
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
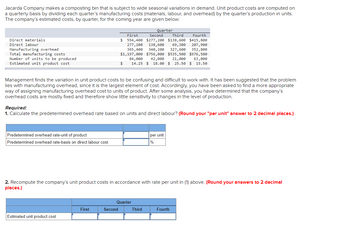
Transcribed Image Text:Jacarda Company makes a composting bin that is subject to wide seasonal variations in demand. Unit product costs are computed on
a quarterly basis by dividing each quarter's manufacturing costs (materials, labour, and overhead) by the quarter's production in units.
The company's estimated costs, by quarter, for the coming year are given below:
Direct materials
Direct labour
Manufacturing overhead
Total manufacturing costs
Number of units to be produced
Estimated unit product cost
Management finds the variation in unit product costs to be confusing and difficult to work with. It has been suggested that the problem
lies with manufacturing overhead, since it is the largest element of cost. Accordingly, you have been asked to find a more appropriate
way of assigning manufacturing overhead cost to units of product. After some analysis, you have determined that the company's
overhead costs are mostly fixed and therefore show little sensitivity to changes in the level of production.
Predetermined overhead rate-unit of product
Predetermined overhead rate-basis on direct labour cost
Required:
1. Calculate the predetermined overhead rate based on units and direct labour? (Round your "per unit" answer to 2 decimal places.)
Quarter
Second
First
Third
Fourth
$ 554,400 $277,200 $138,600 $415,800
277, 200
138,600 69,300 207,900
365,400 340,200 327,600 352,800
$1,197,000 $756,000 $535,500 $976,500
84,000 42,000 21,000 63,000
14.25 $ 18.00 $25.50 $ 15.50
Estimated unit product cost
$
First
2. Recompute the company's unit product costs in accordance with rate per unit in (1) above. (Round your answers to 2 decimal
places.)
Second
Quarter
per unit
%
Third
Fourth
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Domesticarrow_forwardPreble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct material: 4 pounds at $9.00 per pound Direct labor: 3 hours at $15 per hour Variable overhead: 3 hours at $6 per hour Total standard variable cost per unit The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Advertising Sales salaries and commissions Shipping expenses Fixed Cost per Month $36.00 45.00 18.00 $99.00 $ 210,000 $ 120,000 Variable manufacturing overhead cost Variable Cost per Unit Sold $ 13.00 $ 4.00 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 26,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 31,000 units and incurred the following costs: a. Purchased 155,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $7.20 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b. Direct-laborers worked 56,000 hours at a rate of $16.00…arrow_forwardKingsport Containers Company makes a single product with wide seasonal variations in demand. The company uses a job-order costing system and computes plantwide predetermined overhead rates on a quarterly basis using the number of units to be produced as the allocation base. Its estimated costs, by quarter, for the coming year are given below: Direct materials Direct labor Manufacturing overhead Total manufacturing costs (a) Number of units to be produced (b) Estimated unit product cost (a) (b) First $ 200,000 120,000 230,000 $ 550,000 Required 1 Required 2 Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. 120,000 $ 4.58 The as production Quarter Required 3 Required 4 Second $ 100,000 60,000 206,000 $366,000 60,000 $ 6.10 Management finds the variation in quarterly unit product costs to be confusing. Accordingly, you have been asked to find a more appropriate way of applying manufacturing overhead cost to units of product. Required: 1. Assuming the estimated variable…arrow_forward
- Sardi Inc. is considering whether to continue to make a component or to buy it from an outside supplier. The company uses 13,100 of the components each year. The unit product cost of the component according to the company's cost accounting system is given as follows: Direct materials $ 8.90 Direct labor 5.90 Variable manufacturing overhead 1.70 Fixed manufacturing overhead 3.70 Unit product cost $ 20.20 Assume that direct labor is a variable cost. Of the fixed manufacturing overhead, 20% is avoidable if the component were bought from the outside supplier. In addition, making the component uses 2 minutes on the machine that is the company's current constraint. If the component were bought, time would be freed up for use on another product that requires 4 minutes on this machine and that has a contribution margin of $5.30 per unit. When deciding whether to make or buy the component, what cost of making the component should be compared to the…arrow_forwardLehighton Chalk Company manufactures sidewalk chalk, which it sells online by the box at $25 per unit. Lehighton uses an actual costing system, which means that the actual costs of direct material, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead are entered into work-in-process inventory. The actual application rate for manufacturing overhead is computed each year; actual manufacturing overhead is divided by actual production (in units) to compute the application rate. Information for Lehighton's first two years of operation is as follows: Sales (in units) Production (in units) Production costs: Variable manufacturing costs Fixed manufacturing overhead Selling and administrative costs: Variable Fixed Based on absorption costing Finished-goods inventory Retained earnings Year 1 2,600 3,100 $15,500 18,600 Based on variable costing Finished-goods inventory Retained earnings LEHIGHTON CHALK COMPANY Selected Balance Sheet Information End of Year 1 10,400 9,400 $ 5,500 11,100 Selected information…arrow_forwardMission Company is preparing its annual profit plan. As part of its analysis of the profitability of individual products, the controller estimates the amount of overhead that should be allocated to the individual product lines from the information provided below (CMA adapted) Units produced Material moves per product line. Direct labor-hours per product line Budgeted material handling costs: $644,000 Wall Mirrors Specialty Windows 220 20 5 1,100 60 1,200 Under a traditional costing system that allocates overhead on the basis of direct labor-hours, the materials handling costs allocated to one unit of Specialty Windows would be Multiple Choice O $16.800 $54,900 $14,000 $22.700arrow_forward
- Answer all questions and properlyarrow_forwardCost Behavior SmokeCity, Inc., manufactures barbeque smokers. Based on past experience, SmokeCity has found that its total annual overhead costs can be represented by the following formula: Overhead cost = $539,780 + $1.32X, where X equals number of smokers. Last year, SmokeCity produced 19,700 smokers. Actual overhead costs for the year were as expected. Required: 1. What is the driver for the overhead activity? For questions 2-4, Enter the final answers rounded to the nearest dollar. 2. What is the total overhead cost incurred by SmokeCity last year? 3. What is the total fixed overhead cost incurred by SmokeCity last year? 4. What is the total variable overhead cost incurred by SmokeCity last year?arrow_forwardThe following are Silver Corporation's unit costs of making and selling an item at a volume of 8,700 units per month (which represents the company's capacity): Manufacturing: Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Selling and administrative: Variable Fixed Present sales amount to 6,100 units per month. An order has been received from a customer in a foreign market for 2,600 units. The order would not affect regular sales. Total fixed costs, both manufacturing and selling and administrative, would not be affected by this order. The variable selling and administrative costs would have to be incurred for this special order as well as all other sales. Assume that direct labor is a variable cost. Multiple Choice Assume the company has 80 units left over from last year which have small defects and which will have to be sold at a reduced price for scrap. The sale of these defective units will have no effect on the company's other sales. Which of the following costs is…arrow_forward
- The following information relates to the unit product cost for a product manufactured by Nelson Industrial Company:Direct materials: $24 Direct Labor: 15 Variable overhead: 30 Fixed overhead: 18 Unit cost: 87 Line Item Description Cost Direct materials $24 Direct labor 15 Variable overhead 30 Fixed overhead 18 Unit cost $87 In addition, fixed selling costs are $500,000 per year, and variable selling costs are $12 per unit sold. Although production capacity is 600,000 units per year, the company expects to produce only 400,000 units next year. The product normally sells for $120 each. A customer has offered to buy 100,000 units for $90 each.If the firm produces the special order, the effect on income would be a(n): a. increase of $1.050,000. b. decrease of $900,000. c. decrease of $1,0500,000. d. increase of $900,000.arrow_forwardKingsport Containers Company makes a single product that is subject to wide seasonal variations in demand. The company uses a job-order costing system and computes plantwide predetermined overhead rates on a quarterly basis using the number of units to be produced as the allocation base. Its estimated costs, by quarter, for the coming year are given below: Quarter First Second Third Fourth Direct materials $ 200,000 $ 100,000 $ 50,000 $ 150,000 Direct labor 120,000 60,000 30,000 90,000 Manufacturing overhead 240,000 216,000 204,000 ? Total manufacturing costs (a) $ 560,000 $ 376,000 $ 284,000 $ ? Number of units to be produced (b) 120,000 60,000 30,000 90,000 Estimated unit product cost (a) ÷ (b) $ 4.67 $ 6.27 $ 9.47 $ ? Management finds the variation in quarterly unit product costs to be confusing. It has been suggested that the problem lies with manufacturing overhead because it is the largest element of total manufacturing cost. Accordingly, you have…arrow_forwardVishnuarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education