
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
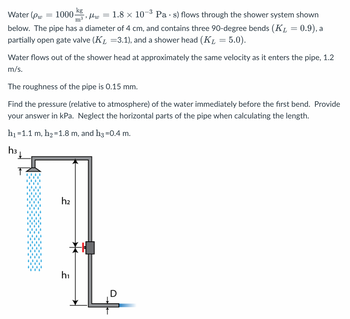
Transcribed Image Text:Water (Pw
-3
1000 kg
μω
"
m³
1.8 x 107 Pas) flows through the shower system shown
below. The pipe has a diameter of 4 cm, and contains three 90-degree bends (K₁ = 0.9), a
partially open gate valve (K₁ =3.1), and a shower head (KL = 5.0).
=
Water flows out of the shower head at approximately the same velocity as it enters the pipe, 1.2
m/s.
=
The roughness of the pipe is 0.15 mm.
Find the pressure (relative to atmosphere) of the water immediately before the first bend. Provide
your answer in kPa. Neglect the horizontal parts of the pipe when calculating the length.
h₁ =1.1 m, h₂=1.8 m, and h3 =0.4 m.
h3
h₂
h₁
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- help me answer, thank you.arrow_forward6.5 BELLOWS 6100mm The horizontal elbow is joined by bellows to the rest of the piping system and it transports water. Determine the X and Y components of the force needed to keep the elbov in posi- tion. The pressure at A and B is 200 kPa, the flow rate is 30 L/s and the pipe diameter is 100 mm. 6.6 Water flows at a rate of 0,055 m³/s through a piping system and then issues from the pipe of 50 mm diameter into the atmosphere. Ø150mm Ø50mm Ignore losses in the pipe and determine the force required at the flange to keep the nozzle in position. (Hint: first determine the pressure at A with Bernoulli's equation.)arrow_forwardCalculate the flow rate of the system by accepting the fluid passing through the reservoir-pipe system shown in the figure as ideal. As D1 = 0.5 m, D2 = 0.30 m and D3 = 0.40 m, determine the velocity heights in each pipe. Calculate and show the water levels in the pressure gauge pipes (it will be taken into account that the pressure gauge pipes are externally connected to the 1st and 2nd pipes, but the end of the pressure gauge pipe on the 3rd pipe is turned to the flow direction). Draw the relative energy and relative piezometer lines of the system.arrow_forward
- 3. Petrol is drained from a tank X to tank Y via pipeline A-B (see figure Q3). A pump is then used to pump the petrol from tank Y to tank Z via pipeline C-D. Pipe lengths, diameters and relative heights of the pump and tank levels are as shown in figure Q3. The density of the petrol is 760 kg/m³ and the Fanning friction factor (f) for all the pipes is 0.0075. • For pipe A-B the entrance loss at A is 0.5 • For pipe C-D the entrance loss at C is 0.5 u² • All valve losses are 0.2 each, 2g Neglect any entrance or exit head losses at the pump and all other pipeline component losses. X • The velocity in the pipe C-D cannot exceed 1.8 m/s The pump mechanical efficiency is 86% 10 m L = 50 m D = 100 mm B 00 30 m Y 5m 20 m and the exit loss at B is and the exit loss at D is D = 75 mm L = 10 m Figure Q3 D = 75 mm L = 50 m pump 2g N 10 marrow_forwardProblem 5: A fluid flows by gravity down an 8-cm galvanized ironpipe. The pressures at the higher and lower locations are 120 kPaand 140 kPa, respectively. The horizontal distance between thetwo locations is 30 m, and the pipe has a slope of 1-m rise per10 m of run (horizontal distance). For a fluid with a kinematicviscosity of 10-6 m2/s and a density of 900 kg/m3, determinethe flow rate (in m3/s).arrow_forward0.95 m3/sec flow rate of water flows downwards in a pipe as shown in figure. If the pressures at points 1 and 2 are to be equal. Determine the diameter of the pipe at point 2.The velocity at point 1 is 6.5 m/sec and the diameter of pipe at point 1 is 330 mm. The height between point 1 and point 2 is 2.8 m?arrow_forward
- Please answer everythingarrow_forwardThe pressure after the pump in a 6-inch inside smooth pipe conducting water is 20 psia. The water is discharged at an open tank 100ft. from the pump. Calculate the rate of discharge of water in ft3/s. ANSWER SHOULD BE (3.579ft^3/s). PROVE.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a turbine with an inlet pipe and a draft tube. If the efficiency of the turbine is only 80 percent and the discharge of the water is 1000 litres per second. Calculate: (a) the power developed by the turbine: (b) The reading of the gauge G:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY