
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
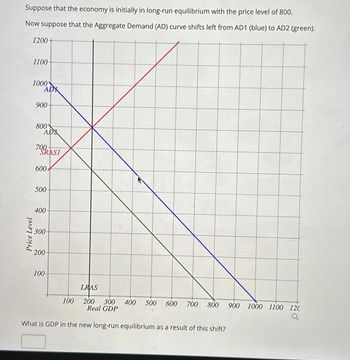
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium with the price level of 800.
Now suppose that the Aggregate Demand (AD) curve shifts left from AD1 (blue) to AD2 (green).
Price Level
1200+
1100
1000
ADX
900-
800
AD
700-
SRASI
600*
500
400
300
200
100
LRAS
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900
Real GDP
What is GDP in the new long-run equilibrium as a result of this shift?
100
1000 1100 120
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The graph below shows the AD-AS diagram for Spain. Suppose that the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium with the price level of 900. Now suppose that the Aggregate Demand (AD) curve shifts left from AD1 (blue) to AD2 (green). 1200 AD 1100 1000 Price Level ADS 900- 800 79R ST 600* 500 400 300 200- 100- LRAS 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 120 Real GDP Q 1. What is the new GDP in the short-run as a result of this shift? I 2. What is the new price level in the short-run as a result of this shift? 3. What is the price new long-run equilibrium as a result of this shift? 4. What is GDP in the new long-run equilibrium as a result of this shift? 5. What causes the economy to move from the short-run equilibrium to the new long-run equilibrium? O Decreased wages. O increased wages. O Increased prices. O Decreased prices.arrow_forward40 AD 3 38 AS 36 - AD 2 34 - 32니 AD, 30 28 - 26 24 - 22 - 20 4 10 12 14 18 18 20 Real Output (quantity in billions per year) Suppose the economy is at full employment when AS = AD2. billion a. The GDP gap when the demand curve is at AD1 is billion o. The GDP gap when the demand curve is at AD3 is Price Level (average price)arrow_forwardThe graphs illustrate an initial equilibrium for some economy. Suppose that the economy experiences a rise in aggregate demand. Use the graphs to illustrate the new positions of AD, SRAS, and LRAS as well as the new short-run and long-run equilibria resulting from this change. Short-Run Graph Long-Run Graph LRAS LRAS SRAS SRAS Equilibrium point Equilibrium point AD AD Real GDP Real GDP Aggregate price level Aggregate price levelarrow_forward
- 3. Determinants of aggregate demand The following graph shows an increase in aggregate demand (AD) in a hypothetical country. Specifically, aggregate demand shifts to the right from AD₁ to AD2, causing the quantity of output demanded to rise at all price levels. For example, at a price level of 140, output is now $400 billion, where previously it was $300 billion. 170 PRICE LEVEL 160 150 140 120 110 100 90 0 +--+ AD2 AD1 600 100 200 300 400 500 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) 700 800arrow_forwardUsing an AD/AS diagram (starting from long-run/full employment equilibrium), graphically show and verbally describe how each of the following events would affect the U.S. economy's equilibrium real GDP and price level. a. Discovery and implementation of new technology b. Mexico's economic growth increases faster than ours c. There is a general increase in the price of raw materials e. The cost of labor (wages) rises g. The price of oil is expected to fall d. The number of workers in the labor force decreases due to pandemic retirements/death f. A new Congress decreases government spending h. Consumer confidence fallsarrow_forwardSuppose that the economy is initially in long-run equilibrium with the price level of 800. Now suppose that the Aggregate Demand (AD) curve shifts left from AD1 (blue) to AD2 (green). 1200 ADX 1100- 1000 Price Level ADX 900- 800 700 600 50% RASI 400* 300- 200 100- LRAS 400 500 600 700 100 200 300 Real GDP What is the new price level in the short-run as a result of this shift? 800 900 1000 1100 120 aarrow_forward
- Please draw on top of grapharrow_forwardOn the following graph, use the black point (cross symbol) to show the short-run equilibrium. Then use the grey point (star symbol) to show the long- run equilibrium. PRICE LEVEL 120 110 100 1 LRAS REAL GOP In the short run, the price level is Natural Real GDP SRAS, SRAS, AD SRAS, AD AD₂ and Real GDP is ++ Short-Run Equilibrium ✡ Long-Run Equilibrium ? Natural Real GDP. In the long run, the price level is and Real GDP is Aarrow_forwardSuppose the economy produces real GDP of $50 billion when unemplo plot the economy's long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve. PRICE LEVEL 132 128 124 120 116 112 108 104 100 0 10 20 30 40 50 REAL GDP (Billions of dollars) 60 70 80arrow_forward
- Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply (AD-AS) Model (Chapter 13) 5.1 Why does the short-run aggregate supply curve slope upward? 5.2 Explain why the long-run aggregate supply curve is vertical. Then, explain how each of the following events would affect the long-run aggregate supply curve. A lower price levels b. A decrease in the labor force A decrease in the quantity of capital goods d. Technological change a. с. 5.3. Starting from long-run equilibrium, use the basic aggregate demand and aggregate supply diagram to show what happens in both the long run and the short run when there is a decline in wealth. Explain how the economy moves back to full employment.arrow_forwardWhich of the following would NOT cause a shift in AD? Select one: a. A reduction in interest rates b. A fall in the cost of production c. A reduction in income tax d. An increase in government spendingarrow_forwardtype plzarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education