
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
i) Write down the equation derived from your Excel generated standard curve and describe its components;
ii) provide the values of the absorbance data of the unknown sample (do NOT show the absorbance data of the glycine standards). Show all details of the working out of your calculation. Indicate all units! Provide the answer with two decimals precision
iii) state the answer in a full sentence. (note: avoid mathematical symbols [=, +, -, etc] in your answer sentence).
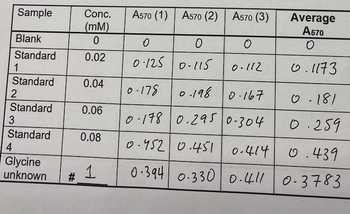
Transcribed Image Text:Sample
Blank
Standard
1
Standard
2
Standard
3
Standard
4
Glycine
unknown
#
Conc.
(mm)
0
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
1
A570 (1) A570 (2) A570 (3)
0
0
0.125 0.115
O
0-112
Average
A570
O
0.1173
0-178
0.198 0.167
0-178 0.295 0-304
0.452 0.451 0.414
0.439
0.394 0.330 0.411 0.3783
0-181
0.259
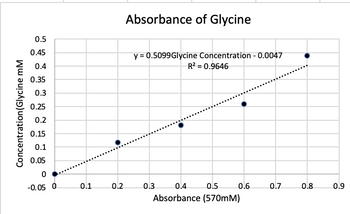
Transcribed Image Text:Concentration (Glycine mM
0.5
0.45
0.4
0.35
0.3
0.25
0.2
0.15
0.1
0.05
0
-0.05 0
0.1
0.2
Absorbance of Glycine
y = 0.5099Glycine Concentration - 0.0047
R² = 0.9646
0.3
0.4
0.5
Absorbance (570mM)
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- You are to prepare capsules that contain 0.125 g of a drug. You have four partial containers of medicatiog, which weigh 3.2 g, 1.784 g, 2.46 g, and 5.87 g. Assume you have weighed each of the four containers with the same scale, and the accuracy is known to the hundredth gram. a Which amount will need to be rounded? b. Which amount is not as accurate as it should be? c. What is the amount of the medication that will be left over after making as many 0.125 g capsules as possible?arrow_forwardA 25 year old male patient requires a 5 mL injection of sodium valproate 200 mg/mL. The displacement volume for sodium valproate is 0.56 mL/g. What volume of water for injections in millilitres should be added to the patient’s dose of sodium valproate for it to be correctly reconstituted? State your answer to 2 decimal places. units= mlarrow_forward(please type answer with explanation).arrow_forward
- number 57.) what's the answerarrow_forwardHighlight your values of A,B,C and D. For your question: A mL of B mol/L sodium phosphate solution is combined with C mL of D mol/L calcium bicarbonate. (Calcium bicarbonate is soluble.) A mL B mol/L C mL D mol/L 75.0 ml 0.300 67.5 0.350 Before you begin your reaction, you must accurately produce 1.500 L of your sodium phosphate solution from sodium phosphate trihydrate solid. Write out a procedure to explain all the steps you will take in the lab when making the solution to ensure that your solution concentration is accurate. Please include calculations that show the required mass of solid. Also include the correct names of all equipment used.arrow_forward6 x 10⁻⁵¹ = (0.15 M)² [S²⁻] [S²⁻] = (6 x 10⁻⁵¹) / (0.15 M)² Calculating, we find the minimum concentration of sulfide ion required: [S²⁻] ≈ 2.7 x 10⁻⁴⁹ M. check it calcution is writearrow_forward
- A student needs 240 mL of a 1/20 dilution of an undiluted stock solution. What volume (mL) of the stock solution will be required? Note: Your answer should be in numerical format to the nearest whole number (with a decimal).arrow_forwardLaemmli buffer, also referred to as SDS-reducing buffer, is added to each of the samples. It is a blue solution and the recipe for 2X Laemmli buffer is: 0.125 M Tris HCl, pH 6.8, 20% glycerol, 4% SDS and 10% β-mercaptoethanol (βME). What is the purpose of each of these ingredients?arrow_forwardAn order was received for 750 mL of 7.5% dextrose solution using 5% D5W and 20% D20W. How many parts of each dextrose solution is needed?(round answers to the nearest tenth)arrow_forward
- Consider a pH titration curve at 298 K for 50 mL of 0.10 M hypobromous acid, HBrO (Ka = 2.8 x 10−9), titrated with 0.10 M KOH solution. a. What volume of KOH is needed to reach the half-equivalence point? b. Calculate the pH of the HBrO sample at the half-equivalence point. c. Calculate the equivalence point pH. d. Identify a satisfactory pH indicator for the equivalence point. The pH range of colour change is indicated in parentheses. A) Methyl orange (3.0 - 4.3) B) Bromocresol purple (5.0 - 6.5) C) Alizarin yellow R (10.0 - 12.0) D) Methyl red (4.2 - 6.2)arrow_forwardWhen 300 mL of 0.0010 M Ca( NO3)2 solution is added exactly to 500 mL of 0.0015 M K3PO4 solution, find the ion product Q and decide whether to precipitate. (However, K_sp of Ca3(PO4)2 = 1.2x 10^-26)arrow_forwardConcentrations in biochemical systems are often very dilute. Consequently, scientific notation and logarithms are often used to express concentrations. In scientific notation, numbers are expressed as coefficient x 10" To convert a number to scientific notation, proceed as follows: 1. Move the decimal place so that there is one digit in front of the decimal. 2. Account for the moved decimal in the value of x. If the decimal moved to the right, x is negative; if it moved to the left, x is positive. A logarithm is basically an exponent. Unless otherwise indicated, a logarithm is the a of 10". The numbers after the decimal point are significant; the number before the decimal just identify the location of the decimal point for the number. Notice that it is easy to estimate a logarithm from scientific notation; it's the exponent! Logarithms are commonly used to express the concentration of H. The pH is defined as pH= log (In), where the base number is 2.303. The same general rules as logs…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON