
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
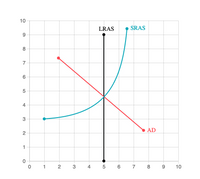
In the past two decades, the government of Qatar has made significant investments to increase the level of infrastructure and human capital in the country.
Suppose the accompanying graph illustrates the aggregate demand (AD), short‑run
Adjust the graph to show Qatar’s new long‑run
Transcribed Image Text:10
LRAS
SRAS
8
7
6
4
3
AD
2
1
1
2
3
4
5 6
7
8
9.
10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Interpret the change you drew on the previous graph by filling in the blanks in the following paragraph: The lower-than-expected price level causes firms to earn more profit than they expected on each unit of output they produce, and, therefore, they decrease their production level. At the same time, the real value of wages and other resource prices are lower than workers and firms expected when they signed long-term contracts. As a result, the economy as a whole produces at a level below the unemployment rate is lower than its natural rate. its potential output, and Now, suppose prices remain lower than expected. As a result, in the next round of labor negotiations, unions accept lower wages for their members. The following graph shows the potential output for this economy as well as the same initial short-run aggregate supply curve as in the first graph. Shift one or both of these lines to illustrate how the economy adjusts to a new long-run equilibrium. PRICE LEVEL 180 SRAS 150…arrow_forwardThe task I am struggling with: The economy is in short-run macroeconomic equilibrium at point E1 in the accompanying diagram (see the picture). Based on the diagram, answer the following questions. a) Is the economy facing an inflationary or recessionary gap? b) What policies can the government implement that might bring the economy back to long-run macroeconomic equilibrium? Illustrate with a diagram. c) If the government did not intervene to close this gap, would the economy return to long-run macroeconomic equilibrium? Explain and illustrate with a diagram.Thank you very much for your help.arrow_forwardEconomists forecast future economic conditions by studying variables that tend to fluctuate in advance of the overall economy. The most significant of these variables are known as leading indicators, and they compose the index of leading economic indicators. Which of the following variables are measured as part of this index? Check all that apply. Supplier deliveries The ratio of elderly to nonelderly workers New orders for consumer goods Stock prices The money supply True or False: Businesses and government care only about long-run economic forecasts, because they cannot adapt policy or output to accommodate short-run fluctuations. False True Suppose the most recent data show that the average initial weekly claims for unemployment insurance have recently decreased. This change suggests ____ period in the coming months.arrow_forward
- Assume the economy of Germany is in a long run equilibrium with full employment. Draw a correctly labeled graph of short run aggregate supply, long run aggregate supply, and aggregate demand. Show each of the following Equilibrium output, labeled Y1. Equilibrium price level, labeled PL1 2. Suppose that there is a significant boom in the German stock market, causing all stocks to increase in value by 15%. On your graph in part A, show the effect this will have on the equilibrium in the short run, labeling the new equilibrium output and price level Y2 and PL2, respectively. 3. Using a correctly labeled graph of the Phillips Curve, show how this change will affect the economy. 4. What two fiscal policy options does the federal government have to fix the market imbalance? Explain how each would affect the economy.arrow_forwardThe following graph represents the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) based on an expected price level of 120. The economy's full- employment output level is $9 trillion. Major unions across the country have recently negotiated three-year wage contracts with employers. The wage contracts are based on an expected price level of 120, but the actual price level turns out to be 160. Show the short-run effect of the unexpectedly high price level by dragging the curve or moving the point to the appropriate position. PRICE LEVEL (CPI) 240 200 160 40 0 0 3 SRAS[120] 6 9 12 REAL GDP (Trillions of dollars) 15 18 SRAS[120] 0 (?) Interpret the change you drew on the previous graph by filling in the blanks in the following paragraph:arrow_forwardThe U.S. economy is initially in short-run macro-equilibrium. Assume oil prices fall. As a result, we observe the following in our economy Question 2 options: a) Both the price level and real GDP decrease b) The price level falls and real GDP increases c) The price level increases and real GDP falls d) Both the price level and real GDP increase.arrow_forward
- The following four equations relate to an economy. Use them to answer the questions that follow. Product Market: y= c(y-c) + i(r) + g Money Market: ṁ= i(r) + k(y) Production function: y= y(N; Ǩ) Labour Market: p,f(N)= Pe * g(N)= P(p) * g(N) Draw the classical model in the price income (P-Y) space graph and explain what happens when the nominal money supply rises. Assuming a complete and correct adjustment (Pe to P), derive the effect of fiscal policy increase in the government expenditure and explain the differences of the fiscal policy when p=0 and when P=1arrow_forwardConfused and not sure how to answerarrow_forwardSuppose that the production function for the economy is given by: Y = AL/3K/3 Suppose that this economy has 1,000 units of Labour, and 125 units of capital, and TFP (A) is equal to 10. The Short-Run Aggregate Supply Curve (AS) here is given by: Y = 5p And when we consider the AEF at a price level of $1,400, the main components of it (C, I, & G) are given by (we are assuming a closed economy NX = 0): C = 300 + 0.8Y I = 300 G = 200 1. What is potential GDP in this question (Y*)? Show your work. Suppose also that for any $10 decrease in price, desired consumption will increase by $5. 2. Write down the equation for the Aggregate Demand Curve (AD) in the form of Y = a + bp. Show your work. 3. What is the current Short-Run Equilibrium value for Real GDP (Y) and the price level (p)? Show your work. 4. Draw the AD, AS, and LRAS curves. Label all x-intercepts and y-intercepts. Are we currently in an Inflationary Gap, Recessionary Gap, or in Long-Run Equilibrium? How do you know?arrow_forward
- The following graph shows an economy's short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS), current equilibrium aggregate price level (P₁), and real GDP ( 21). The economy currently has Natural Real GDP (QN) of $6 trillion. Use this information to place the orange long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS, square symbols) in the correct position on the graph. PRICE LEVEL 10 8 1 A 2 0 0 2 A₁ 4 6 Q₁ REAL GDP (Trillions of dollars) 8 SRAS 10 The equilibrium A₁, shown on the graph, reveals that real GDP (2₁) is shifting SRAS O LRAS Natural Real GDP. As a result, wages will over time,arrow_forwardConsider the basic Macroeconomic model involving: Private sector consumption: C = co+c1(Y-T); Y = GDP, T = Taxes Tax function: T = to+t1Y Business sector investment: I = io+i2r, r=interest rate Government spending: G = Go Exports: X = xo+x1x; x = Exchange rate of the dollar Imports: M = mo+m1Y+m2x; x = Exchange rate (a) Identify and explain the parameters: co, t1, i2, and m2. (b) Solve this model for the equilibrium GDP (Y*).arrow_forwardQUESTION 2 Consider the aggregate supply-aggregate demand (AD-AS) model that we saw in class. Assume that prices are fixed in the short run and are fully flexible in the long run. The initial full-employment level of output is y- g00 and the initial price level is p= 100: The aggregate demand curve is given by y= 1500 - 6P: Scenario 1, long run: A reduction in personal income taxes shifts the demand curve to y=1530 – 6P. In the long run, the output is and the price level is Note: Type in your answer rounded to two decimal places, i.e., your answer must be of the form "999.99". I will not be able to fix correct answers that were entered incorrectly, such as "999.999" or "999,99" or "999". In case the last digit in the correct answer is zero, e.g., "999.90" or "999.00", Blackboard may automatically delete it and you should not do anything about it. In case of percentages, do not type in the percentage symbol "%".arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education