
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
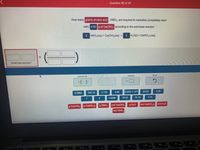
Transcribed Image Text:Question 90 of 97
How many grams of nitric acid , HNO3, are required to neutralize (completely react
with) 4.30 g of Ca(OH)2 according to the acid-base reaction:
2 HNO:(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq)
H20(1) + Ca(NO;)2(aq)
STARTING AMOUNT
ANSWER
RESET
ADD FACTOR
0.116
3.60
6.022 x 1023
63.02
4.30
0.0682
164.10
0.0580
18.02
74.10
7.31
1
mol Ca(OH)2
g H,0
mol Ca(NO3)2
mol H20
g Ca(OH)2 g Ca(NO,)2
g HNO,
mol HNO,
MacBook Air
F10
F9
F8
F7
吕口
888
F6
F5
F4
E3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3), also known as sodium bicarbonate or "baking soda", can be used to relieve acid indigestion. Acid indigestion is the burning sensation you get in your stomach when it contains too much hydrochloric acid (HCI), which the stomach secretes to help digest food. Drinking a glass of water containing dissolved NaHCO3 neutralizes excess HCl through this reaction: HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO₂(9) The CO2 gas produced is what makes you burp after drinking the solution. Suppose the fluid in the stomach of a woman suffering from indigestion can be considered to be 250. mL of a 0.076 M HCl solution. What mass of NaHCO3 would she need to ingest to neutralize this much HCl ? Round your answer to 2 significant digits. x10 Garrow_forwardFor each of the following acid-base reactions, calculate how many grams of each acid are necessary completely react with and neutralize 2.8 g of the base. 2 HNO3 (aq) + Ca(OH)2 (aq) -------> 2 H2O (l) + Ca(NO3)2 (aq)arrow_forwardHow many grams of nitric acid, HNO₃, are required to neutralize (completely react with) 4.30 g of Ca(OH)₂ according to the acid-base reaction: 2 HNO₃(aq) +Ca(OH)₂(aq)→2 H₂O(l)+Ca(NO₃)₂(aq)arrow_forward
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3), also known as sodium bicarbonate or "baking soda", can be used to relieve acid indigestion. Acid indigestion is the burning sensation you get in your stomach when it contains too much hydrochloric acid (HCI), which the stomach secretes to help digest food. Drinking a glass of water containing dissolved NaHCO, neutralizes excess HCI through this reaction: HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) NaCl(aq) + H₂O(1) + CO₂(g) The CO₂ gas produced is what makes you burp after drinking the solution. Suppose the fluid in the stomach of a man suffering from indigestion can be considered to be 200 ml of a 0.050 M HCI solution. What mass of NaHCO, would he need to ingest to neutralize this much HCI? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. Xarrow_forwardComplete the following reaction and balance it. Fe(OH)3(aq) + HCl(aq) → a) FeCl3(aq)+ 3 H2O(l) b) FeCl(aq) + H2O(l) c) Fe(aq) + HOCl(aq) d) FeCl(aq) + 3 OH–(aq) e) H2O(l) + FeCl2(aq)arrow_forwardCalculate the molar concentration HCl when 250 mL of 0.10 M HCl is mixed with 150 mL of 0.10 M NaOH in a beaker. HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)arrow_forward
- a Ammonium chloride and rubidium acetate, RbCH, CO₂, are mixed in water. Choose a balanced equation for the acid-base reaction that could, in principle, occur. O RbCH3CO₂ (s)+NH, Cl(s) + H₂O() = Rb+ (aq) + CH3CO₂¯(aq) +NH, +(aq) +Cl¯(aq) OCH3CO₂ (aq) + NH4+ (aq) CH3CO₂H(aq) + NH3 (aq) RbCH, CO₂ (aq) + NH4Cl(aq) NH₂CH3 CO₂ (aq) + RbCl(aq)arrow_forward7. Identify the given reactions as acid-base, redox, or precipitation reactions. 3NaOH(aq)+FeCl3(aq)=Fe(OH)3(s)+3NaCl(aq) LiOH(aq)+HCl(aq)=H2O(l) + LiCl(aq) 2H2(g)+ O2(g)=2H2O(g)arrow_forwardMolarity of vinegar solution is .8 Marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY