promoter of Gene K disrupts an enzyme binding site and results in the loss of Gene K expression. Is this change in gene expression likely happening at the transcriptional or the translational level? Explain. c. Propose three different mutations to prevent initiation, elongation, and termination of bacterial transcription, respectively. Explain how/why each mutation would prevent its respective step. (Hint: mutations can be in genes that encode proteins or regulatory DNA sequences)arrow_forwardMRNAs and eukaryotic cells receive different modifications than those in prokaryotic cells, because eukaryotic mRNAs must be able to accomplish different things. Which of the following describes events that are necessary for an mRNA to be expressed in a eukaryotic cell, but are not necessary for mRNAs in a prokaryotic cell? select all that apply A) introns must be removed from the eukaryotic mRNA B) The mRNA must leave from the nucleus C) transcription factors must bind to the mRNA in a eukaryotic cell after it is transcribed D) A ribsome must bind to the mRNA .arrow_forward
- The siRNA and miRNA pathways share many similarities and also have some differences. Which of the following is true about these two noncoding RNA classes in regulating gene expression? O Both of them utilize the internally generated RNAS as sources to produce the short regulatory RNAS O Both of them need Dicer to process the long RNAS into short double-strnaded RNAS Both of them required perfect match between the short noncoding RNAS to the MRNAS Both of them end up with complete degradation of the target mRNAsarrow_forwardPlease arrangearrow_forwardA string of 8 adenine nucleotides in the mRNA is required for function of an intrinsic transcription terminator in bacteria. True Falsearrow_forward
- Provide one mechanism by which changes in mRNA levels are not always matched by changes in the protein product of that mRNA.arrow_forwardBelow is a model of a signal transduction pathway that results in the transcribing of mRNA: Receptor protein Transcription factor Phosphorylation cascade DNA mRNA What is the best description of what would happen if the phosphorylation cascade resulted in a phosphate being attached to the transcription factor? O mRN would not stop being transcribed from the DNA. O The phosphorylation cascade would continue to release excess phosphates. O mRNA would stop being translated from the DNA. O Receptor proteins would not bind to the signaling hormone.arrow_forwardA synthetic mRNA added to a cell-free protein-synthesizing system produces a peptide with the following amino acid sequence: Met-ProIle-Ser-Ala. What would be the effect on translation if the following component were omitted from the cell-free protein-synthesizing system? What, if any, type of protein would be produced? Explain your reasoning. Q.Release factors RF-1, RF-2, and RF-3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education