
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:In this problem, we will apply Gauss's law to a conducting shell that surrounds a
charge. This problem is spherically symmetric, which makes it an ideal
candidate for a Gauss's law analysis. A hollow conductor carries a net charge of
+7 nC. In its cavity, insulated from the conductor, is a small, isolated sphere
with a net charge of -5 nC. How much charge is on the outer surface of the
hollow conductor? How much is on the inner surface of the cavity?
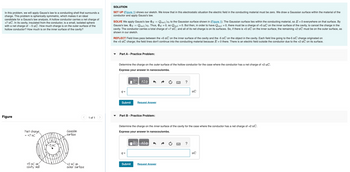
Figure
Net charge
= +7 nC
+5 nC on
cavity wall
Gaussian
surface
+2 nC on
outer surface
1 of 1
SOLUTION
SET UP (Figure 1) shows our sketch. We know that in this electrostatic situation the electric field in the conducting material must be zero. We draw a Gaussian surface within the material of the
conductor and apply Gauss's law.
SOLVE We apply Gauss's law PE = Qencl/€o to the Gaussian surface shown in (Figure 1). The Gaussian surface lies within the conducting material, so E = 0 everywhere on that surface. By
Gauss's law, E = Qencl/€0. Thus, PE = 0, so Qencl = 0. But then, in order to have Qencl = 0, there must be a charge of +5 nC on the inner surface of the cavity, to cancel the charge in the
cavity. The conductor carries a total charge of +7 nC, and all of its net charge is on its surfaces. So, if there is +5 nC on the inner surface, the remaining +2 nC must be on the outer surface, as
shown in our sketch.
REFLECT Field lines pass between the +5 nC on the inner surface of the cavity and the -5 nC on the object in the cavity. Each field line going to the-5 nC charge originated on
the +5 nC charge; the field lines don't continue into the conducting material because E = 0 there. There is an electric field outside the conductor due to the +2 nC on its surface.
Part A - Practice Problem:
Determine the charge on the outer surface of the hollow conductor for the case where the conductor has a net charge of +2 nC.
Express your answer in nanocoulombs.
—| ΑΣΦ
q=
Submit
Part B - Practice Problem:
Request Answer
q=
Submit
Determine the charge on the inner surface of the cavity for the case where the conductor has a net charge of +2 nC.
Express your answer in nanocoulombs.
VE ΑΣΦ
?
Request Answer
nC
?
nC
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Below is a solid sphere of insulating materials (meaning that once placed, charge will not move around even when it feels a force). This sphere has a changing charge density given by the equation below. This tells you that there is more charge near the outer edges (when r is larger) then near the center (when r is small) since the charge density is proportional to r^2. In the image R is the total radius of the sphere and r is the distance from the center you will be asked about. There values are below. You have to calculate the amount of charge enclosed with the radius of r to find the electric field. You'll need to integrate to do this - that's where the charge density equation below will be used. Use Gauss's Law to find the Electric Field magnitude at a distance r from the center of the sphere. Make sure to think about charge enclosed and how to find it. It is a little more complicated in this problem. Be careful with your 2 radial values (R and r).arrow_forwardTwo uniformely charged spheres are suspended by strings of length L from vertically adjustable supports. The spheres are in static equilibrium and at the same height, as shown below. The angles with respect to the vertical are Q=24.1°, and T=12.5°. The mass of Z can be less than that of X. The amount of charge on Z can be less than that on X. The amount of charge on Z can be equal to that on X. The charge on X can be negative and that on Z positive. The charge on X can be negative and that on Z negative. Incorrect. Tries 2/5 Previous Tries Submit Answer The tension in the string supporting sphere X is 2.31E-5 N. Calculate the tension in the other string. Submit Answer Tries 0/5arrow_forwardA disk with radius R and uniform positive charge density o lies horizontally on a tabletop. A small plastic sphere with mass M and positive charge hovers motionless above the center of the disk, suspended by the Coulomb repulsion due to the charged disk. At what height h does the sphere hover? Express your answer in terms of the dimensionless constant v = 20 Mg/ (Qo). Express your answer in terms of some or all of the variables R and v. h = R- 1-v √(2-v)v Submit Part C h = Previous Answers Correct If M = 300 g, Q = 1.0 μC, R = 6.0 cm, and o = 10 nC/cm², what is h? Express your answer with the appropriate units. μᾶ Value 2 Units Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ? <arrow_forward
- An infinitely long rod lies along the x-axis and carries a uniform linear charge density λ = 5 μC/m. A hollow cone segment of height H = 27 cm lies concentric with the x-axis. The end around the origin has a radius R1 = 8 cm and the far end has a radius R2 = 16 cm. Refer to the figure. a. Consider the conic surface to be sliced vertically into an infinite number of rings, each of radius r and infinitesimal thickness dx. Enter an expression for the electric flux differential through one of these infinitesimal rings in terms of λ, x, and the Coulomb constant k. b. Integrate the electric flux over the length of the cone to find an expression for the total flux through the curved part of the cone (not including the top and bottom) in terms of λ, H, and the Coulomb constant k. Enter the expression you find. c. Calculate the electric flux, in N•m2/C, through the circular end of the cone at x = 0. d. Calculate the electric flux, in N•m2/C, through the circular end of the cone at x = H. e.…arrow_forwardThe first part is the question, however I'm asking for help on subpart D & E.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON