
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
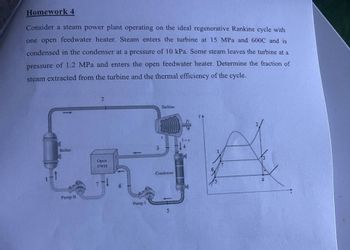
Transcribed Image Text:Homework 4
Consider a steam power plant operating on the ideal regenerative Rankine cycle with
one open feedwater heater. Steam enters the turbine at 15 MPa and 600C and is
condensed in the condenser at a pressure of 10 kPa. Some steam leaves the turbine at a
pressure of 1.2 MPa and enters the open feedwater heater. Determine the fraction of
steam extracted from the turbine and the thermal efficiency of the cycle.
2
Boiler
Open
FWH
3
Pump II
Pump I
Turbine
Condenser
4
5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- An ideal RANKINE cycle delivers 210 MW of power. Steam enters the turbine at 10 MPa and500C and is cooled in a condenser at 10 kPaa. Determine the thermal efficiency of this cycleb. Mass flow of waterc. Heat rejected in the condenserd. Work inputted to the pump (remember the volume is constant)arrow_forwarda. Calculate the thermal efficiency and turbine-exit quality for an Ideal Rankine Cycle where the steam exits boiler at 5MPa, 450C and the condenser pressure is 15 kPa. Draw the systems and the Ts diagram for the process. b. Calculate also the thermal efficiency and turbine-exit quality if the system is modified to an Ideal Reheat Rankine Cycle where the reheat takes place at 1 MPa and the steam leaves the reheater at 500C. Draw the systems and the Ts diagram for the process and discuss your findings of these two systems.arrow_forwardshow complete and step by step solution with ts diagram illustration. REGENERATIVE CYCLE AN ENGINEarrow_forward
- In a Rankine cycle, steam leaves the boiler and enters the turbine at 4 MPa and 400◦C. The condenser pressure is 10 kPa. Determine the cycle efficiencarrow_forwardSITUATIONAL PROBLEM NO II In a reheat cycle steam at 8.0MPA and 485degC enters the turbine and expands to 1.4MPA. At this point, the steam is withdrawn and passed through a reheater. It reenters the turbine at 1.3 MPa and 720degC. Expansion now occurs to the condenser pressure of 0.0006MPa. For the cycle and 1kg of steam determine: 4. Heat added 5. Work Turbine 6. Work Net Thermal Efficiency 7.arrow_forwardAn Ideal Reheat Cycle , steam enters the high pressure turbine at 750 psia and 800F and leaves at 100 psia. It is then reheated to 800F, passes through the low pressure turbine and exhausts to a condenser at 1 psia. Find the thermal efficiency of the cycle in %. From Steam Table h1 =1401.5 Btu/lb h2 =1189.96 Btu/lb h3 =1429.8 Btu/lb h4 = 1031.13 Btu/lb h5 = 69.72 Btu/lb h6 = 72.09 Btu/lb (include the diagram)arrow_forward
- The net power (NOT TURBINE POWER) of the following steam power cycle is desired to be 25MW.Steam enters the turbine at 16 MPa, 450C, condenser at 10kPa pressure saturated liquid-steamIt enters as a mixture. Compressed liquid enters the pump at 9kPa at 35C and at 17MPacomes out. The inlet pressure to the boiler is 16.8MPa and 33C. The output from the boiler is 16.2MPa and 575C.The isentropic efficiency of the turbine is 90%, and that of the pump is 83%. Find the mass flow rate that will provide the required net power.arrow_forwardIn an ideal reheat-regenerative cycle, steam enters the engine at 8 MPa and 400°C. Afterexpansion to 280°C the steam is withdrawn and reheated to 340°C. Extractions forfeedwater heating occur at 1.6 MPa and 0.70 MPa and the condenser pressure is 0.005 MPa.For the ideal cycle find Wnet and e. For the ideal engine, find W and e.arrow_forward3.) A steam power plant uses the ideal Reheat-Regenerative Rankine cycle where the steam enters the high-pressure turbine at 4 MPa and 300C. It partially expands to 600 kPa where some steam is extracted for feedwater heating while the rest is reheated to the same temperature. After expanding again, it enters the condenser at 10 kPa. Sketch the schematic diagram and the TS diagram with labeled points, and solve for mass taken for feedwater heating, Qa, Qr, Wt, Wp, Wnet, thermal efficiency, and Steam rate. Neglect the condensate pump work. kJ kj kJ kJ kJ kg 1715.88- 20.01%, 2667.84- 955.97 3.74 951.96 35.68%, 3.78. " J kg kg kg kg kWh kg "arrow_forward
- 2.) A steam power plant uses the ideal Regenerative Rankine cycle with single open feedwater heater where the steam enters the high-pressure turbine at 4 MPa and 300C. It partially expands to 600 kPa then some steam is extracted at this point. The remaining steam expands and enters the condenser at 10 kPa. Sketch the schematic diagram and the TS diagram with labeled points, and solve for mass taken for feedwater heating, Qa, Qr, Wt, Wp, Wnet, thermal efficiency, and Steam rate. Neglect the condensate pump work. kJ kg 20.01%, 2286.801457.51,832.54 3.34,829.2936.26%, 4.34. ) kg kWharrow_forwardConsider a steam power plant operating on the ideal regenerative Rankine Cycle Steam enters the turbine at 15 MPa and 600°C and is condensed, in the Condenser at a pressure of lo kPa. Some steam leaves the turbine at a pressure of 1.2 MPa and திை Determine the fraction of steam extracted from the turbine and the thermal efficiency of the cycle? Assume you = ?arrow_forwardIn a reheat cycle steam at 15 Mpa, 540°C enters the engine and expands to 1.95 Mpa. At this point the steam is withdrawn and passed through a reheater. It reenters the engine at 540°C. Expansion now occurs to the condenser pressure of 0.0035 Mpa. (a) For the ideal cycle, find ee (b) A 60,000 kW turbine operates between the same state points except that the steam enters the reheater at 1.95Mpa and 260°C, departs at 1.8 Mpa and 540°C. The steam flow is 147,000 kg/hr; generator efficiency is 96%. For actual engine, ek, mk, and nk, (c) Determine the approximate enthalpy of the exhaust steam if the heat lost through the turbine casing is 2% of the combined work.4. Steam at 200 bar, 760°C enters the throttarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY