
Concept explainers
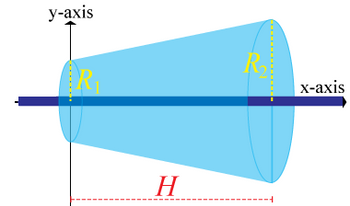
An infinitely long rod lies along the x-axis and carries a uniform linear charge density λ = 5 μC/m. A hollow cone segment of height H = 27 cm lies concentric with the x-axis. The end around the origin has a radius R1 = 8 cm and the far end has a radius R2 = 16 cm. Refer to the figure.
a. Consider the conic surface to be sliced vertically into an infinite number of rings, each of radius r and infinitesimal thickness dx. Enter an expression for the electric flux differential through one of these infinitesimal rings in terms of λ, x, and the Coulomb constant k.
b. Integrate the electric flux over the length of the cone to find an expression for the total flux through the curved part of the cone (not including the top and bottom) in terms of λ, H, and the Coulomb constant k. Enter the expression you find.
c. Calculate the electric flux, in N•m2/C, through the circular end of the cone at x = 0.
d. Calculate the electric flux, in N•m2/C, through the circular end of the cone at x = H.
e. Enter an expression for the total electric flux through the entire surface of the cone in terms of defined quantities.
f. Enter an expression for the total electric flux through the cone in terms of the net charge Qenc contained inside the cone. Note that the total flux does not depend on the size of the cone, but on the amount of charge enclosed in it.
g. Calculate the total flux through the surface of the cone in units of kN•m2/C
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 9 steps with 10 images

- The figure shows two parallel nonconducting rings with their central axes along a common line. Ring 1 has uniform charge qi and radius R; ring 2 has uniform charge q2 and the same radius R. The rings are separated by distance d = 3R. The net electric field at point P in the common line, at distance R from rina 1, is zero. What is the ratio q1/q2? Ring I Ring 2arrow_forwardIn the figure a solid sphere of radius a = 3.00 cm is concentric with a spherical conducting shell of inner radius b = 2.00a and outer radius c = 2.40a. The sphere has a net uniform charge q1 = +5.10 fC; the shell has a net charge q2 = –q1. What is the net charge on the (g) inner and (h) outer surface of the shell? The outer surface is 0 C. I tried -5.10 for the inner surface and it said it was incorrect.arrow_forwardFive charged particles are equally spaced around a semicircle of radius 100 mm, with one particle at each end of the semicircle and the remaining three spaced equally between the two ends. The semicircle lies in the region x<0 of an xy plane, such that the complete circle is centered on the origin. If each particle carries a charge of 6.00 nC , what is the electric field at the origin? Where could you put a single particle carrying a charge of -5.00 nC to make the electric field magnitude zero at the origin?arrow_forward
- Consider two nested, spherical conducting shells shown in grey and red in the figure 7. The first has inner radius a and outer radius b. The second has inner radius c and outer radius d. Case I A positive charge +Q is introduced into the center of the inner spherical shell (the grey shell). Asnwer case Iarrow_forwardA thin, circular disk of radius R = 45 cm is oriented in the yz-plane with its center as the origin. The disk carries a total charge Q = 6.0 μC distributed uniformly over its surface. Calculate the magnitude of the electric field due to the disk at the point x = 12 cm along the x-axis.arrow_forwardThe total charge on the outer surface of the conducting shell at r = c = 20 cm isarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





