
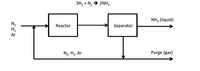
In the famous Haber process to manufacture ammonia, the reaction is carried out at pressures of 800 to 1000 atm and at 500 to 600C using a suitable catalyst. Only a small fraction of the material entering the reactor reacts on one pass, so recycle is needed. Also, because the nitrogen is obtained from air, it contains almost 1% rare gases (chiefly argon) that do not react. The rare gases would continue to build up in the recycle until their effect on the reaction equilibrium would become adverse, so that a small purge stream is needed. As shown below, the fresh feed of gas composed of 75.16% H2, 24.57% N2 and 0.27% Ar is mixed with the recycled gas and enters the reactor with a composition of 79.52% H2. The gas stream leaving the ammonia separator contains 80.01% ?H2 and no ammonia. The product ammonia contains no dissolved gases. Per 100. Moles of fresh feed: a. How many moles are recycled and purged? b. What is the percent single pass conversion of hydrogen?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- Please show every step you used to solve each problem. A vapor mixture of 100 mol/s comprising 55 mol% benzene and 45 mol % toluene is sent to a partial condenser operating at 760 mm Hg. 75 mol% of the toluene in the feed is recovered in the liquid product. Determine all unknown flow rates, compositions, and required heat removal. and do a degree a. Draw a process flow diagram of freedom analysis b. Write out equations used to solve and to calculate all specifications used in Excel Solver unknown flow rates, compositions, C. F Specify the temperature and pressure of the feed as T₁ = 102°C and P₁ = 760 mm Hg. Choose the lowest enthalpy stream (liquid product stream) for a reference condition. Calculate the required heat removal analytically by hand (No Excel Solver). d. Create Enthalpy Tablearrow_forwardUse the chemical reaction below to answer the following questions HCI(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (I) AH298 = -58 kJ/mol (a) How much heat is produced when 200 mL of 0.3 M HCL (density = 1.00 g/mL) and 250 mL of 0.25 M NaOH (density = 1.00 g/mL) are mixed? (b) If both of the solutions at the same temperature and the heat capacity of the products are 5.39 J/g °C , how much will the temperature increase? (c) What assumptions are made when calculating your answersarrow_forwardA chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: BF 3(aq)+NH3(aq) → BF ,NH3(aq) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.3. The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with boron trifluoride and ammonia, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction expected change in concentration compound concentration vessel BE3 I decrease (no change) 0.48 M f increase NH3 I decrease (no change) 0.55 M f increase A BF,NH3 f increase I decrease (no change) 1.01 M 0.41 M f increase I decrease (no change) BF, NH3 I decrease (no change) 0.48 M f increase В BF,NH3 f increase I decrease (no change) 1.08 M BF3 I decrease (no change) 1.07 M ↑ increase NH3 I decrease (no change) 1.14 M f increase C…arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





