
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
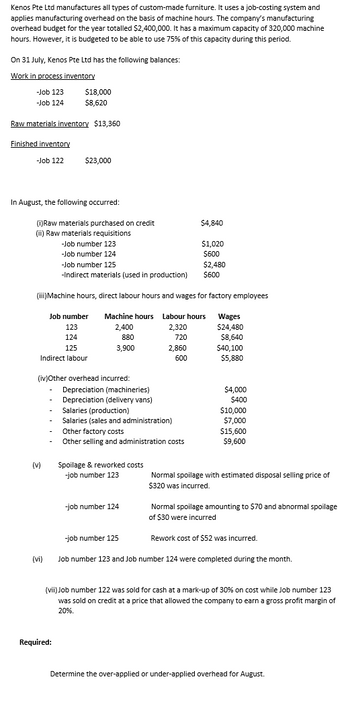
Transcribed Image Text:Kenos Pte Ltd manufactures all types of custom-made furniture. It uses a job-costing system and
applies manufacturing overhead on the basis of machine hours. The company's manufacturing
overhead budget for the year totalled $2,400,000. It has a maximum capacity of 320,000 machine
hours. However, it is budgeted to be able to use 75% of this capacity during this period.
On 31 July, Kenos Pte Ltd has the following balances:
Work in process inventory
-Job 123
-Job 124
Raw materials inventory $13,360
Finished inventory
-Job 122
$18,000
$8,620
In August, the following occurred:
(i)Raw materials purchased on credit
(ii) Raw materials requisitions
$23,000
(v)
Job number
123
124
125
Indirect labour
(vi)
-Job number 123
-Job number 124
-Job number 125
-Indirect materials (used in production)
(iii)Machine hours, direct labour hours and wages for factory employees
(iv)Other overhead incurred:
Required:
Depreciation (machineries)
Depreciation (delivery vans)
Machine hours Labour hours
2,400
2,320
880
720
3,900
2,860
600
Salaries (production)
Salaries (sales and administration)
Other factory costs
Other selling and administration costs
Spoilage & reworked costs
-job number 123
$4,840
-job number 124
$1,020
$600
-job number 125
$2,480
$600
Wages
$24,480
$8,640
$40,100
$5,880
$4,000
$400
$10,000
$7,000
$15,600
$9,600
Normal spoilage with estimated disposal selling price of
$320 was incurred.
Normal spoilage amounting to $70 and abnormal spoilage
of $30 were incurred
Rework cost of $52 was incurred.
Job number 123 and Job number 124 were completed during the month.
(vii) Job number 122 was sold for cash at a mark-up of 30% on cost while Job number 123
was sold on credit at a price that allowed the company to earn a gross profit margin of
20%.
Determine the over-applied or under-applied overhead for August.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Cavy Company estimates that the factory overhead for the following year will be $1,699,200. The company has determined that the basis for applying factory overhead will be machine hours, which is estimated to be 28,800 hours. There are 1,660 machine hours for all of the jobs in the month of April. What amount will be applied to all of the jobs for the month of April?arrow_forwardABC Inc. computes its plantwide predetermined overhead rate annually on the basis of direct labor-hours. At the beginning of the year, it estimated that 25,000 direct labor hours would be required for the period's estimated level of production. The company also estimated $520,000 of fixed manufacturing cost for the coming period and variable manufacturing overhead of $4 per direct labor-hour. ABC's actual manufacturing overhead cost for the year was $671,925 and its actual total direct labor was 25,500 hours. Compute the company's plantwidew predetermined overhead rate for the year.arrow_forwardWinston Company estimates that total factory overhead for the following year will be $1,050,300. The company has decided that the basis for applying factory overhead should be machine hours, which are estimated to be 38,900 hours. The total machine hours for the year were 54,200. The actual factory overhead for the year was $1,455,000. a. Determine the total factory overhead applied. Round to the nearest dollar. b. Compute the over- or underapplied factory overhead for the year. c. Journalize the entry to transfer the over- or underapplied factory overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.arrow_forward
- Eli Lilly Corporation has their headquarters in Indiana. Lilly uses a predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor-hours to apply manufacturing overhead to jobs. Lilly has provided the following estimated costs for next year: Direct Materials Direct Labor Rent on Factory Building Sales Salaries Depreciation on Factory Equipment Indirect Labor Production Supervisor's Salary Lilly estimates that 20,000 direct labor-hours will be worked during the year. The predetermined overhead rate per hour will be: Multiple Choice O O $4.18 $2.88 $1.95 $7,000 $21,000 $16,000 $26,000 $9,500 $13,500 $18,500 $2.40arrow_forwardMartin Manufacturing assigns overhead to jobs based on machine hours. At the beginning of the current year, estimated overhead costs were $200,000 and estimated machine hours were 40,000. During the year, 140 machine hours were used on Job 88. By the end of the year, actual overhead costs were calculated to be $202,500 and actual machine hours were 45,000.How much overhead was applied to Job 88 during the year?arrow_forwardCavy Company estimates that the factory overhead for the following year will be $1,788,000. The company has decided that the basis for applying factory overhead should be machine hours, which is estimated to be 29,800 hours. The machine hours for the month of April for all of the jobs were 4,770. If the actual factory overhead for April totaled $280,190, determine the over- or underapplied amount for the month. Enter the amount as a positive number.arrow_forward
- Harris Fabrics computes its plantwide predetermined overhead rate annually on the basis of direct labor-hours. At the beginning of the year, it estimated that 43,000 direct labor-hours would be required for the period's estimated level of production. The company also estimated $537,000 of fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the coming period and variable manufacturing overhead of $2.00 per direct labor-hour, Harris's actual manufacturing overhead cost for the year was $702,019 and its actual total direct labor was 43,500 hours. Required: Compute the company's plantwide predetermined overhead rate for the year. (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Predetermined overhead rate per DLHarrow_forwardRichey Company uses an actual cost accounting system that applies overhead on the basis of direct labor hours. At the beginning of the year, management estimated that during the year, the company would work 26,000 direct labor hours and budgeted $1,300,000 for MOH. The company actually worked 24,000 direct labor hours and incurred the following actual manufacturing costs: Direct materials used in production $1,240,000 Direct labor 1,800,000 Indirect labor 300,000 Indirect materials 220,000 Insurance 150,000 Utilities 190,000 Repairs and Maintenance 180,000 Depreciation 320,000 Determine the amount of underapplied or overapplied overhead for the year.arrow_forwardGibson Manufacturing Co. expects to make 30,800 chairs during the year 1 accounting period. The company made 3,300 chairs in January. Materials and labor costs for January were $17,800 and $24,500, respectively. Gibson produced 1,400 chairs in February. Material and labor costs for February were $9,400 and $12,900, respectively. The company paid the $770,000 annual rental fee on its manufacturing facility on January 1, year 1. The rental fee is allocated based on the total estimated number of units to be produced during the year. Required Assuming that Gibson desires to sell its chairs for cost plus 25 percent of cost, what price should be charged for the chairs produced in January and February? (Round intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forward
- Harris Fabrics computes its plantwide predetermined overhead rate annually on the basis of direct labor-hours. At the beginning of the year, it estimated that 20,000 direct labor-hours would be required for the period’s estimated level of production. The company also estimated $94,000 of fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the coming period and variable manufacturing overhead of $2.00 per direct labor-hour. Harris's actual manufacturing overhead cost for the year was $123,900 and its actual total direct labor was 21,000 hours. Required: Compute the company's plantwide predetermined overhead rate for the year. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forwardThe chief cost accountant for Voltaire Beverage Co. estimated that total factory overhead cost for the Blending Department for the coming fiscal year beginning May 1 would be $2,340,000 and total direct labor costs would be $1,800,000. During May, the actual direct labor cost totaled $145,000 and factory overhead cost incurred totaled $192,100. Question Content Area a. What is the predetermined factory overhead rate based on direct labor cost? Enter your answer as a whole percent not in decimals. fill in the blank 1772e2fb3039fb1_1 % Question Content Area b. Journalize the entry to apply factory overhead to production for May. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. blank - Select - - Select - - Select - - Select - Question Content Area c. What is the May 31 balance of the account Factory Overhead—Blending Department? Amount: $fill in the blank 1ea1070e903a021_1 Debit or Credit? d. Does the balance in part (c) represent overapplied or underapplied factory…arrow_forwardBaird Manufacturing Co. expects to make 30,500 chairs during the year 1 accounting period. The company made 4,600 chairs in January. Materials and labor costs for January were $16,600 and $24,200, respectively. Baird produced 1,800 chairs in February. Material and labor costs for February were $9,900 and $13,700, respectively. The company paid the $518,500 annual rental fee on its manufacturing facility on January 1, year 1. The rental fee is allocated based on the total estimated number of units to be produced during the year. Required Assuming that Baird desires to sell its chairs for cost plus 30 percent of cost, what price should be charged for the chairs produced in January and February? (Round intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) January February Price per unitarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education