
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
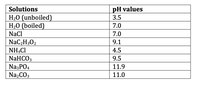
Transcribed Image Text:### Table of pH Values for Various Solutions
#### pH Measurements
The table below shows the pH values of various solutions, indicating the acidity or basicity of each solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with lower values indicating higher acidity, 7 being neutral, and higher values indicating higher alkalinity (basicity).
| Solutions | pH Values |
|-------------------|-----------|
| H₂O (unboiled) | 3.5 |
| H₂O (boiled) | 7.0 |
| NaCl | 7.0 |
| NaC₂H₃O₂ | 9.1 |
| NH₄Cl | 4.5 |
| NaHCO₃ | 9.5 |
| Na₃PO₄ | 11.9 |
| Na₂CO₃ | 11.0 |
#### Explanation
1. **H₂O (unboiled)**: The pH of unboiled water is 3.5, indicating slight acidity. This may be due to the presence of dissolved carbon dioxide forming carbonic acid.
2. **H₂O (boiled)**: The pH of boiled water is neutral (7.0). Boiling removes dissolved gases, neutralizing the water.
3. **NaCl**: Sodium chloride solution has a neutral pH of 7.0.
4. **NaC₂H₃O₂**: The pH of sodium acetate solution is 9.1, indicating it is basic (alkaline).
5. **NH₄Cl**: Ammonium chloride solution has a pH of 4.5, indicating it is acidic.
6. **NaHCO₃**: Sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) has a pH of 9.5, indicating it is basic.
7. **Na₃PO₄**: Sodium phosphate solution is strongly basic with a pH of 11.9.
8. **Na₂CO₃**: Sodium carbonate solution also shows strong alkalinity with a pH of 11.0.
Using this table, students can understand the pH levels of different solutions and how different compounds affect the acidity or basicity of solutions.
![**Lab Report #3-2-3:**
**0.1 M NaC₂H₃O₂ solution, using the given pH data, write expression for equilibrium constant (Ka or Kb):**
1. \( \text{Kb} = \frac{[\text{C₂H₃O₂}^-][\text{H}^+]}{[\text{HC₂H₃O₂}]} \)
2. \( \text{Ka} = \frac{[\text{C₂H₃O₂}^-][\text{H}^+]}{[\text{HC₂H₃O₂}]} \)
3. \( \text{Ka} = \frac{[\text{HC₂H₃O₂}][\text{OH}^-]}{[\text{C₂H₃O₂}^-]} \)
4. \( \text{Kb} = \frac{[\text{HC₂H₃O₂}][\text{OH}^-]}{[\text{C₂H₃O₂}^-]} \)
Select the correct expression for the equilibrium constant based on the given pH data and the dissociation of the 0.1 M NaC₂H₃O₂ solution.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/6a70e2d2-d641-435a-b212-d4266cff05fc/b69d1a87-2c4f-41b6-9bbd-bd612b8366b7/62g5tk_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:**Lab Report #3-2-3:**
**0.1 M NaC₂H₃O₂ solution, using the given pH data, write expression for equilibrium constant (Ka or Kb):**
1. \( \text{Kb} = \frac{[\text{C₂H₃O₂}^-][\text{H}^+]}{[\text{HC₂H₃O₂}]} \)
2. \( \text{Ka} = \frac{[\text{C₂H₃O₂}^-][\text{H}^+]}{[\text{HC₂H₃O₂}]} \)
3. \( \text{Ka} = \frac{[\text{HC₂H₃O₂}][\text{OH}^-]}{[\text{C₂H₃O₂}^-]} \)
4. \( \text{Kb} = \frac{[\text{HC₂H₃O₂}][\text{OH}^-]}{[\text{C₂H₃O₂}^-]} \)
Select the correct expression for the equilibrium constant based on the given pH data and the dissociation of the 0.1 M NaC₂H₃O₂ solution.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- View Assessment + adamson.blackboard.com/ultra/courses/_11404_1/outline/assessment/_1398313_1/overview/attempt/_4454538_1?courseld=_11404_1 Question 12 What is the pH of a grapefruit that contains 0.007 M citric acid solution (C6H8O7)? C6H8O7(aq) + H20(e) = C6H¬07(aq) + H3O*(aq) Ka = 7.5 x 10-4 Round your answer to 2 decimal places. Add your answer Ouestion 12 8:28 PM O Type here to search 26°C Mostly cloudy 11/23/2021 ... >arrow_forwardSolutions for question 1 pleasearrow_forwardNitesharrow_forward
- MISSED THIS? Watch IWE 14.8; Read Section 14.9. You can click on the Review link to access the section in your e Text. Calculate the pH of each solution. Part A [H3O+] = 7.4 x 10-¹⁰ M Express your answer using two decimal places. pH = = Submit Part B VE ΑΣΦ pH = = Request Answer [H3O+] = 8.6 x 10-² M Express your answer using two decimal places. IVE ΑΣΦ P Pearson ? Copyright © 2023 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Permissions | Contact Us |arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of a 0.20 M solution of KCN at 25.0 °C. Express the pH numerically using two decimal places. ► View Available Hint(s) pH = Submit Part D 17 ΑΣΦ pH = Calculate the pH of a 0.20 M solution of NH4 Br at 25.0 °C. Express the pH numerically using two decimal places. ► View Available Hint(s) 0 —| ΑΣΦ ? www.arrow_forwardYou make a solution of a weak acid with a pH of 3.75 and the pKa is 5.42 1. Is the solution acidic or basic? 2. Calculate the [H3O+]. 3. Calculate the pOH 4. Calculate the [OH-] HO(sc) OM (0+1) 5. Calculate the pKb DM 6. Calculate the Kb. 041 halched 109arrow_forward
- Typed and correct answer pleasearrow_forwardSolutions to question 3 pleasearrow_forwardHi can you answer the following question: Using the data from questions 3 and 4, calculate the experimental value of Ka for this unknown acid using an ICE table. The data from question 3 and 4 are attached. Thank you! Aditional information if needed: unknown acid concentration: 0.042mol/L unknown acid volume: 0.25L NaOH concentration: 0.1M NaOH volume at the equivalence point: 0.105L Initial [H30+] is 5.01 x 10-4 mol/Larrow_forward
- 7:09 1 4 7 +/- What is the pH of a 0.770 M solution of C5H5NHBr (Kb of C5H5N is 1.7 x 10-⁹)? 2 5 8 Question 6 of 11 . 3 60 9 O Submit Tap here or pull up for additional resources XU x 100arrow_forwardfind Ka for acetic acid from following half equivalence data point of half equivalence : 5 mLhalf equivalence pH value: 0.88concentration of NaOH: 0.99/ mol L-1 Volume of NaOH at equivalence point: 10mLVolume of acetic acid/mL: 40 mLarrow_forwardPost-lab Question #3: Compare with the pH of a 0.1 M solution of KC2H3O2, the pH of a 0.1 M solution of NaC2H3O2 is (same/higher/lower)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY