
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
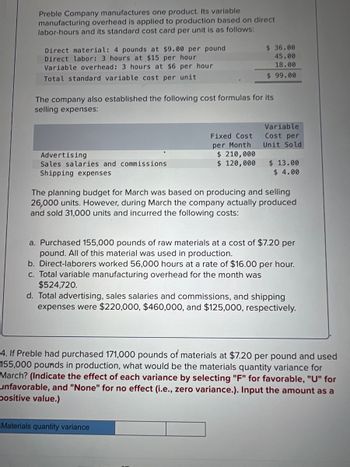
Transcribed Image Text:Preble Company manufactures one product. Its variable
manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct
labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows:
Direct material: 4 pounds at $9.00 per pound
Direct labor: 3 hours at $15 per hour
Variable overhead: 3 hours at $6 per hour
Total standard variable cost per unit
The company also established the following cost formulas for its
selling expenses:
Advertising
Sales salaries and commissions
Shipping expenses
Fixed Cost
per Month
$36.00
45.00
18.00
$99.00
$ 210,000
$ 120,000
Variable
Cost per
Unit Sold
Materials quantity variance
$ 13.00
$ 4.00
The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling
26,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced
and sold 31,000 units and incurred the following costs:
a. Purchased 155,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $7.20 per
pound. All of this material was used in production.
b. Direct-laborers worked 56,000 hours at a rate of $16.00 per hour.
c. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was
$524,720.
d. Total advertising, sales salaries and commissions, and shipping
expenses were $220,000, $460,000, and $125,000, respectively.
4. If Preble had purchased 171,000 pounds of materials at $7.20 per pound and used
155,000 pounds in production, what would be the materials quantity variance for
March? (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for
unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance.). Input the amount as a
positive value.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Preble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct material: 4 pounds at $9.00 per pound Direct labor: 3 hours at $15 per hour Variable overhead: 3 hours at $6 per hour Total standard variable cost per unit The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Advertising Sales salaries and commissions Shipping expenses $36.00 45.00 18.00 $99.00 Fixed Cost per Month $ 210,000 $ 120,000 Variable Cost per Unit Sold $ 13.00 $ 4.00 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 26,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 31,000 units and incurred the following costs: Variable overhead efficiency variance a. Purchased 155,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $7.20 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b. Direct-laborers worked 56,000 hours at a rate of…arrow_forwardMartinez Company's relevant range of production is 7,500 units to 12,500 units. When it produces and sells 10,000 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Average Cost per Unit $6.10 $3.60 $1.40 Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling expense Fixed administrative expense $4.00 $3.10 $2.10 $1.10 $0.55 Sales commissions Variable administrative expense 3. If 8,000 units are produced and sold, what is the variable cost per unit produced and sold? (Round your answer to 2 decimal places.) Variable cost per unit soldarrow_forwardKesterson Corporation has provided the following information: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Sales commissions Variable administrative expense Fixed selling and administrative expense Cost per Unit $ 6.30 $ 3.30 $ 1.25 $ 1.30 $ 0.60 Cost per Period $ 15,000 $ 4,200 If 7,000 units are produced, the total amount of indirect manufacturing cost incurred is closest to:arrow_forward
- Preble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct material: 4 pounds at $9.00 per pound $ 36.00 Direct labor: 3 hours at $12 per hour 36.00 Variable overhead: 3 hours at $8 per hour 24.00 Total standard variable cost per unit $ 96.00 The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Fixed Cost per Month Variable Cost per Unit Sold Advertising $ 230,000 Sales salaries and commissions $ 160,000 $ 15.00 Shipping expenses $ 6.00 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 28,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 33,000 units and incurred the following costs: Purchased 165,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $7.20 per pound. All of this material was used in production. Direct-laborers worked 58,000 hours at a rate of…arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Preble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct material: 4 pounds at $9.00 per pound Direct labor: 3 hours at $15 per hour Variable overhead: 3 hours at $6 per hour Total standard variable cost per unit The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Advertising Sales salaries and commissions Shipping expenses $ 36.00 45.00 18.00 $ 99.00 Fixed Cost per Month $ 210,000 $ 120,000 Variable Cost per Unit Sold $ 13.00 $ 4.00 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 26,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 31,000 units and incurred the following costs: Variable overhead rate variance a. Purchased 155,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $7.20 per pound. All of this…arrow_forward[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Preble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct material: 5 pounds at $8.00 per pound Direct labor: 3 hours at $15 per hour Variable overhead: 3 hours at $9 per hour Total standard variable cost per unit The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Variable Cost per Unit Sold Advertising Sales salaries and commissions Shipping expenses Fixed Cost per Month $ 350,000 $ 400,000 $ 40.00 45.00 27.00 $112.00 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 21,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 26,000 units and incurred the following costs: Direct labor cost $ 27.00 $18.00 a. Purchased 160,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $6.50 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b.…arrow_forward
- Preble Company manufactures one product Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: $40.00 Direct material: 4 pounds at $10.00 per pound Direct labor: 2 hours at $16 per hour Variable overhead: 2 hours at $6 per hour 12.00 Total standard variable cost per unit The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Variable Cost, per Unit Sold Fixed Cost per Month $ 270,000 $ 240,000 Advertising $19.00 Shipping expenses The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 30,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 34,500 units and incurred the following costs: a. Purchased 150,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $9.20 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b. Direct-laborers worked 62,000 hours at a rate of $1700 per hour c. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was $390,600. d. Total…arrow_forwardPreble Company manufactures one product Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: $40.00 Direct material: 4 pounds at $10.00 per pound Direct labor: 2 hours at $16 per hour Variable overhead: 2 hours at $6 per hour Total standard variable cost per unit The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Fixed Cost Variable Cost per Month per Unit Sold Advertising Sales salaries and commissions Shipping expenses $ 240,000 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 30,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 34,500 units and incurred the following costs: a. Purchased 150,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $9.20 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b. Direct-laborers worked 62,000 hours at a rate of $17.00 per hour. C. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was $390,600.…arrow_forwardPreble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct material: 5 pounds at $8.00 per pound $ 40.00 Direct labor: 2 hours at $14 per hour 28.00 Variable overhead: 2 hours at $5 per hour 10.00 Total standard variable cost per unit $ 78.00 The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Fixed Cost per Month Variable Cost per Unit Sold Advertising $ 200,000 Sales salaries and commissions $ 100,000 $ 12.00 Shipping expenses $ 3.00 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 25,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 30,000 units and incurred the following costs: Purchased 160,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $7.50 per pound. All of this material was used in production. Direct-laborers worked 55,000 hours at a rate of…arrow_forward
- T4.arrow_forward一 Preble Company manufactures one product Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct material: 4 pounds at $10.00 per pound Direct labor: 2 hours at $16 per hour Variable overhead: 2 hours at $6 per hour Total standard variable cost per unit The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Variable Cost per Unit Sold, Fixed Cost per Month $ 270,000 Advertising, Sales salaries and commissions Shipping expenses $19.00 0000 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 30,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 34,500 units and incurred the following costs: a. Purchased 150,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $9.20 per pound, All of this material was used in production. b. Direct-laborers worked 62,000 hours at a rate of $17.00 per hour. c. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was…arrow_forwardPreble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct material: 5 pounds at $10.00 per pound $ 50.00 Direct labor: 3 hours at $17 per hour 51.00 Variable overhead: 3 hours at $7 per hour 21.00 Total standard variable cost per unit $ 122.00 The company also established the following cost formulas for its selling expenses: Fixed Cost per Month Variable Cost per Unit Sold Advertising $ 330,000 Sales salaries and commissions $ 360,000 $ 25.00 Shipping expenses $ 16.00 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 24,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 30,600 units and incurred the following costs: Purchased 170,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $9.00 per pound. All of this material was used in production. Direct-laborers worked 68,000 hours at a rate of…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education