
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
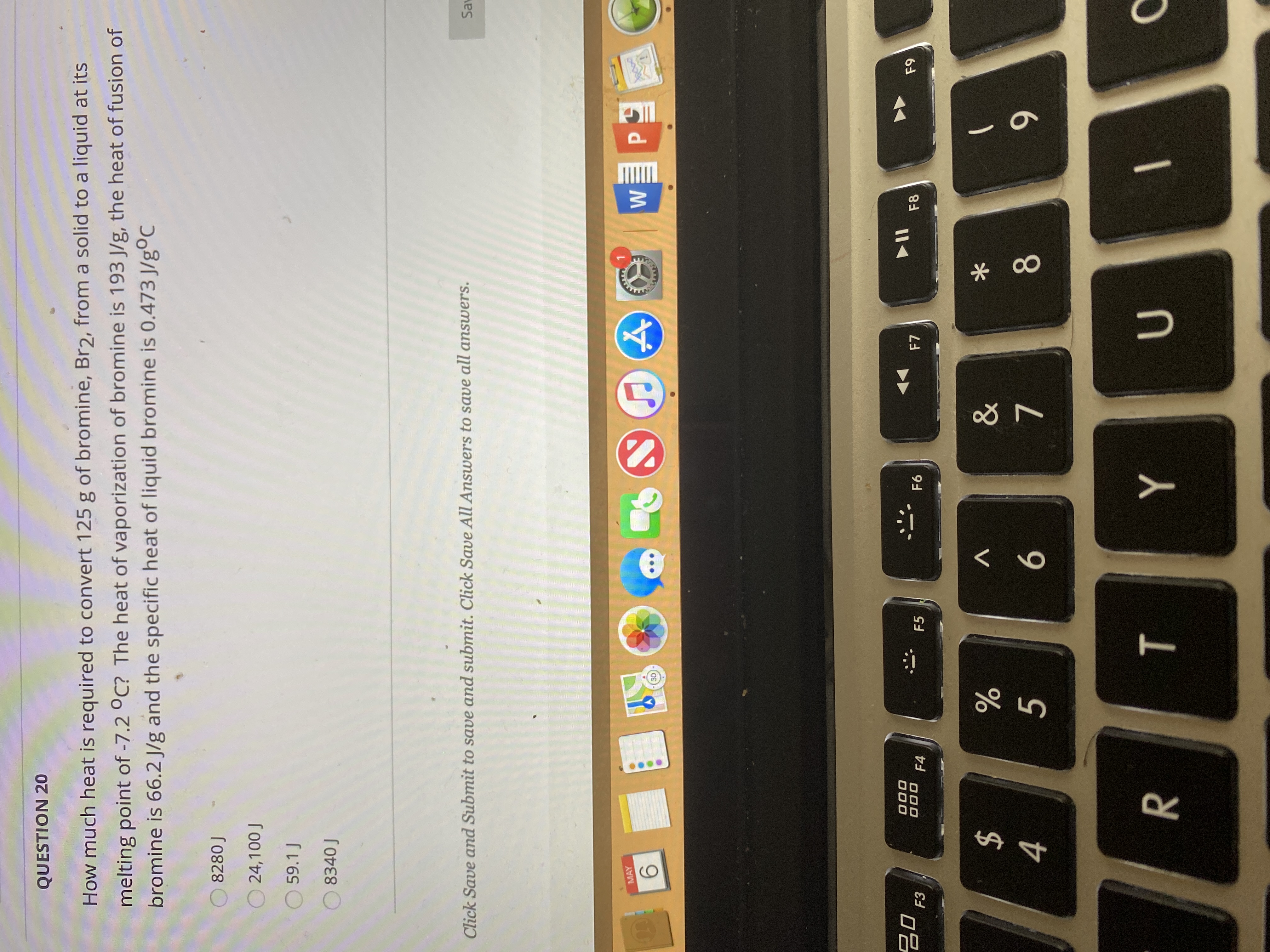
Transcribed Image Text:huch heat is required to convert 125 g of bromine, Br2, from a solid to a liquid at its
g point of -7.2 °C? The heat of vaporization of bromine is 193 J/g, the heat of fusion of
he is 66.2 J/g and the specific heat of liquid bromine is 0.473 J/gºC
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How much heat energy is required to convert 39.6 g of solid ethanol at -114.5 °C to gaseous ethanol at 147.2 °C? The molar heat of fusion of ethanol is 4.60 kJ/mol, and its molar heat of vaporization is 38.56 kJ/mol. Ethanol has a normal melting point of-114.5 °C and a normal boiling point of 78.4 °C. The specific heat capacity of liquid ethanol is 2.45 J/g °C, and that of gaseous ethanol is 1.43 J/g. °C. 9= kJarrow_forwardHow much heat is required to convert 87.1 g of acetone from a solid at –154.0°C to a liquid at –42.0°C? You may find the tabulated data useful. Molar mass of acetone 58.08 g/mol Melting point of acetone –94.5°C cliquid 2.16 J/g°C csolid 1.65 J/g°C ΔHvaporization 31.3 kJ/mol ΔHfusion 5.70 kJ/molarrow_forwardThe heat of vaporization of an organic solvent is 39.8kJ/mol. Find the temperature in degrees Celsius qt which the solvent boils on a day in ski resort when the barometric pressure is 0.734atm. The normal boiling point of the liquid is 70.6•C (R=8.314 J/K mol)arrow_forward
- How much heat is required to convert 25g of ice at -6.0 ˚C to water vapor at 102 ˚C? (ΔHfus = 6.02kJ/mol; ΔHvap = 40.7kJ/mol ; specific heat of water is 4.184J/g●oC; specific heat of ice is 2.06J/g●oC; specific heat of water vapor is 2.03J/g●oC)arrow_forwardConsider the following selected properties of water: Density (liquid water): d = 1.00 g/mL Heat of fusion: AH fus Heat of vaporization: AHvap = 40.67 kJ/mol Specific heat (liquid water): cp = 4.184 J/(g∙K) = 4.184 J/(g•°C) = 6.8 kJ 380 J 68 kJ 3.8 kJ 75 J 6.01 kJ/mol How much heat is needed to heat 36 mL of water from 5 °C to 50 °C?arrow_forwardButane is a common fuel used in cigarette lighters and camping stoves. Normally supplied in metal containers under pressure, the fuel exists as a mixture of liquid and gas, so high temperatures may cause the container to explode. At 25.0 ° C, the vapor pressure of butane is 2.30 atm. What is the pressure in the container at 130.0 ° C? ( Δ H ° vap = 24.3 kJ/mol.)arrow_forward
- A particular refrigerator cools by evaporating liquefied dichlorodifluoromethane, CCl,F. How many kilograms of this liquid must be evaporated to freeze a tray of water at 0°C to ice at 0°C? The mass of the water is 549 g, the heat of fusion of ice is 6.01 kJ/mol, and the heat of vaporization of dichlorodifluoromethane is 17.4 kJ/mol. kgarrow_forwardLiquid ammonia can be used as a refrigerant and heat transfer fluid. How much energy is required to convert 25.0g of NH3(l) at -76 degrees Celsius into NH3(g)? In other words how much heat is needed to turn the liquid ammonia into a gas? molar mass: 17.03g/mol normal boiling point: -33.4 degrees Celsius specific heat of NH3(l): 4.7 J/g . Degrees Celsius specific heat of NH3(g): 2.2J/g . Degrees Celsius molar heat of vaporization: 23.5 kj/molarrow_forward13. How much heat in kJ is needed to warm 31.6 g of ice from 10 °C to steam at 175 °C. The heat capacity of ice is 2.09 J/g °C, liquid water has a heat capacity of 4.18 J/g °C, and that of šteam is 1.84 J/g °C. The AHtus for water is 6.02 kJ/mol and the AHvap for water is 40.7 kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- 3. The enthalpy of fusion for Lauric acid (C12H24O2) is 32.86 kJ/mol and enthalpy of vaporization is 63.82 kJ/mol. The melting point is 43.2°C. How much heat is absorbed to raise the temperature of a 0.650g sample from 22.0°C to 56.3°C? The heat capacity of the solid is 2.15 J/g.C and the heat capacity of the liquid is 3.62 J/g°C.arrow_forward79.2 grams of H2O is cooled from 115 °C to -43.1°C. What is the heat change in joules?The molar heat of vaporization of H2O is 40.8 kJ/mol. The molar heat of fusion of H2O is 6.02 kJ/mol. Cp (solid) for H2O is 2.11 J/g°C. Cp (liquid) for H2O is 4.18 J/g°C. Cp (gas) for H2O is 2.00 J/g°C. The melting point of H2O is 0.0 °C and the boiling point is 100.0 °C.arrow_forwardThe heat of vaporization for ethanol is 0.826 kJ/g0.826 kJ/g. Calculate the heat energy in joules required to boil 20.65 g20.65 g of ethanol.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY