
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337399074
Author: John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
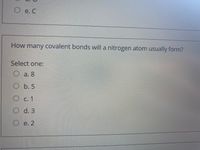
Transcribed Image Text:e. C
How many covalent bonds will a nitrogen atom usually form?
Select one:
O a. 8
O b. 5
С. 1
O d. 3
O e. 2
O O O O
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- escribe the type of bonding that exists in the Cl2(g)molecule. How does this type of bonding differ from that found in the HCl(g)molecule? How is it similar?arrow_forward7.97 Consider the structure shown below for as well as any other important resonance structures. (a) What is the expected O—N—O bond angle in this structure? (b) The molecule contains N—O bonds of two different lengths. How many sborter N—O bonds would be present?arrow_forwardWhy is the geometric structure of a molecule important, especially for biological molecules?arrow_forward
- a. How many sticks did you need to make the skeleton structure?____________ b. How many sticks are left over? ____________ If your model is to obey the octet rule, each ball must have four sticks in it except for hydrogen atom balls, which need and can only have one. Each atom in an octet rule species is surrounded by four pairs of electrons. c. How many holes remain to be filled? ____________ Fill them with the remaining sticks, which represent nonbonding electron pairs. Draw the complete Lewis structure for NH2Cl using lines for bonds and pairs of dots for nonbonding electrons.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is false concerning bonding? Elements with extremely different electronegativities tend to form ionic bonds with each other. In an N—O bond. electron density is greater near the O atom. An N—O bond is an example of a polar covalent band. In general, chemical bonds form to minimize energy. The bond in KBr is formed by sharing electrons.arrow_forward11. Which is a compound? steel water a. b. 12. If the volume of a substance is 98.2 cc and it has a mass 56.12 grams, it should have a density of kg/m³. a. 570 C. 571.5 b. 572 d. Answer is not among the choices 13. When the electronegativities of two atoms are about the same,_______result/s. a. Ionic bonds C. Polar covelent bonds b. Non-polar covalent bonds d. Both a and b 14. 80.45 g of charcoal was combined with 160.18 g of oxygen to produce ash and gases. How much ash, in grams, were left if 220.3 g of gases were produced? a. 20.3 b. 60.1 15. CH4 is the C. oxygen d. Both a and b a. structural b. empirical formula for methane. 16. Which is an element? a. sugar b. alcohol C. d. C. d. C. d. 79.7 Answer is not among the choices molecular Both b and c water None of the choices are elementsarrow_forward
- Which of the following compounds is likely to have the strongest H-X bond? a.HBr (141 pm) b.HI (161 pm) c.HF (92 pm) d.H2S (134 pm) e.HCl (127 pm)arrow_forward41.How many single bonds that are not part of any double bonds can be found in the best Lewis stucture of CO 2? A. 0 B. 1 C. 2 D. 3arrow_forwardHelparrow_forward
- Rank each of the molecules below in order of the shortestto the longest sulfur-oxygen bond length.a. S O 2 b. S O 3 2— c. S O 4 2—arrow_forwardWhich statement below is correct? A. Molecules with the formula EO2 or OE2 (E = a non metal) will be nonpolar. B. A molecule which contains polar bonds will always be polar. C. Most, but not all molecules with lone pairs are polar. D. If all the bonds attached to a central atom are the same, the molecule will be nonpolar.arrow_forward10. Which of the following is technically considered a nonpolar covalent bond? A. C – H B. O – N C. P – Cl D. O – F E. S – Clarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781133949640
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning