
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:In the short run, given a market price equal to $15 per romper, the firm should produce a daily quantity of
On the preceding graph, use the blue rectangle (circle symbols) to fill in the area that represents profit or loss of the firm given the market price of
$15 and the quantity of production from your previous answer.
Note: In the following question, enter a positive number regardless of whether the firm earns a profit or incurs a loss.
thousand per day for the firm.
The rectangular area represents a short-run
rompers.
of $
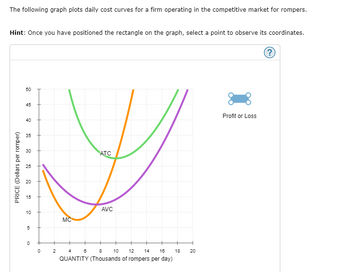
Transcribed Image Text:The following graph plots daily cost curves for a firm operating in the competitive market for rompers.
Hint: Once you have positioned the rectangle on the graph, select a point to observe its coordinates.
(?)
PRICE (Dollars per romper)
50
45
40
3.5
30
20
15
10
10
5
0
+
0
2
MC
ATC
AVC
4 6 8
12 14 16
QUANTITY (Thousands of rompers per day)
10
18
H
20
Profit or Loss
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that the market for dress shirts is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. 50 18, 42 45 40 35 30 ATC 25 20 15 AVC 10 MC 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 QUANTITY (Thousands of shirts) For each price in the following table, calculate the firm's optimal quantity of units to produce, and determine the profit or loss if it produces at that quantity, using the data from the graph to identify its total variable cost. Assume that if the firm is indifferent between producing and shutting down, it will produce. (Hint: You can select the purple points [diamond symbols] on the graph to see precise information on average variable cost.) Price Quantity Total Revenue Fixed Cost Variable Cost Profit (Dollars per shirt) (Shirts) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) (Dollars) 12.50 7,500 135,000 27.50 135,000 45.00 135,000 If the firm shuts down, it must incur its fixed costs (FC) in the short run. In this case, the firm's fixed cost is…arrow_forwardOn the graph input tool, change the number found in the Quantity Demanded field to determine the prices that correspond to the production of 0, 6, 12, 15, 18, 24, and 30 units of output. Calculate the total revenue for each of these production levels. Then, on the following graph, use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot the results. Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 6 versus 5 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the sixth unit produced. The marginal revenue of the sixth unit produced is________. Calculate the total revenue if the firm produces 12 versus 11 units. Then, calculate the marginal revenue of the 12th unit produced. The marginal revenue of the 12th unit produced is_________.arrow_forwardYou are the manager of a train company. Recently total sales have been a bit low and you are now considering means to give sales a boost. Market research has shown that currently the price of train tickets is historically low. Market research has also shown that the demand curve for train tickets is downward sloping. You may assume that your company is not a price taker on the market. 1.One of your colleagues has suggested that it is important to lower the price of train tickets. In that case, she argues, the demand will increase. Do you agree with her? Explain why. 2.She continues her argument by concluding that if the demand goes up, the total value of sales of train tickets should therefore increase. Do you agree with her? Explain why.arrow_forward
- Am. 106.arrow_forwardA10arrow_forwardHomework (Ch 14) PRICE (Dollars per instant pot) 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 MC 5 ATC AVC 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Thousands of instant pots per day) Profit or Loss In the short run, given a market price equal to $50 per instant pot, the firm should produce a daily quantity of The rectangular area represents a short-run (?) On the preceding graph, use the blue rectangle (circle symbols) to fill in the area that represents profit or loss of the firm given the market price of $50 and the quantity of production from your previous answer. Note: In the following question, enter a positive number regardless of whether the firm earns a profit or incurs loss. thousand per day for the firm. of $ instant pots.arrow_forward
- Suppose the imaginary company of Panthera is a small, Raleigh-based American apparel manufacturer specializing in athleisure. The following table presents the brand's total cost of production at several different quantities. Fill in the remaining cells of the following table. Quantity Total Cost (Pairs) (Dollars) Marginal Cost (Dollars) Fixed Cost Variable Cost (Dollars) (Dollars) Average Variable Cost (Dollars per pair) Average Total Cost (Dollars per pair) 0 120 1 210 2 270 3 315 4 380 475 6 630arrow_forwardProfit maximization using total cost and total revenue curves Suppose Caroline runs a small business that manufactures shirts. Assume that the market for shirts is a competitive market, and the market price is $20 per shirt. The following graph shows Caroline's total cost curve. Use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot total revenue and the green points (triangle symbol) to plot profit for shirts quantities zero through seven (inclusive) that Caroline produces. Caroline's profit is maximized when she produces______ shirts. When she does this, the marginal cost of the last shirt she produces is ______, which is (GREATER OR LESS) than the price Caroline receives for each shirt she sells. The marginal cost of producing an additional shirt (that is, one more shirt than would maximize her profit) is _____, which is (GREATER OR LESS) than the price Caroline receives for each shirt she sells. Therefore, Caroline's profit-maximizing quantity corresponds to the…arrow_forwardRespond to the question with a concise and accurate answer, along with a clear explanation and step-by-step solution, or risk receiving a downvote.arrow_forward
- The following graph plots the marginal cost (MC) curve, average total cost (ATC) curve, and average variable cost (AVC) curve for a firm operating in the competitive market for jumpsuits. COSTS (Dollars) 80 72 64 56 24 16 8 0 0 8 0 MC ATC AVC Price (Dollars per jumpsuit) 4 8 12 36 48 60 ■ 16 24 32 40 48 56 QUANTITY (Thousands of jumpsuits) ☐ Quantity (Jumpsuits) 64 For every price level given in the following table, use the graph to determine the profit-maximizing quantity of jumpsuits for the firm. Further, select whether the firm will choose to produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. (Assume that when price exactly equals average variable cost, the firm is indifferent between producing zero jumpsuits and the profit-maximizing quantity of jumpsuits.) Lastly, determine whether the firm will earn a profit, incur a loss, or break even at each price. 72 80 Produce or Shut Down? Profit or Loss?arrow_forwardpshotic 166& 5. Profit maximization and shutting down in the short run Suppose that the market for microwave ovens is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a firm operating in this market. 100 90 80 ATC 70 60 40 30 AVC 20 10 MC 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Thousands of ovens) Σ 50 PRICE (Dollars per oven)arrow_forwardPrice ($/slice) For the pizza seller whose marginal, average variable, and average total cost curves are shown in the graph below, what is the profit- maximizing level of output and how much profit will this producer earn if the price of pizza is $2.50 per slice? Instructions: In the graph below, label all three curves by clicking on the dropdown to select the appropriate label. Then, indicate the profit-maximizing level of output on the graph. 3.50 3.25 3.00 2.75 2.50 2.25 2.00 1.75 1.50 1.25 1.00 0.75 0.50 0.25 0 Cost Curves Tools -O Select ▼ Select ▼ Select ▼ Q* 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 Quantity (slices/day)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education