
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Table 17-1
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Rochelle and Alec, own wells that produce safe drinking water. Each week Rochelle and Alec work together to decide how many gallons of water to pump. They bring the water to town and sell it at whateverprice the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Rochelle and Alec can pump as much water as they want without cost so that the marginal cost of water equals zero. The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for water is shown in the table below:
Refer to Table 17-1. If this market for water wereperfectly competitive instead of monopolistic, what price would be charged?
Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Rochelle and Alec, own wells that produce safe drinking water. Each week Rochelle and Alec work together to decide how many gallons of water to pump. They bring the water to town and sell it at whatever
|
Quantity
(in gallons) |
Price
|
Total Revenue
(and Total Profit) |
|
0
|
$60
|
$0
|
|
100
|
55
|
5,500
|
|
200
|
50
|
10,000
|
|
300
|
45
|
13,500
|
|
400
|
40
|
16,000
|
|
500
|
35
|
17,500
|
|
600
|
30
|
18,000
|
|
700
|
25
|
17,500
|
|
800
|
20
|
16,000
|
|
900
|
15
|
13,500
|
|
1,000
|
10
|
10,000
|
|
1,100
|
5
|
5,500
|
|
1,200
|
0
|
0
|
Refer to Table 17-1. If this market for water were
Group of answer choices
$0
$30
$40
$60
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
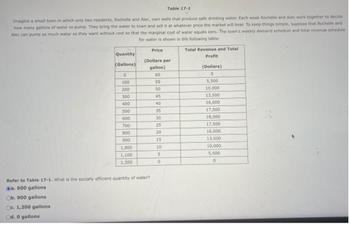
Transcribed Image Text:Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Rochelle and Alec, own wells that produce safe drinking water. Each week Rochelle and Alec work together to decide
how many gallons of water to pump. They bring the water to town and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Rochelle and
Alec can pump as much water as they want without cost so that the marginal cost of water equals zero. The town's weekly demand schedule and total revenue schedule
for water is shown in the following table:
Quantity
(Gallons)
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1,000
1,100
1,200
Table 17-1
Price
Refer to Table 17-1. What is the socially efficient quantity of water?
Ca. 600 gallons
Ob. 900 gallons
Oc. 1,200 gallons
Od. 0 gallons
(Dollars per
gallon)
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
Total Revenue and Total
Profit
(Dollars)
0
5,500
10,000
13,500
16,000
17,500
18,000
17,500
16,000
13,500
10,000
5,500
0
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Imagine a small town in which only two residents, Rochelle and Alec, own wells that produce safe drinking water. Each week Rochelle and Alec work together to decide
how many gallons of water to pump. They bring the water to town and sell it at whatever price the market will bear. To keep things simple, suppose that Rochelle and
Alec can pump as much water as they want without cost so that the marginal cost of water equals zero. The town's weekly demand schedule and total revenue schedule
for water is shown in the following table:
Quantity
(Gallons)
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1,000
1,100
1,200
Table 17-1
Price
Refer to Table 17-1. What is the socially efficient quantity of water?
Ca. 600 gallons
Ob. 900 gallons
Oc. 1,200 gallons
Od. 0 gallons
(Dollars per
gallon)
60
55
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
Total Revenue and Total
Profit
(Dollars)
0
5,500
10,000
13,500
16,000
17,500
18,000
17,500
16,000
13,500
10,000
5,500
0
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Viral infections such as flu are highly contagious. The number of infections and thus the spread of the disease can be prevented by getting vaccinated. However, the decision to take vaccine is voluntary and some people choose not to go for it for various reasons.] [What type of externality occurs by getting vaccinated against contagious diseases? Explain your answer in 100 words or less. [In a diagram, show the market equilibrium quantity of the vaccine. Is the quantity also socially efficient? Explain in 100 words or less and demonstrate using the same diagram. [Suggest one method to achieve a socially efficient outcome. Explain your answer in 100 or less words.arrow_forwardwhere does the green goarrow_forwardDon’t know if what I have is correct and unsure how to solve the first part to method 2arrow_forward
- In markets with strong network externalities: a. It is common for the market to be split equally across several firms. b. Market shares typically fluctuate in opposite directions, i.e. high market share today implies lower market share tomorrow. c. Market entry happens frequently. d. A single firm tends to dominate the market.arrow_forwardHelparrow_forwardD. Pollution problem You know the marginal cost of reducing pollution for four factories. Each unit of pollution can be eliminated according to the following marginal costs. A B C D First Unit $65 $15 $30 $10 Second Unit $75 $55 $65 $30 Third Unit $85 $85 $110 $40 Fourth Unit $120 $155 $120 $60 1. The total cost of Firm D eliminating 4 units of pollution 2. Determine the total cost of each firm eliminating one unit of production. 3. The community has decided that the managers of the firms are allowed to produce a total of 4 units of production. Identify the firm(s) that will pollute.arrow_forward
- Please fill in the blanks. Thank youarrow_forwardQuantity (in gallons) Total Price Revenue $8 $0 50 7 350 100 600 150 750 200 4 800 250 3 750 300 600 350 1 350 400 Imagine a small town in a remote area where only two residents, Maria and Miguel, own dairies that produce milk. Their respective dairies are equal in size. Each week Maria and Miguel work together to decide how many gallons of milk to produce and what price to charge. To keep things simple, suppose that Maria and Miguel can produce as much milk as they want without cost so that the marginal cost is zero and there are no fixed costs. The weekly town demand schedule and total revenue schedule for milk is shown in the table above. Suppose the town enacts new antitrust laws that prohibit Maria and Miguel from operating as a cartel. Assuming that each producer can only modify quantity in increments of 50, which of the following is consistent with the Nash equilibrium for this scenario? Maria will charge a price of $5 for each gallon. Miguel will sell 100 gallons. Milk will…arrow_forwardChapter 10 The first government employee suggests reducing pollution through regulation. To meet the pollution goal, the government requires each firm reduce its pollution by 2 units. Complete the following table with the total cost to each firm of reducing its pollution by 2 units. Firm Total Cost of Eliminating Two Units of Pollution (Dollars) Firm A Firm B Firm C ☐☐ Method 2: Tradable Permits Meanwhile, the other employee proposes using a different strategy to achieve the government's goal of reducing pollution in the area from 1 6 units. This employee suggests that the government issue two pollution permits to each firm. For each permit a firm has in its possession, i 1 unit of pollution. Firms are free to trade pollution permits with one another (that is, buy and sell them) as long as both firms can agree on For example, if firm A agrees to sell a permit to firm B at an agreed-upon price, then firm B would end up with three permits and would nee reduce its pollution by only 1 unit…arrow_forward
- Acres Sophia Amber Cedric 1 $12 $24 $6 2 8 18 3 10 4 3 8 3 1 6. 2 6 4 1 7 2 Consider the town of Springfield with only three residents, Sophia, Amber, and Cedric (see the Table). The three residents are trying to determine how large, in acres, they should build the public park. Suppose the cost to build the park is $12 per acre and that the residents have agreed to split the cost of building the park equally. If the residents vote to determine the size of park to builo basing their decision solely on their own willingness to pay (and trying to maximize their own surplus), what is the largest park size for which the majority of residents would vote "yes?" 1 acre 2 acres 3 acres 4 acresarrow_forwardTwo firms each currently dump 20 tons of pollution a piece into a local river. The government wants to reduce the amount of pollution in the river so they issue 5 permits to each firm. The cost for firm A to reduce their pollution by 1 ton is $1000 and the cost for firm B to reduce their pollution by 1 ton is $800. When answering the questions below simply enter the number for your answer do not write a full sentence. Question 1 If trade is NOT allowed what will be the cost of reducing pollution will be for firm A. total. for firm B, and inarrow_forwardWhich are the two key ’problems’ encountered in aggregating on the consumer side, and why it not occurs on the producer side ? Pls short answer in 15-20 Sentencesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education