
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Jax Incorporated reports the following data for its only product. The company had no beginning finished goods inventory and it uses absorption costing.
| Sales price | $ 56.70 | per unit |
|---|---|---|
| Direct materials | $ 9.70 | per unit |
| Direct labor | $ 7.20 | per unit |
| Variable |
$ 11.70 | per unit |
| Fixed overhead | $ 944,700 | per year |
1. Compute gross profit assuming (a) 67,000 units are produced and 67,000 units are sold and (b) 94,000 units are produced and 67,000 units are sold.
2. By how much would the company’s gross profit increase or decrease from producing 27,000 more units than it sells?
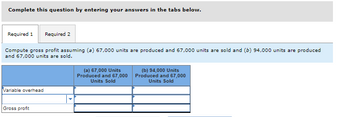
Transcribed Image Text:Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1 Required 2
Compute gross profit assuming (a) 67,000 units are produced and 67,000 units are sold and (b) 94,000 units are produced
and 67,000 units are sold.
Variable overhead
Gross profit
(a) 67,000 Units
Produced and 67,000
Units Sold
(b) 94,000 Units
Produced and 67,000
Units Sold
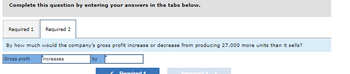
Transcribed Image Text:Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Required 1 Required 2
By how much would the company's gross profit increase or decrease from producing 27,000 more units than it sells?
Gross profit
increases
by
L Required 1
Required 2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nelter Corporation, which has only one product, has provided the following data concerning its most recent month of operations: Selling price Units in beginning inventory Units produced Units sold Units in ending inventory Variable costs per-unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative expense Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expense $ 122 290 6,600 6,590 300 $ 42 $ 26 $ 2 $ 21 $ 151,800 $ 46,130 The company produces the same number of units every month, although the sales in units vary from month to month. The company's variable costs per unit and total fixed costs have been constant from month to month. Required: a. Prepare a contribution format income statement for the month using variable costing. b. Prepare an income statement for the month using absorption costing.arrow_forwardJax Incorporated reports the following data for its only product. The company had no beginning finished goods inventory and it uses absorption costing Sales price Direct materials Direct labor $ 56.40 per unit $9.40 per unit $6.90 per unit $11.40 per unit $844,800 per year Variable overhead Fixed overhead 1. Compute gross profit assuming (a) 64,000 units are produced and 64,000 units are sold and (b) 88,000 units are produced and 64,000 units are sold. 2. By how much would the company's gross profit increase or decrease from producing 24,000 more units than it sells? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Compute gross profit assuming (a) 64,000 units are produced and 64,000 units are sold and (b) 88,000 units are produced and 64,000 units are sold 1 rces (a) 64,000 Units Produced and $4,000 Units Sold (b) 55.000 Units Produced and 64,000 Units Sold Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Required 2 >arrow_forwardTrez Company began operations this year. During this year, the company produced 100,000 units and sold 80,000 units. The absorption costing income statement for this year follows. Income Statement (Absorption Costing) Sales (80,000 units × $45 per unit) $ 3,600,000 Cost of goods sold 2,000,000 Gross profit 1,600,000 Selling and administrative expenses 560,000 Income $ 1,040,000 Additional Information Selling and administrative expenses consist of $400,000 in annual fixed expenses and $2 per unit in variable selling and administrative expenses. The company's product cost of $25 per unit consists of the following. Direct materials $ 4 per unit Direct labor $ 10 per unit Variable overhead $ 4 per unit Fixed overhead ($700,000 / 100,000 units) $ 7 per unit Required:Prepare an income statement for the company under variable costing.arrow_forward
- Grainger Company produces only one product and sells that product for $90 per unit. Cost information for the product is as follows: Direct Material $16 per Unit Direct Labor $26 per Unit Variable Overhead $4 per Unit Fixed Overhead $27,200 Selling expenses are $5 per unit and are all variable. Administrative expenses of $20,000 are all fixed. Grainger produced 4,000 units; sold 3,200; and had no beginning inventory. A. Compute net income under i. Absorption Costing $ ii. Variable Costing B. Which costing method provide higher net income? By how much? The method provided more net income by $arrow_forwardGabuat Corporation, which has only one product, has provided the following data concerning its most recent month of operations: Selling price Units in beginning inventory $136 0 Units produced 3,400 Units sold 2,920 Units in ending inventory 480 Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead $46 $24 $4 Variable selling and administrative expense $7 Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expenses $68,000 $14,600 The total gross margin for the month under the absorption costing approach is: a. $108,040 b. $122,640 c. $102,200 d. $210,240arrow_forwardGrainger Company produces only one product and sells that product for $90 per unit. Cost information for the product is as follows: Direct Material $15 per Unit Direct Labor $26 per Unit Variable Overhead $4 per Unit Fixed Overhead $34,000 Selling expenses are $3 per unit and are all variable. Administrative expenses of $15,000 are all fixed. Grainger produced 5,000 units; sold 4,000; and had no beginning inventory. A. Compute net income under i. Absorption Costing $fill in the blank 1 ii. Variable Costing $fill in the blank 2 B. Which costing method provide higher net income? By how much? The method provided more net income by $fill in the blank 4 .arrow_forward
- arded ed Krepps Corporation produces a single product. Last year, Krepps manufactured 26,160 units and sold 20,900 units. Production costs for the year were as follows: Mc Graw Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Sales totaled $971,850 for the year, variable selling and administrative expenses totaled $108,680, and fixed selling and administrative expenses totaled $190,968. There was no beginning inventory. Assume that direct labor is a variable cost. Under variable costing, the company's net operating income for the year would be: Multiple Choice O $32,086 lower than under absorption costing. $ 188,352 $ 112,488 $ 224,976 $ 470,880 O $32,086 higher than under absorption costing. O $94,680 lower than under absorption costing.arrow_forwardDowell Company produces a single product. Its income statements under absorption costing for its first two years of operation follow. Income Statements (Absorption Costing) Sales ($54 per unit) Cost of goods sold ($40 per unit) Year 2 Year 1 $ 1,512,000 1,120,000 $ 3,132,000 2,320,000 Gross profit Selling and administrative expenses Income 392,000 293,000 812,000 323,000 $ 99,000 $ 489,000 Additional Information a. Sales and production data for these first two years follow. Units Units produced Units sold Year 1 43,000 28,000 Year 2 43,000 58,000 b. Variable costs per unit and fixed costs per year are unchanged during these years. The company's $40 per unit product cost using absorption costing consists of the following. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead ($387,000/43,000 units) Total product cost per unit $ 13 13 5 9 $ 40 c. Selling and administrative expenses consist of the following. Selling and Administrative Expenses Variable selling and administrative…arrow_forwardDowell Company produces a single product. Its income statements under absorption costing for its first two years of operation follow. Income Statements (Absorption Costing) Year 1 Year 2 Sales ($50 per unit) $ 1,350,000 $ 2,550,000 Cost of goods sold ($39 per unit) 1,053,000 1,989,000 Gross profit 297,000 561,000 Selling and administrative expenses 247,000 271,000 Income $ 50,000 $ 290,000 Additional Information Sales and production data for these first two years follow. Units Year 1 Year 2 Units produced 39,000 39,000 Units sold 27,000 51,000 Variable costs per unit and fixed costs per year are unchanged during these years. The company's $39 per unit product cost using absorption costing consists of the following. Direct materials $ 16 Direct labor 9 Variable overhead 5 Fixed overhead ($351,000/39,000 units) 9 Total product cost per unit $ 39 Selling and administrative expenses consist of the following. Selling and…arrow_forward
- Trez Company began operations this year. During this year, the company produced 100,000 units and sold 80,000 units. The absorption costing income statement for this year follows. Income Statement (Absorption Costing) Sales (80,000 units x $45 per unit) Cost of goods sold Gross profit Selling and administrative expenses Income Additional Information $ 3,600,000 2,000,000 1,600,000 490,000 $ 1,110,000 a. Selling and administrative expenses consist of $350,000 in annual fixed expenses and $1.75 per unit in variable selling and administrative expenses. b. The company's product cost of $25 per unit consists of the following. Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead ($700,000 / 100,000 units) Required: $ 5 per unit $ 10 per unit $ 3 per unit $ 7 per unit Prepare an income statement for the company under variable costing. TREZ Companyarrow_forwardKrepps Corporation produces a single product. Last year, Krepps manufactured 33,930 units and sold 28,300 units. Production costs for the year were as follows: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Sales totaled $1,287,650 for the year, variable selling and administrative expenses totaled $164,140, and fixed selling and administrative expenses totaled $206,973. There was no beginning inventory. Assume that direct labor is a variable cost. The contribution margin per unit was: (Round your Intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.) Multiple Choice $19.50 per unit $24.20 per unit O $18.40 per unit $288,405 $145,899 $288,405 $542,880 $13.90 per unitarrow_forwardGrainger Company produces only one product and sells that product for $110 per unit. Cost information for the product is as follows: Direct Material $16 per Unit Direct Labor $26 per Unit Variable Overhead $6 per Unit Fixed Overhead $27,200 Selling expenses are $5 per unit and are all variable. Administrative expenses of $20,000 are all fixed. Grainger produced 4,000 units; sold 3,200; and had no beginning inventory. A. Compute net income under i. Absorption Costing $fill in the blank 1 ii. Variable Costing $fill in the blank 2 B. Which costing method provide higher net income? By how much? The method provided more net income by $fill in the blank 4 .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education