
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
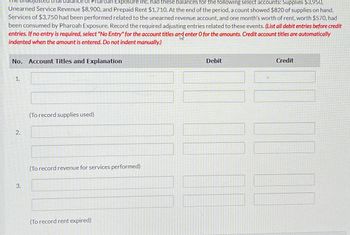
Transcribed Image Text:balance of Pharoah Exposure Inc. had these balances for the following select accounts: Supplies $3,950,
Unearned Service Revenue $8,900, and Prepaid Rent $1,710. At the end of the period, a count showed $820 of supplies on hand.
Services of $3,750 had been performed related to the unearned revenue account, and one month's worth of rent, worth $570, had
been consumed by Pharoah Exposure. Record the required adjusting entries related to these events. (List all debit entries before credit
entries. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter O for the amounts. Credit account titles are automatically
indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually.)
No. Account Titles and Explanation
1.
2.
3.
(To record supplies used)
(To record revenue for services performed)
(To record rent expired)
Debit
Credit
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Sellall Department Stores reported the following amounts in its adjusted trial balance preparedas of its December 31 year-end: Administrative Expenses, $2,400; Cost of Goods Sold, $22,728;Income Tax Expense, $3,000; Interest Expense, $1,600; Interest Revenue, $200; General Expenses,$2,600; Sales Revenue, $42,000; Sales Discounts, $2,200; Sales Returns and Allowances, $1,920;and Delivery (freight-out) Expense, $300. Prepare a multistep income statement for distribution toexternal financial statement users, using a format similar to Exhibit 6.9 .arrow_forwardDuring February, $98,100 was paid to creditors on account, and purchases on account were $125,570. Assuming that the February 28 balance of Accounts Payable was $42,180, determine the account balance on February 1. b. On October 1, the accounts receivable account balance was $44,700. During October, $388,900 was collected from customers on account. Assuming that the October 31 balance was $51,400, determine the fees billed to customers on account during October.$ c. On April 1, the cash account balance was $23,340. During April, cash receipts totaled $354,770 and the April 30 balance was $16,800. Determine the cash payments made during April.$arrow_forwardAfter preparing the unadjusted trial balance, review the entries to determine what accounts need to be adjusted and prepare the adjusting journal entries. Additional information is below: •A physical count of office supplies noted a balance of $35,270 •A review of the unearned account noted that 30% of the revenue was earned. •After reviewing the A/R aging, management estimated that 10% of the Accounts receivable balance would not be collected. •Building has a useful life of 20 years and a salvage value of $25,000 •Equipment has a useful life of 5 years and a salvage value of 5,000. •Employee’s salaries for the last week of December and not yet paid total $40,350•Services provided but not yet billed totaled $85,000•Utilities Expense incurred but not recorded totaled $7,250 I need help in the adjusting process for 12/31. the picture added in the undjusted trial. I need hel adjusting this infoarrow_forward
- A business sells $100,000 of products to a customer on account and collects 6% sales tax. Cost of the merchandise sold was $70,000. At the end of the month, the company pays the total sales tax collected ($185,000) to the state department of revenue. Required: Record the entries for (a) 'the sale' and for (b) 'the payment of the sales tax.' Indicate Dr. or Cr. in front of each account.arrow_forwardThe following selected transactions were taken from the records of Rustic Tables Company for the year ending December 31: June 8. Wrote off account of Kathy Quantel, $9,030. Aug. 14. Received $6,410 as partial payment on the $16,160 account of Rosalie Oakes. Wrote off the remaining balance as uncollectible. Oct. 16. Received the $9,030 from Kathy Quantel, whose account had been written off on June 8. Reinstated the account and recorded the cash receipt. Dec. 31. Wrote off the following accounts as uncollectible (record as one journal entry): Wade Dolan $2,620 Greg Gagne 1,630 Amber Kisko 6,230 Shannon Poole 3,610 Niki Spence 990 Dec. 31. If necessary, record the year-end adjusting entry for uncollectible accounts. a. Journalize the transactions under the direct write-off method. June 8 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Accounts Receivable-Kathy Quantel Aug. 14 Cash Bad Debt Expense Accounts Receivable-Rosalie Oakes…arrow_forwardAt the end of October, the ABC Company needed to make accrual adjustments to the accounts, using the following information: Depreciation for the month is £50 An inventory count on October 31 revealed that 125units were in the company’s warehouse. The cost flow assumption followed for the preparation of statements is FIFO. On September 1, ABC Company issued a 3-month, annual rate 6%, $1,000 Note Payable to Credit Bank. Capital and interest are to be paid at the end of November. Prepare a worksheet showing the October transactions and the October accrual adjustments for the ABC Company. The work sheet is attached below, which is solvevd. But I wonder how to get the lastest amount of inventory, which is 125? Can you please show me the calculation process?arrow_forward
- Cleaning services sold on account to Cara Caterers for the week were $430, and for cash were $22,804. What would be the correct General Ledger Entry?arrow_forwardYork Company engaged in the following transactions for Year 1. The beginning cash balance was $86,000 and the ending cash balance was $59,100. 1. Sales on account were $548,000. The beginning receivables balance was $128,000 and the ending balance was $90,000. 2. Salaries expense for the period was $232,000. The beginning salaries payable balance was $16,000 and the ending balance was $8,000. 3. Other operating expenses for the period were $236,000. The beginning other operating expenses payable balance was $16,000 and the ending balance was $10,000. 4. Recorded $30,000 of depreciation expense. The beginning and ending balances in the Accumulated Depreciation account were $12,000 and $42,000, respectively. 5. The Equipment account had beginning and ending balances of $44,000 and $56,000, respectively. There were no sales of equipment during the period. 6. The beginning and ending balances in the Notes Payable account were $36,000 and $44,000, respectively. There were no payoffs of…arrow_forwardChabon Corp. had a beginning "Supplies" account balance of $500 on December 1, 20X1. It had the following occur during 20X1: On December 4, supplies costing $4,000 were purchased on account. On December 15, the company paid $4,000 for the supplies previously purchased on account. On December 31, 20X1, a physical count shows $900 of supplies to still be on hand (unused) Where should the "Supplies" account balance be reported on the financial statements?arrow_forward
- Triple Tier Bakery is a locally-owned business offering custom cakes, cupcakes, desserts and wedding cakes. At year end, Triple Tier's balance of Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts is $530 (credit before adjustment. The Accounts Receivable balance is $21,500, During the next year, Triple Tier estimates that 15% of accounts will be uncollectible. Record the adjustment required for Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts? (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.) View transaction list Journal entry worksheet Record the adjusting entry for Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction General Journal Debit Credit Record entry Clear entry View general journalarrow_forwardBolton sold a customer service contract with a price of $37,000 to Sammy's Wholesale Company. Bolton offered terms of 1/10, n/30 and uses the gross method. Required: Hide Prepare the journal entry assuming the payment is made after 10 days (after the discount period). Account and Explanation Debit Credit Record collection of accounts receivablearrow_forwardQuality Move Company made the following expenditures on one of its delivery trucks: Mar. 20 Replaced the transmission at a cost of $1,990. June 11 Paid $1,455 for installation of a hydraulic lift. Nov. 30 Paid $57 to change the oil and air filter. Prepare journal entries for each expenditure. Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles. CHART OF ACCOUNTSQuality Move CompanyGeneral Ledger ASSETS 110 Cash 111 Petty Cash 112 Accounts Receivable 114 Interest Receivable 115 Notes Receivable 116 Merchandise Inventory 117 Supplies 119 Prepaid Insurance 120 Land 123 Delivery Truck 124 Accumulated Depreciation-Delivery Truck 125 Equipment 126 Accumulated Depreciation-Equipment 130 Mineral Rights 131 Accumulated Depletion 132 Goodwill 133 Patents LIABILITIES 210 Accounts Payable 211 Salaries Payable 213 Sales Tax Payable 214 Interest Payable 215 Notes Payable EQUITY 310 Owner's…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education