
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Macmillan Learning
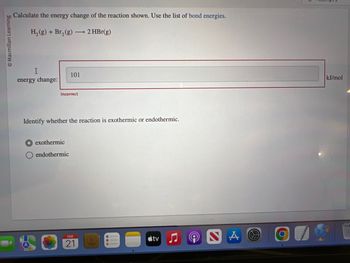
Calculate the energy change of the reaction shown. Use the list of bond energies.
H₂(g) + Br₂(g) →→→ 2 HBr(g)
I
energy change:
101
Incorrect
Identify whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
exothermic
endothermic
FEB
21
tv
NA
kJ/mol
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the reaction below: CH₂ + Cl₂ CH₂-CI + H-CI a. Estimate the gas phase enthalpy change using bond dissociation enthalpies from the OWL Table Reference, not data from your text. Click the References button and then click the Tables link on the drop-down that appears. Include algebraic sign and units. b. Is the reaction exothermic or endothermic? c. Is the reaction likely to proceed spontaneously in the direction written?arrow_forward1. Energy is released/required to break bonds and released /required when new bonds are formed. 2. Given the chart of bond energies, calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction below.arrow_forward3. A. Draw and label an energy diagram for a slow endothermic reaction B. A weather balloon contains 222 L of helium gas at 20.8 °C and 754 mm Hg. What is the volume in liters of the balloon when it rises to an altitude where the pressure is 552 mm Hg and the temperature is -40.0 °C C. Draw two different Lewis structures for C2H4O2, connecting the atoms differently in your two structures. Label the shape of each carbon atom in both structures.arrow_forward
- Create a lewis dot structure for CaCO3. Draw it like the picture attached.arrow_forwardIn each row, pick the compound with the bigger lattice energy. Note: lattice energy is always greater than zero. Which compound has the bigger lattice energy? Nal Na Cl O Rb Br Cao O X Sr Br₂ CaF₂ 5arrow_forwardI need help calculating the enthalpy of the reaction and whether the reaction is endothermic or exothermic.arrow_forward
- we would predict that the imaginary ionic compound XF would have a (higher /lower) lattice energy than YyF2 becausearrow_forwardO Macmillan Learning Calculate the energy change of the reaction shown. Use the list of bond energies. H₂(g) + Br₂(g) → 2 HBr(g) energy change: 101 Incorrect Identify whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic. exothermic endothermic FEB 21 tv MacBook Pro N A O Attempt 1 kJ/molarrow_forwardThe charges and sizes of the ions in an ionic compound affect the strength of the electrostatic interaction between the ions and thus the strength of the lattice energy of the ionic compound. Arrange the compounds according to the magnitudes of their lattice energies based on the relative ion charges and sizes. Highest lattice energy Lowest lattice energy Answer Bank KCI MgO NaF MgF₂arrow_forward
- Question 2 pleasearrow_forwardUse the graph to answer the following questions: What type of reaction is shown by the graph below? How does the bond energy of the reactants compare to the bond energy of the products? Activation energy +AH Reactants Products Time O The graph shows an exothermic The bond energy of the reactants is higher than the bond energy of the products. O The graph shows an endothermic reaction. The bond energy of the reactants is lower than the bond energy of the products. O The graph shows an endothermic The bond energy of the reactants is higher than the bond energy of the products. O The graph shows an exothermic reaction. The bond energy of the reactants is lower than the bond energy of the products. Potential energy (kJ)arrow_forwardOnly typed answer with explanation otherwise leave itarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY