
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
PART 1:
Raw Materials Inventory Turnover
A. How is this ratio calculated?
What does the ratio show?
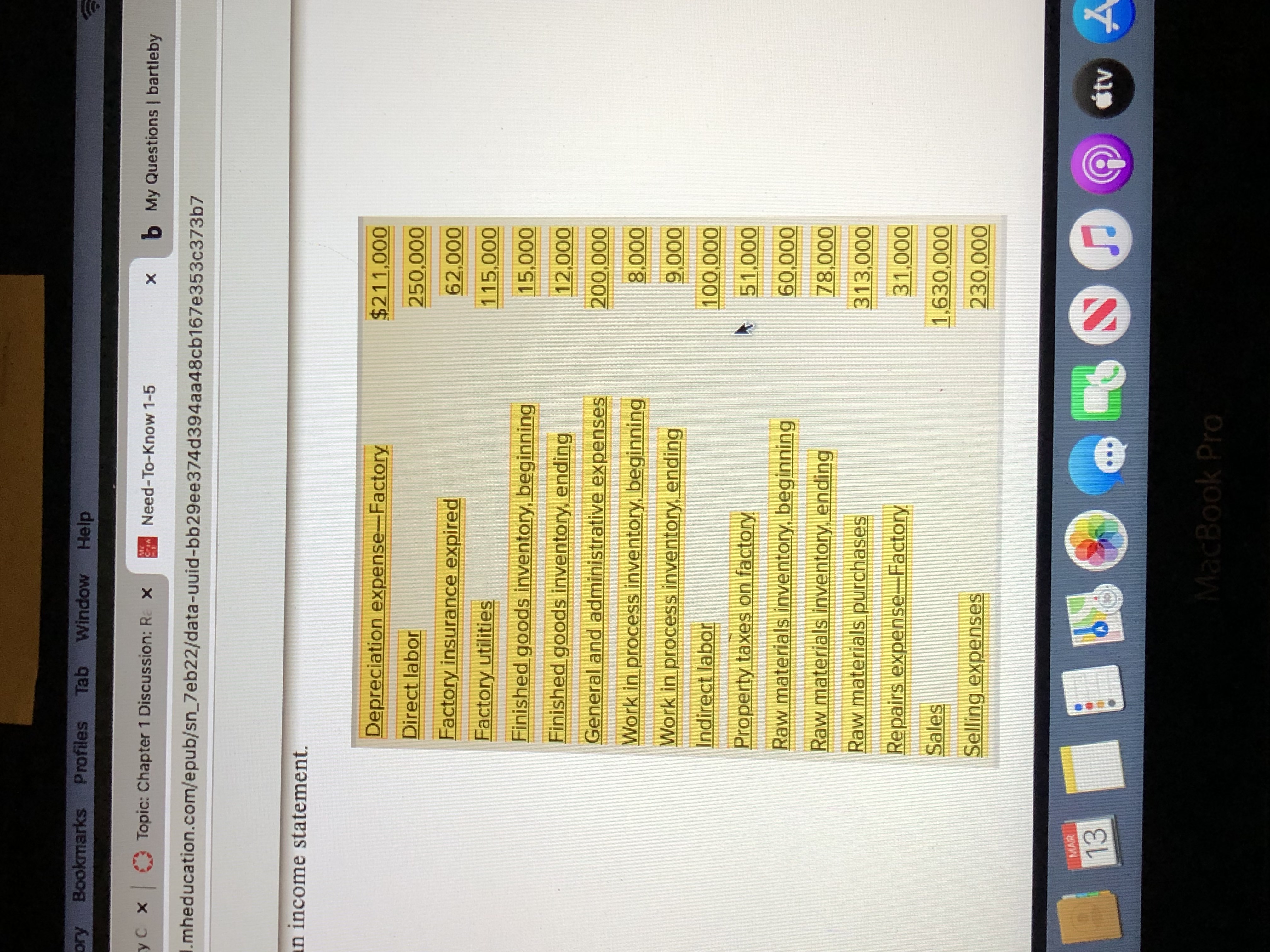
Using the data below (Sunn Corporation) , calculate and discuss the implications of Sunn's RM Inventory Turnover.
Days' Sales in Raw Materials Inventory
B. How is this ratio calculated?
What does the ratio show?
Using the data below (Sunn Corporation) calculate and discuss the implications of Sunn's Days' Sales in RM Inventory
Transcribed Image Text:Bookmarks Profiles Tab
Window Help
yC x Topic: Chapter 1 Discussion: Re x
Need-To-Know 1-5
b My Questions | bartleby
Cran
I.mheducation.com/epub/sn_7eb22/data-uuid-bb29ee374d394aa48cb167e353c373b7
an income statement.
Depreciation expense-Factory
$211,000
Direct labor
250,000
Factory insurance expired
62,000
Factory utilities
115,000
Finished goods inventory, beginning
15,000
Finished goods inventory, ending
12,000
General and administrative expenses
000'007
Work in process inventory, beginning
000
Work in process inventory, ending
Indirect labor
Property taxes on factory
000'
Raw materials inventory, beginning
000'09
Raw materials inventory, ending
000'8
Raw materials purchases
313,000
Repairs expense-Factory
000
Sales
1,630,000
Selling expenses
230,000
MAR
13
étv A
MacBook Pro
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Requirement 3. Calculate the cost of goods sold for each company Begin by calculating the cost of goods sold for Company A.arrow_forwardScrappers Supplies tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each accounting period but applies its inventory costing method at the end of each period, as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume its accounting records provided the following information at the end of the annual accounting period, December 31. Units Unit Cost $30 Transactions Beginning inventory, January 1 Transactions during the year: a. Purchase on account, March 2 b. Cash sale, April 1 ($46 each) c. Purchase on account, June 30 d. Cash sale, August 1 ($46 each) 200 300 32 (350) 250 36 (50) TIP: Although the purchases and sales are listed in chronological order, Scrappers determines the cost of goods sold after all of the purchases have occurred. Required: 1. Compute the cost of goods available for sale, cost of ending inventory, and cost of goods sold at December 31 under each of the following inventory costing methods: (Round "Cost per Unit" to 2 decimal places.) a. Last-in, first-out. LIFO…arrow_forwardWhen creating financial statements, why is it essential to create the income statement before the balance sheet? O Because sales is an essential component of the balance sheet O Because net income is required to determine the balance in retained earnings Because cost of goods sold is a component of inventory O Because S&A costs are required to determine the balance in Plant & Equipment (net). O Actually, the balance sheet must always be created first and used to create the income statement.arrow_forward
- A measures how successfully a company buys and sells merchandise at a profit. Gross Profit Margin B Return on Assets C) Return on Sales D Asset Turnover Ratioarrow_forwardWhat are expenses like sales salaries expense, advertising expense, etc. called that are incurred directly in the selling of merchandise inventory? Group of answer choices administrative expenses other expenses selling expenses cost of goods soldarrow_forwardCruz Company uses LIFO for inventory costing and reports the following financial data. It also recomputed inventory and cost of sold using FIFO for comparison purposes. LIFO inventory LIFO cost of goods sold FIFO inventory FIFO cost of goods sold Current assets (using LIFO) Current assets (using FIFO) Current liabilities 1. Compute its current ratio, inventory turnover, and days' sales in inventory for Year 2 using (a) LIFO numbers and (b) FIFO number Current ratio Inventory turnover Days' sales in inventory Answer is not complete. (a) Compute its current ratio, inventory turnover, and days' sales in inventory for Year 2 using LIFO numbers. Current ratio Inventory turnover Days' sales in inventory Current ratio Inventory turnover Days' sales in inventory $ $ $ $ Year 2 $ 290 870 360 825 350 420 170 Numerator 1 Denominator 350.0 / $ $ 870.0 111.0 X $ $ $ Numerator 1 350.0 / (a) Compute its current ratio, inventory turnover, and days' sales in inventory for Year 2 using LIFO numbers.…arrow_forward
- The management of Milque Corp. is considering the effects of inventory-costing methods on its financial statements and its income tax expense. Assuming that the cost the company pays for inventory is increasing, which method will: (a) (b) (c) Provide the highest net income? Provide the highest ending inventory? Result in the lowest income tax expense? 10arrow_forwardWhich of the following types of companies may be the least likely to carry inventory on its balance sheet? A. Retail B. Wholesale C. Manufacturing D. servicearrow_forwardAccounting for Merchandising Businesses and Inventory and Assets Define the following: Cost of goods sold Credit memo Credit terms Debit memo FIFO FOB Gross profit Invoice LIFO Net sales Periodic inventory Perpetual inventory Sales Selling expense Subsidiary ledger Trade discount Weighted averagearrow_forward
- A bank that is examining the ratio of annual costs of goods sold to average inventory, is examining which category of ratios? a.Profit measures b.Operating efficiency measures c.Liquidity measures d.Expense control measuresarrow_forwardWhich of the following items should not be included in the cost of inventory? Select one: O a. The initial purchase price of inventory O b. Freight out cost to deliver inventory to a customer c. Insurance cost paid to purchase the inventory d. Delivery cost paid to purchase the inventoryarrow_forwardSelect all that apply Determine which of the following statements are correct regarding the difference between physical flow and the cost flow of inventory Check all that apply) A business may adopt any cost flow assumption when accounting for perishable sems Perishable-items Usually have an actual physical flow of FIFO Penshable items neve an actual physical flow of LIFO Cost flow in an assumption about which goods/items are sold Physical flow refers to the actual movement of goodsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education