
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
i) Ray parallel to the optical axis; ii) Focal ray; iii) Central ray, iv) Draw the image of the arrow, v) Indicate in the same figure, from where to where di (image-lens distance) is. Use the figure, Do not substitute it with any other figure. Don't forget to put the direction on each ray, both the incident rays and the transmitted rays. Label each ray.
Image characteristics for Case 3: Object distance d0=R. Choose the ones that apply:
a) Virtual
b) Real
c) Inverted
d) Increased
e) No image is formed
f) Equal size
g) Reduced
h) Erect
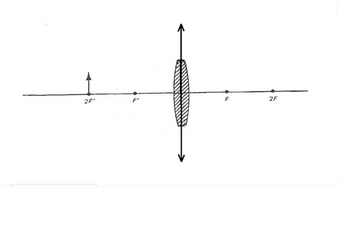
Transcribed Image Text:2F'
7
2F
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Case 1: Object distance d0= infinity. The figure below shows light rays coming from an object located at infinity, in front of a convex lens. Extend the 9 incident rays to the lens, and draw the transmitted rays in the correct direction. Use the figure, DO NOT substitute it with any other figure. Use the line to trace the 9 rays. Don't forget to place the arrow on each transmitted beam. Label each ray with its corresponding name: parallel ray, central ray, and focal ray. Image characteristics for Case 1: Object distance d0= infinity. Select those that apply: a) Reduced b) Real c) Erect d) Inverted e) Equal size f) Increased g) Virtual h) No image is formedarrow_forwardPlease explain everything in detail and step by step pleasearrow_forward1.)The diverging lens of the figure produces an image of an object to the left of the lens and 5.00 cm away from the center of the lens. The refracting index of the lens is 1.50. The magnitude of the focal length of the lens is 12.0 cm and the radius of curvature R1 is 15.0 cm. A.) Calculate the radius of curvature R2 of the lens. Show your work. B.) Fill in the following table with the focal length of the lens, the distance of the image and the distance of the object (you have to calculate that) with the correct signs! f s s' C.) Is the object to the left or to the right of the lens? (Select one.) D.) Is the image formed by the lens upright or inverted compared to the object? (Select one.)arrow_forward
- IF YOU CAN NOT ANSWER BOTH DO NOT ANSWER ALSO ANSWER IN 3 SIG FIG USING SCIENTIFIC NOTATION USING Earrow_forwardTwo plane mirrors are at an angle of ?1 = 53.6° with each other as in the side view shown in the figure below. If a horizontal ray is incident on mirror 1, at what angle ?2 does the outgoing reflected ray make with the surface of mirror 2? Answer in degrees °arrow_forwardPart A How far apart are an object and an image formed by an 95 -cm -focal-length converging lens if the image is 3.20 x larger than the object and is real? Express your answer using two significant figures. ? do + d; = Cimarrow_forward
- A beam of light is incident from air on the surface of a liquid. If the angle of incidence is 36.2° and the angle of refraction is 25.0°, find the critical angle for the liquid when surrounded by air. Step 1 When light goes from one material into another having a higher index of refraction, the light bends toward the normal line as shown in part (a) of the diagram. 02 air liquid (a) (b) We are given that when = 36.2°, the angle of refraction in the liquid is = 25.0°. Thus, from Snell's law, the index of refraction of the liquid is nliquid = nair sin sin e = (1.00) sin sin 25.0° 0 (0.423)arrow_forwardCan you fix my mistake pleasearrow_forwardPart A A sharp image is located 391 mm behind a 263-mm-focal-length converging lens. Find the object distance. Follow the sign conventions. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. HA do = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Next>arrow_forward
- Please answer in Boldarrow_forwardProblem 2: What is the smallest angle 1 for which a laser beam will undergo total internal reflection on the hypotenuse of the glass prism in figure? a. Draw the refracted and reflected rays inside the glass prism, and the refracted ray as it exits the prism. b. Clearly mark all angles. Show all your calculations here. Ꮎ 30° 60%arrow_forwardPart A A reflecting telescope (Figure 1) has a radius of curvature of 3.00 m for its objective mirror and a radius of curvature of -1.50 m for its secondary mirror. rea If the distance between the two mirrors is 0.92 m, how far in front of the secondary mirror should you place the electronic sensor to record the image of a star? ent Sharing ettings Express your answer to two significant figures and Include the approprlate units. e Tools HA ? d; = Value Units %3D Figure 1 of 1 Submit Request Answer < Return to Assignment Provide Feedback Secondary mirror Sensorarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON