
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Here are the dimensions, sorry for not having them earlier b = 0.4 m, d =0.5 m , t =0.1 m.
3) The force, FT = 1 kN, and moment, MT = 0.5 kN-m, at the tip are caused by a wing tip vortex
and a winglet, not shown. L = 12 m and the spar has an elastic modulus of E = 70 GPa and a
Poisson’s ratio of
n = 0.33. The mass of the wing is 4000 kg, and the weight of the engine is 107
kN. Use 9.8 m/s 2 for the acceleration due to gravity.
a) The aerodynamic center for problem 3 is 0.1 m from the y axis (neutral axis). Calculate the
twist angle caused by the lift force.
b) For problem 3, calculate the reactions at the fixed end.
and a winglet, not shown. L = 12 m and the spar has an elastic modulus of E = 70 GPa and a
Poisson’s ratio of
n = 0.33. The mass of the wing is 4000 kg, and the weight of the engine is 107
kN. Use 9.8 m/s 2 for the acceleration due to gravity.
a) The aerodynamic center for problem 3 is 0.1 m from the y axis (neutral axis). Calculate the
twist angle caused by the lift force.
b) For problem 3, calculate the reactions at the fixed end.
c) Assume the engine in problem 3, applies a torque around the x – axis of the spar of 100 kN-m,
calculate the angular delfection of the wing at x = 3 m due to the engine.
calculate the angular delfection of the wing at x = 3 m due to the engine.
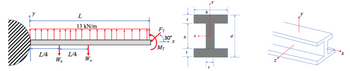
Transcribed Image Text:L/4
We
L
13 kN/m
L/4
Ww
FT
30°
MT
t
H
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Determine the twist angle, the reactions at the fixed end, and angular deflection of the wing.
VIEW Step 2: Calculate the twist angle.
VIEW Step 3: Find the reactions at the fixed end.
VIEW Step 4: Find the shear modulus, the polar moment of inertia, and the angular deflection.
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 18 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ]: A horizontal beam with a length of 4.5 m is subjected to the shown loading. The forces are vertical and the couple moment is applied at point D. The figure is not to scale. 3 kN/ m 1 kN/ m 3 kNm A В C D E 1 т 1.5 m 0.5m 1.5m 0.6 KN 1.35KN (a) Motivate with substantiating explanations and clear and applicable calculations why the beam is in equilibrium. (b) Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams for the beam. Calculate all local maxima and minima, zeros and points where the diagrams change shape, and show these values and points on the diagrams.arrow_forwardA bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position to the vertical position, determine the following. (4) the work done by the reaction force of the pin.____________ (J)arrow_forwardA bar is attached to the spring at the point C. The left end of the bar is pin supported and can rotates about the pin at Point A. The mass of the bar is m=20kg. The total length of the bar is LAB=3m and LAC=2m. Point A is 0.6 m below the ceiling. A clockwise constant couple moment M= 30Nm is applied on the bar so that the bar rotates from the horizontal position with θ=0° to the vertical position with θ=90°. The spring always maintains at the vertical position. The spring’s stiffness coefficient is k=30N/m and its unstretched length is 0.5 m. The acceleration due to gravity g=9.81 m/s2. During the process that the bar rotates from the horizontal position to the vertical position, determine the following. (2) ) the work done by the couple moment. __________(J) (two decimal places)arrow_forward
- A ladder with a length of L= 8 m and a mass of M=50 kg rests on a rough ground (providing friction) and on a roller without friction at the top of the wall at h= 5 m above the ground (see figure). The angle θin the picture is 60°, and the ladder is just about to slip. (A) Draw a force diagram whichshows all forces acting on the ladder.Take the force that the roller exerts to be perpendicular to the ladder. (B) Use a net torque equation to calculate the force that the roller exerts on the ladder. (C) Use net force equations to calculate the normal from the ground, the force of static friction, and the coefficient of static friction.arrow_forwardA lifeboat hangs from two ship’s davits, asshown in the figure. A pin of diameter d = 0.80 in.passes through each davit and supports two pulleys,one on each side of the davit.Cables attached to the lifeboat pass over the pulleysand wind around winches that raise and lowerthe lifeboat. The lower parts of the cables are verticaland the upper parts make an angle α =15° with thehorizontal. The allowable tensile force in each cableis 1800 lb, and the allowable shear stress in the pinsis 4000 psi. If the lifeboat weighs 1500 lb, what is the maximumweight that can be carried in the lifeboat?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY