
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
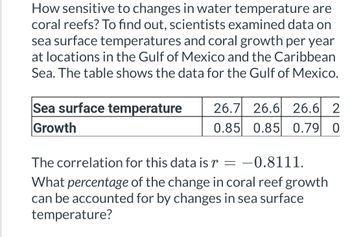
Transcribed Image Text:**Understanding the Sensitivity of Coral Reefs to Water Temperature Changes**
Researchers have been investigating how sensitive coral reefs are to changes in sea surface temperatures. To explore this relationship, scientists collected and examined data on sea surface temperatures and coral growth rates per year from various locations in the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea. Below is a table that presents the data for the Gulf of Mexico.
| Sea Surface Temperature | 26.7 | 26.6 | 26.6 | 26.4 |
|--------------------------|------|------|------|------|
| Growth | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.79 | 0.82 |
### Analysis of the Data
The correlation coefficient (\(r\)) for this dataset is \(-0.8111\). This negative correlation indicates that as sea surface temperatures increase, coral growth tends to decrease. The strength and nature of this relationship are quantified by the correlation coefficient value.
### Key Consideration
What percentage of the change in coral reef growth can be attributed to changes in sea surface temperature? This is an important question for understanding the extent to which temperature impacts coral health, helping guide conservation efforts and strategies.
For further exploration and detailed analysis, students and researchers can apply statistical methods to determine the precise impact of sea surface temperature changes on coral reef growth.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The data below was collected from manufacturer advertisements of their vehicles horsepower (x) and highway gas mileage (mpg=y). Use this data to answer the following questions. horsepower 146 250 340 350 390 190 220 mpg 33 28 15 17 11 35 42 1. Find the p-value to determine if there is a linear correlation between horsepower and highway gas mileage (mpg). Record the p-value below. Round to four decimal places.p-value==2. Is there a linear correlation between horsepower and highway gas mileage (mpg)? 3. If there is a linear correlation, write the correlation coefficient below. Otherwise, leave it blank. Round your final answer to four decimal places. Be careful with your sign.r=r= 4. If there is a linear correlation, write the regression equation below. Otherwise, leave it blank. Round all numbers to four decimal places.ˆy=y^=5. Using the data shown above, predict the the highway gas mileage (mpg) for a car that has a horsepower of 225. Round your final answer to two decimal…arrow_forwardThe authors of a paper presented a correlation analysis to investigate the relationship between maximal lactate level x and muscular endurance y. The accompanying data was read from a plot in the paper. X 390 740 760 y 3.90 r 3.90 5.00 5.30 4.10 3.60 6.20 OH₂: P = 0 Ha: P 0 1,465 1,470 1,495 2,190 t = P-value = 6.98 7.45 4.85 7.70 4.55 6.70 8.80 OH₂: P = 0 H₂: P = 0 Compute the value of the sample correlation coefficient, r. (Round your answer to four decimal places.) Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to one decimal place and your P-value to three decimal places.) State the conclusion in the problem context. O Fail to reject Ho. A positive correlation exists between maximum lactate level and muscular endurance. Reject Ho. A positive correlation exists between maximum lactate level and muscular endurance. O Fail to reject Ho. A positive correlation does not exist between maximum lactate level and muscular endurance. O Reject Ho. A…arrow_forwardA random sample of college students was surveyed about how they spend their time each week. The scatterplot below displays the relationship between the number of hours each student typically works per week at a part- or full-time job and the number of hours of television each student typically watches per week. The correlation between these variables is r = –0.63, and the equation we would use to predict hours spent watching TV based on hours spent working is as follows: Predicted hours spent watching TV = 17.21 – 0.23(hours spent working) Since we are using hours spent working to help us predict hours spent watching TV, we’d call hours spent working a(n) __________________ variable and hours spent watching TV a(n) __________________ variable. The correlation coefficient, along with what we see in the scatterplot, tells us that the relationship between the variables has a direction that is _________________ and a strength that is ______________________. According to the…arrow_forward
- 1945 is paired with cancer rates for 1975. The cigarette consumption data is from 1945 to 1975 in 5-year increments. There is a strong positive linear association between annual cigarette consumption and lung cancer rates. The correlation is 0.81. If we use the line to make predictions of the number of lung cancer deaths per 100,000 people, which of the following is an example of extrapolation? a. Predict Y when cigarette consumption is 3,500 cigarettes per person. b. Predict Y when cigarette consumption is 3,800 cigarettes per person. c. Predict Y when cigarette consumption is 4,600 cigarettes per person.arrow_forwardThe results from a research study indicate that adolescents who watch more violent content on television also tend to engage in more violent behavior than their peers. The correlation between amount of TV violent content and amount of violent behavior is an example of Question 25 options: a positive correlation a negative correlation a correlation near zero a correlation near onearrow_forwardAfter gathering data about the number of starfish and measuring the pollution in areas of the ocean you find a negative linear correlation between pollution levels and number of starfish. What can you conclude based on this information? a. There is a confounding variable that is affecting both pollution and starfish. b. As pollution rises the number of starfish falls c. That pollution is causing starfish to die, leading to the negative correlation d. That pollution is supporting starfish, leading to the negative correlationarrow_forward
- The trend of thinner beauty pageant winners has generated charges that the contest encourages unhealthy diet habits among young women. Listed below are body mass indexes (BMI) for beauty pageant winners from two different time periods. Find the coefficient of variation for each of the two sets of data, then compare the variation. BMI (from the 1920s and 1930s): 20.5 21.9 22.1 22.3 20.3 18.7 18.8 19.4 18.3 19.2 BMI (from recent winners): 19.4 20.3 19.6 20.3 17.7 17.9 19.2 18.7 17.7 16.8 The coefficient of variation for the BMI's of beauty pageant winners from the 1920s and 1930s is %. (Round to one decimal place as needed.) The coefficient of variation for the BMI's of recent beauty pageant winners is %. (Round to one decimal place as needed.) Is there a difference in variation between the two data sets? O A. The BMI's of beauty pageant winners from the 1920s and 1930s have considerably less variation than the BMI's of recent winners. O B. The BMI's of recent beauty pageant winners have…arrow_forwardThe following shows a linear correlation between weight and height. Image result for scatter plot scatter plot positive histogram negative O pie chart random frequency polygon biasedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman