
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
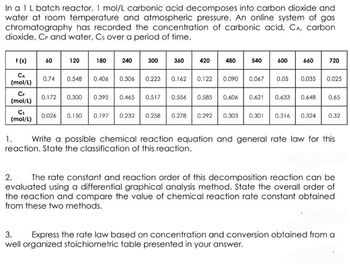
Transcribed Image Text:In a 1 L batch reactor, 1 mol/L carbonic acid decomposes into carbon dioxide and
water at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. An online system of gas
chromatography has recorded the concentration of carbonic acid, CA, carbon
dioxide, CP and water, Cs over a period of time.
+ (5) 60
CA
(mol/L)
CP
(mol/L)
Cs
(mol/L)
120
0.74 0.548
180
0.026 0.15
0.406
240 0 300 360
0.306
0.223
0.162
0.172 0.300 0.395 0.465 0.517 0.556
0.258 0.27
420
0.122
480 540 600 660
0.090 0.067 0.05 0.035 0.025
0.585 0.606 0.621
720
0.292 0.3
0.633 0.648 0.65
0.301 0.316 0.324 0.32
1. Write a possible chemical reaction equation and general rate law for this
reaction. State the classification of this reaction.
2. The rate constant and reaction order of this decomposition reaction can be
evaluated using a differential graphical analysis method. State the overall order of
the reaction and compare the value of chemical reaction rate constant obtained
from these two methods.
3. Express the rate law based on concentration and conversion obtained from a
well organized stoichiometric table presented in your answer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 14 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Please show every step you used to solve each problem. A vapor mixture of 100 mol/s comprising 55 mol% benzene and 45 mol % toluene is sent to a partial condenser operating at 760 mm Hg. 75 mol% of the toluene in the feed is recovered in the liquid product. Determine all unknown flow rates, compositions, and required heat removal. and do a degree a. Draw a process flow diagram of freedom analysis b. Write out equations used to solve and to calculate all specifications used in Excel Solver unknown flow rates, compositions, C. F Specify the temperature and pressure of the feed as T₁ = 102°C and P₁ = 760 mm Hg. Choose the lowest enthalpy stream (liquid product stream) for a reference condition. Calculate the required heat removal analytically by hand (No Excel Solver). d. Create Enthalpy Tablearrow_forwardThe formation of NO from Na and O is to be carried out in a small batch reactor. As a first approximation, we shall consider that the reaction time is more rapid than the time of cylinder compression, consequently, the reaction takes place isothermally in car eylinder at 2700 K, in a constant volume reactor (cylinder) and under a pressure of 20 atm, the initial concentration of N2 is 0.0696 mol/liter. By a specifying constant volume, we are assuming that reaction take place rapidly with respect to the movement of the piston in the cylinder. Consider that the feed consists of 77% N2, 15% Oz and 8% other gases, which may be considered inert. At this temperature the equilibrium constant (Ke-0.01). The reaction is reversible: Na + 0z + 2NO With a rate equation: Cho -TN, = k ( CN, Co, Ke Calculate: a) The equilibrium conversion of N2. b) The time required to achieve 80% of the equilibrium conversion. The formation reaction rate- constant k at this temperature is 1.11 liter mol.h' Hint: dx…arrow_forwardShort Answer: When you add salt to water, the boiling point is elevated. Briefly connect this to ideal solutions vs non-ideal solutions and mention how inter-molecular forces are involved. If two components were added together and the resulting mixture approximated an ideal solution, what do you expect to be true about the molecular nature of the two components, do you expect them to be similar or dissimilar, why?arrow_forward
- 11.7 mole dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) enter a reactor with 21.6 mole hydrogen (H2) and 37.5 mole oxygen (O2). The following reaction takes place: CH2Cl2 + H2 + 3/2 O2 → COCl2 + 2 H2O 6.4 mole of H2O are produced. Calculate the extent of the reaction.arrow_forwardProblem 2. There has been a lot of recent interest in oxygen-enhanced combustion. In this process, pure oxygen is added to air which is then fed to a furnace along with the fuel. This increases the combustion temperature, thereby reducing the amount of pollutants and increasing the concentration of CO₂ in the flue gas, making it easier to sequester the CO₂. An Orsat analysis of the flue gas from a furnace which burns methane is as follows: 11.1 mol % CO2, 5.5 mol % O2, and 83.4 mol % N₂ (dry basis). The amounts of CO, SO₂, and CH4 in the flue gas are negligible. a.) How many moles of air were fed to the furnace per mole of pure O₂? b.) What was the percent excess oxygen fed to the furnace?arrow_forwardFor the electrolysis of CuCl2 (molten) to form Cu(s) and Cl2(g):E°Cu2+/Cu = 0.339 VE°Cl-/Cl2 = 1.360 V What minimum voltage must be used to carry out the reaction? If 1.5V is used, how much electrical energy (in kJ) will be used to produce 2g of Cl2(s)?arrow_forward
- A feed stream containing 15% wt solids and 85% wt water is introduced in a certain process where the solids are being crushed. The crushed solids and preservatives are mixed in a 4:5 mass ratio and the mixture is heated to evaporate water. The residue has 1/3 water by mass. write step by step process: how many unknowns how many independent equations can be made? calculate the mass fraction of the solids in the product stream after producing 100 g of the product residue. Report your answer to 4 decimal places.arrow_forwardcan you help me solve this, this is what i have so far but is there a different way of doing this. please type solution in word. calculate how much KNO3 can be removed as solid (filtered) from a 1-kilogram solution of 60 wt% KNO3 in water (40 wt%) at 65 °C, when it is cooled to 25 °C. Note that the 60 wt% value is given on a basis of total solution mass, which is different than the values presented in the graph.arrow_forwardQ1): Tw~362 K; Tn~342 Karrow_forward
- Fresh methanol (CH3OH) reactant is combined with recycled reactant and vaporized before being sent to a fixed-bed reactor. The reactor effluent is then cooled before being sent to the first of two distillation columns. DME (CH3)2O product is taken overhead from the first column. The second column separates the water from the unused methanol. The methanol is recycled back to the front end of the process, and the water is sent to wastewater treatment to remove trace amounts of organic compounds. Draw a block flow diagram for this process. The main reaction is 2CH3OH → (CH3)2O + H2Oarrow_forwardIn the separation process illustrated below, fresh feed stream F consists of 20% A and 80% B on a mass basis. F mixes with recycle stream R to produce mixed stream M, which enters the separator. The mass ratio of A:B in stream M is 2:3. Product stream P, which leaves the separator at 100 kg/h, is pure A, while waste stream W is 5 mass % A. Recycle stream R is 80 mass % A. (a) Find all unknown stream flow rates. (b) Calculate the recycle ratio.arrow_forwardCalculate the amount of heat required to pass through each section of the graph. Here are the heat capacities and phase change enthalpies of water. ΔHfus or enthalpy of fusion or the first phase change from solid to liquid ΔHfus = 6.01kJ/mol ΔHvap or enthalpy of vaporization or the second phase change from liquid to gas ΔHvap = 40.7kJ/mol cliquid water or specific heat of water in the liquid phase cliquid water = 4.184J/g℃ cice or specific heat of water in the solid phase cice = 2.108J/g℃ cwater vapor or the specific heat of water in the gas phase cwater vapor= 1.996J/g℃arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The