
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
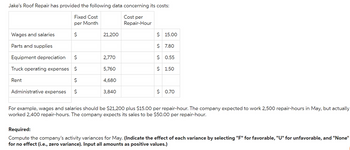
Transcribed Image Text:Jake's Roof Repair has provided the following data concerning its costs:
Fixed Cost
per Month
Cost per
Repair-Hour
$
Wages and salaries
Parts and supplies
Equipment depreciation $
Truck operating expenses $
$
Administrative expenses $
Rent
21,200
2,770
5,760
4,680
3,840
$ 15.00
$ 7.80
$ 0.55
$ 1.50
$ 0.70
For example, wages and salaries should be $21,200 plus $15.00 per repair-hour. The company expected to work 2,500 repair-hours in May, but actually
worked 2,400 repair-hours. The company expects its sales to be $50.00 per repair-hour.
Required:
Compute the company's activity variances for May. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None"
for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following table provides data concerning a company’s costs: Fixed Cost per Month Cost per Car Washed Cleaning supplies $ 0.40 Electricity $ 1,400 $ 0.08 Maintenance $ 0.15 Wages and salaries $ 4,900 $ 0.30 Depreciation $ 8,400 Rent $ 1,800 Administrative expenses $ 1,400 $ 0.04 For example, electricity costs are $1,400 per month plus $0.08 per car washed. The company expects to wash 8,000 cars in August and to collect an average of $6.10 per car washed. Prepare the company’s planning budget for August. Budgeted Cars Washed Revenue Expenses: Cleaning Supplies Electricity Maintenance Wages and Salaries Depreciation Rent Administrative Expenses Total Expenses Net Operating Income $arrow_forwardSandhill Company makes three models of tasers. Information on the three products is given below. Tingler Shocker Stunner Sales $296,000 $504,000 $200,000 Variable expenses 151,700 207,900 138,200 Contribution margin 144,300 296,100 61,800 Fixed expenses 117,800 231,800 95,000 Net income $26,500 $64,300 $(33,200) Fixed expenses consist of $300,000 of common costs allocated to the three products based on relative sales, as well as direct fixed expenses unique to each model of $29,000 (Tingler), $80,600 (Shocker), and $35,000 (Stunner). The common costs will be incurred regardless of how many models are produced. The direct fixed expenses would be eliminated if that model is phased out. James Watt, an executive with the company, feels the Stunner line should be discontinued to increase the company's net income. (a) Compute current net income for Sandhill Company. Net income Aarrow_forwardI b) Refer to the following data: Direct material used $180 000 Advertising costs $ 5 000 Indirect labour $ 8 000 Rent on corporate office $ 20 000 Depreciation on factory equipment $ 60 000 Direct labour $ 30 000 Factory cleaners wages $ 20 000 Indirect materials $ 35 000 Required (show your workings for each question): Determine each of the following costs: (list the costs under each cost category when calculating the answer). Period costsarrow_forward
- Please help mearrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardThe following data is available for Sheridan Repair Shop for 2022: Repair technicians' wages Employee benefits Overhead Total $410000 90000 $122. $140. $152. $112. 60000 $560000 The desired profit margin is $40 per labor hour. The material loading charge is 40% of invoice cost. It is estimated that 5000 labor hours will be worked in 2022. Sheridan' labor charge per hour in 2022 would bearrow_forward
- Jake's Roof Repair has provided the following data concerning its costs: Fixed Cost Cost per per Month Repair-Hour Wages and salaries Parts and supplies $ 21,400 $ 15.00 $ 7.20 Equipment depreciation $ 2,740 $ 0.55 Truck operating expenses Rent $ 5,720 $ 1.70 $ 4,660 $ 3,880 $ 0.70 Administrative expenses For example, wages and salaries should be $21,400 plus $15.00 per repair-hour. The company expected to work 2,700 repair-hours in May, but actually worked 2,600 repair-hours. The company expects its sales to be $47.00 per repair-hour. Required: Compute the company's activity variances for May. Note: Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Revenue Expenses: Jake's Roof Repair Activity Variances For the Month Ended May 31 Wages and salaries Parts and supplies Equipment depreciation Truck operating expenses Rent Administrative expenses Total expense Net…arrow_forwardAmerican Investor Group is opening an office in Portland, Oregon. Fixed monthly costs are office rent ($8,800), depreciation on office furniture ($1,800), utilities ($2,500), special telephone lines ($1,500), a connection with an online brokerage service ($2,400), and the salary of a financial planner ($4,000). Variable costs include payments to the financial planner (9% of revenue), advertising (11% of revenue), supplies and postage (4% of revenue), and usage fees for the telephone lines and computerized brokerage service (6% of revenue). Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Use the contribution margin ratio approach to compute American's breakeven revenue in dollars. If the average trade leads to $750 in revenue for American, how many trades must be made to break even? Begin by showing the formula and then entering the amounts to calculate the required sales dollars for American to break even. (Abbreviation used: CM = contribution margin.) Fixed costs Target profit ) + CM ratio =…arrow_forwardJake's Roof Repair has provided the following data concerning its costs: Fixed Cost per Month $ 23, 200 Cost per Repair-Hour $16.30 $ 8.60 $ 0.40 $ 1.70 Wages and salaries Parts and supplies Equipment depreciation Truck operating expenses Rent Administrative expenses Revenue Expenses: $ 1,600 $ 6,400 For example, wages and salaries should be $23,200 plus $16.30 per repair-hour. The company expected to work 2,800 repair-hours in May, but actually worked 2,900 repair-hours. The company expects its sales to be $44.50 per repair-hour. $ 3,480 $ 4,500 Required: Compute the company's activity variances for May. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) Wages and salaries Parts and supplies Equipment depreciation Truck operating expenses Rent Jake's Roof Repair Activity Variances For the Month Ended May 31 Administrative expenses Total expense Net operating…arrow_forward
- Please help me with show all calculation don't provide Excel workarrow_forwardJake's Roof Repair has provided the following data concerning its costs: Cost per Repair-Hour Fixed Cost per Month $ Wages and salaries Parts and supplies Equipment depreciation $ Truck operating expenses $ Rent $ Administrative expenses $ 21,100 2,750 5,780 4,660 3,840 $ 16.00 $ 7.20 $ 0.55 $ 1.70 $ 0.40 For example, wages and salaries should be $21,100 plus $16.00 per repair-hour. The company expected to work 2,600 repair-hours in May, but actually worked 2,500 repair-hours. The company expects its sales to be $48.00 per repair-hour. Required: Compute the company's activity variances for May. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) Need to make sure my notes coincide with this example problem from video. please include how you calculated each part. Thank youarrow_forwardJake's Roof Repair has provided the following data concerning its costs: Fixed Cost Cost per per Month Repair-Hour $ 21,500 $ 15.00. $7.30 Wages and salaries Parts and supplies Equipment depreciation Truck operating expenses Rent Revenue Expenses: Administrative expenses $ 0.50 For example, wages and salaries should be $21,500 plus $15.00 per repair-hour. The company expected to work 3,000 repair-hours in May, but actually worked 2,900 repair-hours. The company expects its sales to be $54.00 per repair-hour. $ 2,760 $ 5,740 Required: Compute the company's activity variances for May. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) Wages and salaries Parts and supplies Equipment depreciation Truck operating expenses Rent $ 4,630 $ 3,820 Jake's Roof Repair Activity Variances For the Month Ended May 31 Administrative expenses Total expense Net operating income $…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education