
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
INSTRUCTIONS: Solve the following problem by manually applying the finite element method, following these steps:
Pre-processing:
- Geometry identification.
- Material properties identification.
- Load identification.
- Boundary condition identification.
- Development of the connectivity matrix for nodes and elements.
Processing:
- Calculation of local stiffness matrices.
- Assembly of the global stiffness matrix.
- Assembly of the global force matrix (if required).
- Application of boundary conditions.
- Resolution of the system of equations.
- Derivation of the complete displacement
vector (u).
Post-processing:
- Reaction forces calculation.
- Stress analysis.
Problem Statement: the truss nodes and elements (in parentheses) are already numbered. The areas (are in cm^2 ) are underlined. members are made of structural steel, modulus of elasticity is (E) of 20×10^6 N/cm^2 . the lengths are given in cm.
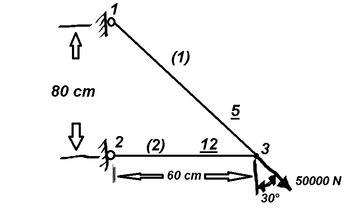
Transcribed Image Text:80 cm
(1)
501
(2)
12
3
60 cm=
50000 N
30°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 21. The programmer uses three-point method for UT[2] setup for a sharp-tip pointer. If the programmer recorded each of three-points by precisely contacting the sharp-tip to the tip of the stationary reference pointer on the table, then (a) UT[2] setup is accurate (b) UT[2] setup is not accurate (c) the accuracy of UT[2] setup is still uncertain 22. User frame UF[3] is accurately set up on the part reference surface which is unparallel to the surface where the robot is mounted. To jog the robot TCP to move perpendicularly to the part reference surface, the programmer (a) needs to select World jogging coordinate system (b) needs to activate UF[3] and select User Frame jogging coordinate systemarrow_forwardQ4arrow_forwardchange in the forces so D is 300N and B is 200N. Need help solving for Ay and Cy.arrow_forward
- You are given a linear resonant actuator used for haptic vibration cues in phones - a device that might produce the vibration that happens when you get a notification. A basic model is shown on the left. For this problem, you'll need to derive the EOMS for the system (it will be a second order system) and then put it into a number of different system representation forms. Your tasks: karm Carm • I1 = Act • X2 = *1 • I3 = IP Actuator electromagnetic force Fact • I4 = 3 • U = FAct mp Fact kact Cact Xp mact Xact CHALOS CURRENT CONDUCTING PRECISION MICRODRIVES PRECISION HAPTIC™ NOVING MASS No 8 NEOUTMUN FLOCCUT BAGNET 0:0 AND VOICECORIS Z-AXIS LINEAR RESONANT ACTUATOR Credit Precision Microdrives. Ltd. FLYING LEADS FLEX CIRCENT NEOUT MALAET SELFDESVE CASA VERATING BASS ASSEMBLY A. Using Newton's Laws of Motion, derive equations of motion for the system using the variable names given in the figure on the left…arrow_forwardPlease follow the instructions and the requirements according to the pictures above and I kinda need the solution quickly. The language of the code is in Matlab, thank you in advance.arrow_forwardHelp with a and b pleasearrow_forward
- O 17161489 C Get Homework Help With b My Questions | bartleby O Mail - Castro Alvarez, Flavic X Content A learn-us-east-1-prod-fleet01-xythos.s3.amazonaws.com/5c1270dbb5a74/17161489?response-cache-control=private%2C%20max-age%3D21600&respon. ☆ ME 3022 - HW 19 1. (More practice from Monday) A 90° elbow in a horizontal pipe is used to direct a flow of oil (SG = 0.87) upward at a rate of 40 kg/s. The cross- sectional diameter of the elbow is a constant 20 cm. The elbow discharges at A into a large holding tank where the level of oil is 1.8 m above A. The 50 cm "weight" of the elbow and the oil in it is 50 kg. Determine (a) the gage pressure at the inlet of the elbow and (b) the anchoring force needed to hold the elbow stationary. Take the momentum-flux correction factor to be 1.03 40 kg/s at both the inlet and the outlet. Activar Windows Ve a Configuración para activar Windows. Esperando blackboard.ohio.edu. 17:07 P Escribe aquí para buscar a ) ENG 14/10/2020 近arrow_forwardI am trying to find a Direction Cosine Matrix (DCM) for the Euler angle body 1-2-3 sequence. I tried making my own function and using the MATLAB function, but the result is a matrix that is transpose of each other. I mean that transpose(EA123toDCM) = E123toDCM. Why is that? Also, for the E123toDCM line, I am using the sequence 'ZYX'. Is that correct or should it be 'XYZ'? I know that that for a DCM of sequence 1-2-3 = R3(theta1)*R2(theta2)*R1(theta3). Is ZYX sequence the same as a 1-2-3 sequence? EA = [pi/3; -pi/4; -pi/6];EA123toDCM = EA123DCM(EA) E123toDCM = angle2dcm(EA(1,1), EA(2,1), EA(3,1), 'ZYX') function [R] = EA123DCM(EA) theta1 = EA(1,1); theta2 = EA(2,1); theta3 = EA(3,1); R1 = @(a)[1 0 0 ; 0 cos(a) -sin(a); 0 sin(a) cos(a)]; R2 = @(a)[cos(a) 0 sin(a) ; 0 1 0 ; -sin(a) 0 cos(a)]; R3 = @(a)[ cos(a) -sin(a) 0; sin(a) cos(a) 0;…arrow_forwardAsaparrow_forward
- Given the trasnfer function G(s) numerator and denominator coefficients for Matlab code should be: O s³+2s+1 2s4+2s²+1' the num= [1 0 2 1] and den=[2 020 1] O num=[1 2 1] and den=[2 0 2 1 1] O num=[1 2 1] and den=[2 2 1] O num=[1 0 2 1] and den=[2 2 0 1]arrow_forwardkamihq.com/web/viewer.html?state%=D%7B"ids"%3A%5B"1vSrSXbH_6clkKyVVKKAtzZb_GOMRwrCG"%5D%... lasses Gmail Copy of mom it for.. Маps OGOld Telephone Ima. Preview attachmen... Kami Uploads ► Sylvanus Gator - Mechanical Advantage Practice Sheet.pdf rec Times New Roman 14px 1.5pt BIUSA A Xa x* 三三 To find the Mechanical Advantage of ANY simple machine when given the force, use MA = R/E. 1. An Effort force of 30N is appliled to a screwdriver to pry the lid off of a can of paint. The screwdriver applies 90N of force to the lid. What is the MA of the screwdriver? MA =arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ......arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY