
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:+
Moore 5e_Ch11 SP2020.pptx: SP X
* OWLV2 | Online teaching and lea X
oping Cart | The UAB Blazer x
VtakeAssignment/takeCovalentActivity.do?locator=assignment-take
[Review Topica)
[References)
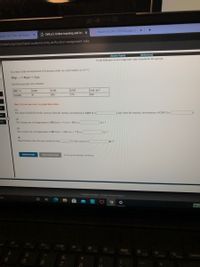
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
In a study of the decomposition of hydrogen iodide on a gold surface at 150 °C
HI(g)% H2(g) + % I(g)
the following data were obtained:
HI), M
0.401
0.201
0.101
5.05x102
seconds
519
779
910
Hint: It is not necessary to graph these data.
(1)
The observed half life for this reaction when the starting concentration is 0.401 M is
s and when the starting concentration is 0.201 M is
req
(2)
2req
The average rate of disappearance of HI from t=0 s to t= 519 s is
Ms!
(3)
The average rate of disappearance of HI from t = 519 s to t= 779 s is
Ms!
(4)
Based on these data, the rate constant for this
v order reaction is
Submit Answer
Retry Entire Group
9 more group attempts remaining
Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support
Tch
55
F7
F8
F9
24
F10
F11
F12
Deiete
sert
&
Prd
4
6
8
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following data are for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in dilute sodium hydroxide at 20 °C.H2O2(aq) H2O(l) + ½ O2(g) [ H2O2 ], M 9.24×10-2 4.62×10-2 2.31×10-2 1.16×10-2 time, min 0 7.05 14.1 21.2 Hint: It is not necessary to graph these data.(1)The half life observed for this reaction is min .(2)Based on these data, the rate constant for this _______zero/first/second order reaction is_______ min -1.arrow_forwardSuppose the decomposition of dinitrogen monoxide proceeds by the following mechanism: step elementary reaction rate constant N,0 (g) → N, (g) +0 (g) k1 1 2 N,0 (g)+0 (g) → N, (g) + 0, (g) k2 Suppose also k, « k,. That is, the first step is much slower than the second. Write the balanced chemical ローロ equation for the overall chemical reaction. Write the experimentally- observable rate law for the overall chemical reaction. rate = k ] Note: your answer should not contain the concentrations of any intermediates. Continue ©2021 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rightsarrow_forwardAt a certain temperature the rate of this reaction is first order in Cl,0, with a rate constant of 0.0629 s 2C1,0; (3)– 2C1, (3) +50, (3) Suppose a vessel contains Cl,0; at a concentration of 1.01 M. Calculate how long it takes for the concentration of Cl,0; to decrease to 0.253 M. You may assume no other reaction is important. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forward
- The first order rate constant for the decomposition of a certain hormone in water at 25 degrees C is 3.42 x 10-4 day-1. a)If a 0.0200 M solution of the hormone is stored at 25 degrees C for 2 months, what will its concentration be at the end of that period? b)How long will it take for the ocncentration of the oslution to drop from 0.0200 M to 0.00350 M? c)What is the half-life of the hormone?arrow_forwardThe decomposition of dinitrogen pentoxide in carbon tetrachloride solution at 30 °C N,052 NO, + ½ O2 is first order in N,05 with a rate constant of 4.10x103 min!. If the initial concentration of N,O3 is 0.348 M, the concentration of N,Og will be 8.63×102 M after| have passed. minarrow_forwardUsing the information provided, determine the activation energy for the reaction. Please explain why the hilighted answer is correct.. thank you!arrow_forward
- In a study of the decomposition of ammonia on a tungsten surface at 1100 °C NH31/2 N2 + 3/2 H, the following data were obtained: NH3), M seconds 7.30x10-3 440 1.46x10-2 3.65x103 1.83×10-3 660 770 Hint: It is not necessary to graph these data. (1) The observed half life for this reaction when the starting concentration is 1.46x1o-² M i starting concentration is 7.30×103 M is| s and when the (2) The average rate of disappearance of NH3 from t= 0 s to t= 440 s is Ms. (3) The average rate of disappearance of NH3 from t= 440 s to t= 660 s is |Ms. (4) Based on these data, the rate constant for this| order reaction is Ms!.arrow_forwardThe Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded in 1995 to Paul Crutzen, Mario Molina and Sherwood Rowland for research showing the chlorofluorcarbons (CFCs) were catalyzing the destruction of ozone in the stratosphere. The catalytic process can be described by a two step mechanism: (1) Cl + O3 --> ClO + O2 (slow) (2) ClO + O --> Cl + O2 (fast) Determine the overall reaction for this mechanism, and answer the following question: In this mechanism Cl acts as a(n) ______________ and ClO acts as a(n) ___________________. a. reagent, intermediate b. intermediate, catalyst c. catalyst, intermediate d. intermediate, productarrow_forwardThe frequency factor and activation energy for a chemical reaction are A = 5.48 x 10-12 cm/(molecule-s) and E, = 15.6 kJ/mol at 382.7 K, respectively. Determine the rate constant for this reaction at 382.7 K. cm/(molecule•s)arrow_forward
- In a study of the decomposition of nitrous oxide at 565 °CN2O(g)N2(g) + ½ O2(g)the following data were obtained: [N2O], M 2.10 1.05 0.525 0.263 seconds 0 602 1.81×103 4.21×103 Hint: It is not necessary to graph these data.(1)The observed half life for this reaction when the starting concentration is 2.10 M is s and when the starting concentration is 1.05 M is s.(2)The average (1/[N2O]) / t from t = 0 s to t = 602 s is M-1 s-1.The average (1/[N2O]) / t from t = 602 s to t = 1.81×103 s is M-1 s-1.(3)Based on these data, the rate constant for this order reaction is M-1 s-1.arrow_forwardPls show all steps with explanationarrow_forward[4] The reaction: 21 (aq) + S2O;²-(aq) → I½(aq) + 2SO,²-(aq) is first order with respect to I and first order with respect to S20g. The rate constant k was determined at different temperatures and a plot of In(k) versus 1/T was constructed resulting in the straight line: y = -5781.8x + 14.1. Assume k has units of M's. (a) Determine the activation energy for this reaction. (b) Calculate the value of k at 20 °C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY