
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Ozone may decompose according to the following reaction mechanismI pictured below)
a) Determine the rate law for the proposed mechanism assuming that oxygen radical is unstable and highly radical
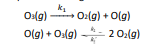
Transcribed Image Text:k
Os(g)
O:(g) + O(g)
Olg) + Oslg)
- 20:(g)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The rate of a reaction was experimentally determined to double if the concentration of reactant A is doubled, and is determined to increase 9 times when the concentration of reactant B is tripled. What is the rate law expression described above?arrow_forwardPlease compose a short answer in which you compare and contrast the following terms: -Rate Expression -Rate Law -Integrated Rate Law In your discussion, you should include… -the uses of each -the limitations of each -the important variables associated with eacharrow_forwardFor the an elementary reaction which one of the following statements is true 1) There are no transition states in an elementary reaction 2) A quaternary elementary reaction is commonly found 3) An elementary reaction is a single state 4) Stoichiometrt coefficients cannot br used in writing the rate law for an elementary reaction 5) There are multiple steps in an elementary reactionarrow_forward
- Problem: Given the reaction H₂ (g) + N₂ (g) → NH3(g) (a) write the corresponding expressions for the reaction rate in terms of each reactant and product (hint: you may need to balance the equation first) (b) if oxygen gas is consumed at a rate of 4.96×10-5 M/s, what is the corresponding reaction rate and what is the rate of consumption of H₂ (g) and the rate of formation of NH3 (g)?arrow_forwardOrganic Chemistry Loudon | Parise SEVENTH EDITION presented by Macmillan Learning The rate law for an addition reaction of bromine to an alkene is k[alkene][Br, 1? rate = The order of the alkene is The order of the bromine is: The overall kinetic order of the reaction is The units of the rate constant are: M-'s-! M-2s-1 M²s-1 ) s-1arrow_forwardQuestion: How can one derive the potential energy surface for a chemical reaction involving multiple transition states and intermediates using high-level quantum chemical methods, and how does this impact the reaction dynamics and overall reaction mechanism?arrow_forward
- Describe how the catalytic mechanism of serine protease enzyme work, for amide hydrolysisarrow_forwardThere are two factors associated with the Arrhenius Rate Constant Equation pre-exponential term, A. What are these factors and explain the meaning of each one?arrow_forwardThe sucrose hydrolysis reaction is pseudo-first order, which means that...(1). The rate constant is practically 1.(2). The rate of transformation of sucrose into glucose and fructose is practically constant over time.(3). the concentrations of the products (glucose and fructose) will be approximately equal to 1 at the end of the reaction.(4). The plot of the logarithm of sucrose concentration versus time should be approximately a straight line.arrow_forward
- Problem 2 Consider the following reaction between nitrogen dioxide gas and carbon monoxide gas 21 + 2H* + H2O2 → I2 + 2H20 (g) The experimentally determined rate law for this reaction is Rate = k [I"] [H2Oz]. The following mechanism has been proposed I + H2O2 → HOI + OH" HOI + I → OH" + I2 (g) Slow Fast H* + OH" → H2O Fastarrow_forward9) If one reaction is a first-order reaction, this reaction should be a (a) simple reaction (b) unimolecular reaction (c) complex reaction (d) all of above are possiblearrow_forwardConsider a reaction taking place in an aqueous solvent. The transition state for this reaction is capable of interacting more strongly with the aqueous solvent (through low potential energy interactions, including hydrogen-bonding) than with the reactant/ground state. Despite these strong potential energy interactions, the reaction rate is not significantly faster than the same reaction taking place in a non-polar solvent. Why? a)The transition enthalpy is unchanged by the aqueous solvent b)The transition Gibbs energy is reduced in the aqueous solvent c) The transition entropy is significantly negative in the aqueous solvated reaction d) The transition state internal energy is significantly negative in the aqueous solvated reaction d) none of the abovearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY