
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
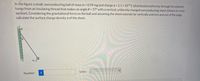
Transcribed Image Text:In the figure a small, nonconducting ball of mass m = 0.99 mg and charge q = 2.1 × 10*8 C (distributed uniformly through its volume)
hangs from an insulating thread that makes an angle 0 = 37° with a vertical, uniformly charged nonconducting sheet (shown in cross
section). Considering the gravitational force on the ball and assuming the sheet extends far vertically and into and out of the page,
calculate the surfaçe charge density o of the sheet.
m, 4
i
Units
Number
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (a) A small amber bead with a mass of 14.0 g and a charge of -0.652 μC is suspended in equilibrium above the center of a large, horizontal sheet of glass that has a uniform charge density on its surface. Find the charge per unit area on the glass sheet (in µC/m²). x μC/m² (b) What If? What are the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the piece of amber if its charge is doubled? (Enter the magnitude in m/s².) magnitude direction upward m/s²arrow_forwardAn infinite sheet of charge, oriented perpendicular to the x-axis, passes through x = 3 μC/m2. 0. It has a surface charge density o1 = A thick, infinite conducting slab, also oriented perpendicular to the x-axis, occupies the region between a = 2.6 cm and b = 4.6 cm. The conducting slab has a net charge per unit area of 02 = 78 µC/m2. (Recall that the surface charge densities oa and oh on the slab surfaces at a and b, respectively, sum to equal the net charge per unit area: oa + ob = 02.) 1) What is Ex(P), the value of the x-component of the electric field at point P, located a distance 7.8 cm from the infinite sheet of charge? N/C Submit 2) What is Ey(P), the value of the y-component of the electric field at point P, located a distance 7.8 cm from the infinite sheet of charge? N/C Submit + 3) What is Ex(R), the value of the x-component of the electric field at point R, located a distance 1.3 cm from the infinite sheet of charge? N/C Submit 4) What is Ey(R), the value of the…arrow_forward(a) Figure (a) shows a nonconducting rod of length L = 5.80 cm and uniform linear charge density λ = +4.87 pC/m. Take V = 0 at infinity. What is Vat point P at distance d= 7.50 cm along the rod's perpendicular bisector? (b) Figure (b) shows an identical rod except that one half is now negatively charged. Both halves have a linear charge density of magnitude 4.87 pC/m. With V=0 at infinity, what is Vat P? L/2 (a) -L/2 L/21/2- (b)arrow_forward
- In the figure a small, nonconducting ball of mass m = 1.1 mg and charge q = 2.0 × 108 C (distributed uniformly through its volume) hangs from an insulating thread that makes an angle 0 = 30° with a vertical, uniformly charged nonconducting sheet (shown in cross section). Considering the gravitational force on the ball and assuming the sheet extends far vertically and into and out of the page, calculate the surface charge density of the sheet. + + + + + + + + + + + + + O aarrow_forwardA -198.7 mC charge is placed at the center of a hollow conducting sphere. Find the Charge density (in C/m²) on the outside of the sphere if its radius is 6.47 cm and if it Contains zero net charge.arrow_forward345 159 A-140.1 mC charge is placed at the center of a hollow conducting sphere. Find the charge density (in C/m²) on the outside of the sphere if its radius is 5.09 cm and if it contains zero net charge.arrow_forward
- A coaxial cable consists of a wire of radius a surrounded by a thin metal cylin-drical shell of radius b. The wire has a uniform linear charge density λ >0 and the outer shell has a uniform linear charge density−λ. ( a) Sketch the field lines for this cable. (b) Find expressions for the magnitude of the electric field in the regionsrarrow_forwardA solid insulating sphere of radius a = 5.1 cm is fixed at the origin of a co-ordinate system as shown. The sphere is uniformly charged with a charge density p = -224 µC/m³. Concentric with the sphere is an uncharged spherical conducting shell of inner radius b = 13.3 cm, and outer radius c = 15.3 cm. P(40) 1) What is Ex(P), the x-component of the electric field at point P, located a distance d = 34 cm from the origin along the x-axis as shown? N/C Submit + 2) What is V(b), the electric potential at the inner surface of the conducting shell? Define the potential to be zero at infinity. V Submit +) 3) What is V(a), the electric potential at the outer surface of the insulating sphere? Define the potential to be zero at infinity. Submit 4) What is V(c) - V(a), the potentital differnece between the outer surface of the conductor and the outer surface of the insulator? Submit 5) A charge Q = 0.0593µC is now added to the conducting shell. What is V(a), the electric potential at the outer…arrow_forwardA solid block of copper, which is a good conductor, has a cavity in its interior. Within the cavity, insulated from the conductor, is a point charge of +3.00 nC. The block of copper itself has an excess charge of -8.00 nC. How much charge is on (a) the outer surface of the block and (b) the surface of the cavity?arrow_forward
- Two isolated metallic solid spheres of radii R and 2R are charged such that both of these have same charge density σ. The spheres are located far away from each other, and connected by a thin conducting wire. Find the new charge density on the bigger sphere.arrow_forwardA charge q = 1 μC is located at the tip of a hollow cone (such as an ice cream cone without the ice cream) with surface charge density o = 6.4 μC/m². The slant height of the cone is L = 4 mm, and the half-angle at the vertex is 0: 10⁰. = L12 L/2 If the top half of the cone is removed and thrown away, what is the force (in Newton's) on the charge 9 due to the remaining part of the cone?arrow_forwardIn part (a) of the figure an electron is shot directly away from a uniformly charged plastic sheet, at speed vs = 3.60 x 105 m/s. The sheet is nonconducting, flat, and very large. Part (b) of the figure gives the electron's vertical velocity component v versus time t until the return to the launch point. What is the sheet's surface charge density? Assume ts = 28.0 ps. (a) v (105 m/s) t (ps) (b)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON