
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
If logical addresses are represented using m bits as shown below, where m=4 and n=2.
What is the size of each frame in the main memory? Please explain why.
Given the page table and the physical memory as shown on the right, what is the character in the corresponding physical address mapped from logical address 1010? Please explain why.
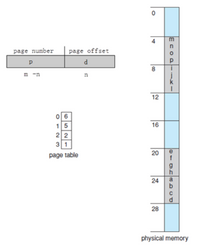
Transcribed Image Text:The image illustrates the concept of paging in memory management. It consists of three main components: a logical address format, a page table, and a depiction of physical memory.
### Logical Address Format:
- **Page Number (p):**
- Size: \( m - n \) bits
- **Page Offset (d):**
- Size: \( n \) bits
This format shows how a logical address is divided into a page number and a page offset.
### Page Table:
The page table maps logical pages to physical frames. It is represented as a table with two columns:
- **Index (Logical Page Number):**
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- **Frame Number (Physical Frame Address):**
- 0 maps to 6
- 1 maps to 5
- 2 maps to 2
- 3 maps to 1
### Physical Memory:
- Represented as a linear array with addresses increasing by a factor of 4, from 0 to 28.
- Each block (of size 4 units) is labeled with a set of letters:
- Address 0-3: Blank
- Address 4-7: m, n, o, p
- Address 8-11: j, k, l
- Address 12-15: Blank
- Address 16-19: e, f, g, h
- Address 20-23: i, j, k, l
- Address 24-27: a, b, c, d
- Address 28: Blank
This setup illustrates how logical pages are translated to physical memory frames using a page table, highlighting the relationship between logical and physical memory using paging.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a computer system uses 16-bit addresses for both its virtual and physical addresses. In addition, assume each page (and frame) has size 256 bytes. How many bits are used for the page number? How many bits are used for the offset? With this system, what’s the maximum number of pages that a process can have? Suppose that each entry in the page table comprises 4 bytes (including the frame number, the valid bit, and miscellaneous “bookkeeping bits”). An OS uses an array to store the page table. What is the size of the page table? Furthermore, suppose the first 6 pages of a process map to frames 222 to 227 (as decimal numbers), and the last 5 pages of the process map to frames 1 to 5 (also decimal numbers). All other pages are invalid. Draw the page table, including the valid bit and the frame number.arrow_forwardCan locality of reference be defined, and if so, how does it help speed up memory access?arrow_forwardWhat advantages over direct translation can segmented memory address translation offer?arrow_forward
- Show how the following values would be stored by machines with 32-bit words, using little endian and then big endian format. Assume each value starts at address 1016. Draw a diagram of memory for each, placing the appropriate values in the correct (and labeled) memory locations. 1234567816 ABCDEF1216 8765432116arrow_forwardHow much of an improvement does segmented memory address translation have over straight translation?arrow_forwardI'm confused about the distinction between a 7CH bit address and a 7CH byte address. When referring to a computer's memory map, what address does 7CH represent?arrow_forward
- Convert the following Compact Memory Notation diagram into an Array Memory Notation diagram. Assume the addresses are 4-bit binary values and the data are 8-bit binary values. Hint: The solution to this question is simply the reformatted diagram in Array Notation.arrow_forwardWhat advantages over direct translation can segmented memory address translation offer?arrow_forwardI have this problem from my textbook that I do not understand, despite re-reading the section on segmentation and paging. "The IBM system/370 architecture uses a two-level memory structure and refers to the two levels as segments and pages, although the segmentation approach lacks many of the features described in Chapter 8. For the basic 370 architecture, the page size may be either 2 KB or 4 KB, and the segment size is fixed at either 64 KB or 1 MB. For the 370/XA and 370/ESA architectures, the page size is 4 KB and the segment size is 1 MB. What advantages of segmentation does this scheme lack? What is the benefit of segmentation for the 370?"Can you help me undertand what they are looking for in this explanation?arrow_forward
- What advantages over direct translation can segmented memory address translation offer?arrow_forwardLet's double the size of the address field from 32b to 64b. What's the largest decimal value now? How might you organize this for readability?arrow_forwardmcq question The Physical address of the String Destination Memory Reference is: DS:DI, DS:SI, and DS:BX SS:SP, and SS:BP ES:DI only ES:DI and ES:SIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education