
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Question 9 could you show all work
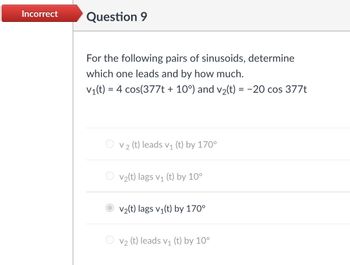
Transcribed Image Text:Incorrect
Question 9
For the following pairs of sinusoids, determine
which one leads and by how much.
V1(t) = 4 cos(377t + 10°) and v2(t) = -20 cos 377t
V2 (t) leads v₁ (t) by 170°
V2(t) lags v₁ (t) by 10°
V2(t) lags v₁(t) by 170°
V2 (t) leads v₁ (t) by 10°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 40 kHz sinusoidal voltage has zero phase angle and a maximum amplitude of 25 mV. When this voltage is applied across the terminals of a capacitor, the resulting steady-state current has a maximum amplitude of 628.32 μA. Part A What is the frequency of the current in radians per second? Express your answer in radians per second to three significant figures. Submit Part B 0₁ = VAΣ vec Submit VI What is the phase angle of the current? Express your answer in degrees to three significant figures. Request Answer VAΣ vec Request Answer ? ? rad/sarrow_forwardConvert the following phasors into sinusoidal waveforms a. Vi = 20+j15 V, w= 10 rad/s b. V1 = 6(8-j3) V, w= 20K rad/s c. I1 = 12-j5+4/j A, w= 3K rad/s d. I 330+j810 mA, w= 50 rad/s 2200-j560arrow_forwardAn electrical circuit with a sinusoidal voltage source, a resistor, and a capacitor all connected in series. The voltage across the capacitor: Select one: a. Leads the current in the capacitor by exactly 90o b. Is in phase with the sinusoidal voltage source c. Is in phase with the voltage across the resistor d. Leads the current in the circuit by 90o e. Lags the current in the circuit by 90oarrow_forward
- Find the period of repetition of the following sinusoidal waveforms and express them in phasor repre- sentation: vi(t) = 12 cos(314t + 10°) V v2(t) = 4 sin(2765t – 75°) V i1(t) = -0.2 sin(600rt – 100°) A i2(t) = -2.5 cos(377nt + 120°) Aarrow_forwardP.3: Find the rms value for the following sinusoidal waveforms a. v= 120 sin(377t + 60°) b. i=6x 10³ sin(2# 1000r) c. u=8 x 10-6 sin(2# 5000 + 30°) P.4: Find the rms value for the following sinusoidal waveforms a. v= 20 sin 754r b. v= 7.07 sin 377r c. i=0.006 sin(400r + 20°) d. i 16 x 10³ sin(377r - 10%) P.5: Write the sinusoidal expressions for voltages and currents having the following rms values at a frequency of 60 Hz with zero phase shifts: a. 4.8 V b. 50 mA c. 2 kVarrow_forwardPlease answer a and b.Note: If not stated, assume a sine function.arrow_forward
- please notice that the result should be (amplitude of the voltage vo )arrow_forwardWrite each of the following phasor expressions as a single sinusoidal time domain expression using a single cosine term. Round all answers to two decimal places. 3+14/30° cos(100t + 2+j7 2ej20° cos(100t +arrow_forwardAn electrical circuit with a sinusoidal current source, a resistor, and a capacitor all connected in parallel. The voltage across the capacitor: Select one: O a. Lags the current of the capacitor by 180° O b. Is in phase with the current of the current source Ос. O c. Lags the current of the capacitor by 90° O d. Leads the current of the current source by 90° O e. Leads the current of the capacitor by exactly 90°arrow_forward
- Shown in the figure below is an "RC" circuit drive by an AC power source. The AC power source has an RMS voltage of Vps (RMS) = 11.58 Volts and is running at a frequency of f = 1.326e+04 Hz. resistor has a resistance of R = 3750 2 and the capacitor has an capacitance of C = 3.17e-09 Farads. Vps R ww Write the FORMULA for the total impedance of the circuit Ztot = Write the FORMULA for the phase of the total impedance of the circuit tot = Determine the numerical value of Ztot = Determine the numerical value of Pztot= Determine the current through the circuit: • I(PEAK) = • I(RMS) = Determine the voltage across the resistor: Amps Amps S2 C degreesarrow_forwardFind the phasor representation of an independent sinusoidal current source given as follows: i(t) = 3cos(300t + 30) + 5sin (100t + 60) A 3230 + 5260 B 3430 + 52 – 30 8430 Cannot be represented as a phasor E None of the abovearrow_forwardPhasors 1.) Transform the following sinusoids to phasors: (a) - 10 cos(4t+ 75) (b) 5 sin(20t – 10°) (c) 4 cos 2t + 3 sin 2tarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,