
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
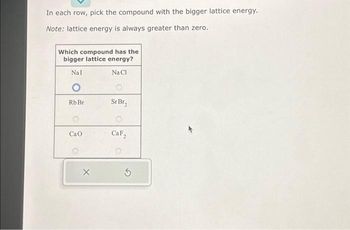
Transcribed Image Text:In each row, pick the compound with the bigger lattice energy.
Note: lattice energy is always greater than zero.
Which compound has the
bigger lattice energy?
Nal
Na Cl
O
Rb Br
Cao
O
X
Sr Br₂
CaF₂
5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of these has the following ionic compounds correctly arranged in order of decreasing ionic bond strength (lattice energy). MgO AlP NaClarrow_forwardUse the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the lattice energy of CaO. A H°(kJ) Ca(s) → Ca(g) 193 Ca(g) → Cat (g) + e 590 Cat (g) → Ca2+(g) + e 1010 20(g) → O2(g) -498 O(g) + e O(g) -141 O(g) + e → O2(g) 878 Ca(s) + O2(g) → CaO(s) -> -635 O-2667 kJ O-3414 kJ O +1397 kJ +3028 kJ O-2144 kJarrow_forwardConsider a boron-chlorine bond (B-Cl). Which atom would have a partial positive charge and which would have a partial negative charge?arrow_forward
- Please help answer this questionsarrow_forwardPredicting the relative lattice energy of binary ionic compounds In each row, pick the compound with the bigger lattice energy. Note: lattice energy is always greater than zero. Which compound has the bigger lattice energy? BaCh BaS Bel₂ KF O BeBr₂ CsF O 1/5arrow_forwardCyanamide is a compound containing two hydrogen atoms and some amount of C and N. There are a total of 5 atoms in the compound. The products of combustion were found to be CO2, NO2, and H2O. If the enthalpy of combustion for cyanamide is – 671.9 kJ/mol and the enthalpy of formation is 58.8 kJ/mol, what is the chemical formula for cyanamide? ( ΔfH (CO2) = - 393.51 kJ/mole; ΔfH (NO2) = + 33.10 kJ/mole; ΔfH (H2O) = - 241.826 kJ/mole)arrow_forward
- Given the following bond energies F-F 157 kJ/mol Cl-CI 243 kJ/mol F-CI 193 kJ/mol estimate AH for this reaction. F2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2CIF(g)arrow_forwardSuppose a chemist discovers a new metallic element and names it "Xercisium" (Xr). Xr exhibits chemical behaviour similar to an alkaline earth. Xr(s) + Cl2(g) → XrCl2(s) Lattice energy for XrCl2 -2020. kJ/mol First Ionization energy of Xr 500. kJ/mol Second Ionization energy of Xr 950. kJ/mol Electron affinity of Cl -348.7 kJ/mol Bond energy of Cl2 239 kJ/mol Enthalpy of sublimation (atomization) of Xr 200. kJ/mol Use the above data to calculate ΔH°f for Xercisium chloride.arrow_forwardAs seen in the table, compounds containing an integer ratio of elements depend on how many cations combine with how many anions to form a stable compound. For example, in table 1, to form a NaCl compound, first Na ionizes from the Na+ cation which is having +1 positive charge, which will lose 1 electron, it is having +1 charge, this electron then goes to Cl and it will change to Cl- anion by gaining the electron, so here 1:1 ratio charge which means 1 Na+ combines with 1 Cl-1 to form NaCl. So here integer ratio is 1:1 for this sodium chloride compound. As listed in table 2, Mg(OH)2, the integer ratio is 1:2 which means, Mg is a neutral atom that loses 2 electrons and forms an Mg+2 cation, which combines with OH which gains 1 electron to form OH- anion, So here Mg2+ can combine with 2 OH- anion, so they both combine to form Mg(OH)2 which has integer ratio as 1:2 . Thus, atom forms as ions by losing or gaining electrons and combines together in whole number ratio to form stable…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY