Question
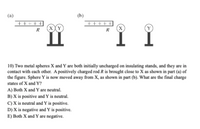
Transcribed Image Text:(a)
(h)
+++++
(X
R
+++ +|
(X)
R
10) Two metal spheres X and Y are both initially uncharged on insulating stands, and they are in
contact with each other. A positively charged rod R is brought close to X as shown in part (a) of
the figure. Sphere Y is now moved away from X, as shown in part (b). What are the final charge
states of X and Y?
A) Both X and Y are neutral.
B) X is positive and Y is neutral.
C) X is neutral and Y is positive.
D) X is negative and Y is positive.
E) Both X and Y are negative.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Two metal spheres of identical mass m = 4.60 g are suspended by light strings 0.500 m in length. The left-hand sphere carries a charge of 0.765 µC, and the right-hand sphere carries a charge of 1.47 μC. What is the equilibrium separation between the centers of the two spheres? 0.6078 x Your response is within 10% of the correct value. This may be due to roundoff error, or you could have a mistake in your calculation. Carry out all intermediate results to at least four- digit accuracy to minimize roundoff error. marrow_forwardI need help with this question. Thank you!arrow_forwardTwo identical metallic blocks resting on a frictionless horizontal surface are connected by a light metallic spring having the spring constant 160N/m and an un- stretched length of 0.32m as shown. A total charge of Q is slowly placed on the system, causing the spring to stretch to an equilibrium length of 0.43m as shown. Determine the value of Q, assuming that all the charge resides on the blocks and modelling the blocks as point charges. State your answer in mC to nearest 0.01 mC. Take electric constant ke to be 8.99x10° Nm2/c² Hwwwww (a) (b)arrow_forward
- Two small spheres each have a mass m of 0.700 g and are suspended as pendulums by light insulating strings from a common point, as shown in the figure below. The spheres are given the same electric charge, and the two come to equilibrium when each string is at an angle of 0= 6.00%; with the vertical. m OK 410 m 1) If each string is 1.00 m long, what is the magnitude of the charge on each sphere? (Express your answer to three significant figures.) x 10-⁹ Carrow_forwardA point charge, q = -5.0 nC, and m = 2.0 x 10-18 kg, is shot vertically upward with an initial speed of 3.0 x 105 m/s from a thin, infinite, planar sheet of uniform charge with surface charge density of σ = +4.0 nC/m^2 . To what vertical elevation will q rise above the sheet of charge? Neglect gravityarrow_forwardThree identical conducting spheres denoted as X, Y, and Z are separated in space. They have initial net charges of −2Q, −3Q, and 5Q, respectively. Sphere Z is touched to X and separated, then touched to Y and separated. Upon reaching electrostatic equilibrium, what is the final net charge of Y?arrow_forward
- Four conducting spheres labeled A, B, C and D are charged to the following values: qA = 2.0 ?C, qB = 3.0 ?C, qC = -2.0 ?C, qD = -6.0 ?C. The following three interactions then occur: qA is brought in contact with qC, then qC is brought in contact with qB and lastly qB is brought in contact with qD. [Report all answers in Coulombs.]What is the final charge of qB? What is the final charge of qC? What is the final charge of qD? What is the total final charge of the system?arrow_forwardA ▬ >E h d - As shown in the figure above, a positively charged ball is placed at point A and slides down the slope from rest. The area has a uniform electric field E = 12.9 N/C, pointing to the right. The mass of the ball is m = 9 kg and the charge is q = +2.6 C. When the ball reaches point B, it travels horizontally there after. The height from A to B is h = 37 m and the horizontal distance between A and B is d = 30 m. You can ignore friction and use g = 10 m/s for your calculation. %3D How much is the kinetic energy of the ball when it reaches at B (in the unit of J)? Submit Answer Tries 0/2 If the electric field ist changed to the opposite direction, How much is the kinetic energy of the ball when it reaches at B (in the unit of J) now? Submit Answer Tries 0/2 What is the minimum strength of electric field E that can be used to stop the particle right at Point B? N/Carrow_forwardYou are given three pith balls. When balls A and B are brought close together (far away from C), the two repel. When A and C are brought close together (far away from B), the two attract. When B and C are brought close together (far away from A), the two attract. Find four solutions for how A, B, and C could be charged (+, - or neutral) relative to one another.arrow_forward
- Two infinite non-conductive parallel plates are separated by a distance of 10.0 cm and have charge distributions of +1.00 µC / m2 and -1.00 µC / m2. What is the force on an electron in the space between the plates? What is the force on an electron located outside the two plates but close to the surface of one of them?arrow_forwardWe wish to calculate the value of eo. Two small metal conducting balls of mass m, each with charge q, are attached to massless strings of length L and suspended from the ceiling. Since the balls are both positively charged, they repel each other, and so at the ceiling the strings make an angle 0 with each other. In terms of m, q, L, 0, and g, what is eo?arrow_forwardTwo spherical, hollow conductors are concentrically nested as shown in the cross-sectional diagram below and electrically isolated from each other. A net charge of -3 nC is divided between the conductors, with a total of -12 nC on the inner conductor and +9 nC on the outer one. The charges are, of course, free to move between the surfaces within each shell but cannot move from one shell to the other. The inner conductor has an inner radius of a=2 cm, outer radius of b=3 cm. The outer conductor has an inner radius of c=6 cm, an outer radius of d=8 cm. a (a) In equilibrium, all of the excess charge is found on the surfaces. Why is there no charge between a and b, nor between c and d? (b) Determine the net charge on each surface (ie how much charge is there at r = a, at r = b, at r = c and at r= = d). (c) Is the charge on the outer surface equal to the net charge on the outer container, the net charge of the system, or some other amount? Explain briefly. (d) Find the surface charge…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios