
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
1. The
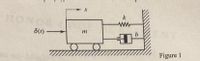
Transcribed Image Text:**Figure 1: Mechanical System Diagram**
The diagram illustrates a classic mechanical system, often referred to in physics and engineering as a mass-spring-damper system.
- **Components:**
- **Mass (m):** Represented by a block, which is free to move horizontally along a surface with wheels.
- **Spring (k):** Connected to the mass and a fixed wall, with a characteristic stiffness constant `k`.
- **Damper (b):** Also connected to the mass and fixed wall, providing a damping force proportional to velocity, with damping coefficient `b`.
- **Input Force (δ(t)):** An external force applied to the mass, indicated by an arrow on the left.
- **Additional Elements:**
- **Position (x):** The horizontal position of the mass, measured from the wall.
This system is frequently used to model and analyze dynamic behavior, showing how the mass responds to forces considering both restoring forces from the spring and resistance due to the damper.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 20 kg weight is attached to a spring with constant k = 320 kg/m and subjected to an external force F(t) = 1200 cos(2t). The weight begins at rest in its equilibrium position. Find its displacement for t> 0, with y(t) measured positive upwards. y(t) =arrow_forwardA foot pedal for a musical instrument is modeled by the sketch in Figure P2.93. With k = 2000 N/m, c = 25 kg/s, m =25 kg, and F(t) = 50 cos 2πt N, numerically simulate the response of the system assuming the system starts from rest. Use the small-angle approximation. F(1) 0.05 m 0.05 m Figure P2.93 0.05 m marrow_forwardFor each of the systems shown in Figure P4.52, the input is the force f andthe outputs are the displacements x1 and x2 of the masses. The equilibriumpositions with f = 0 correspond to x1 = x2 = 0. Neglect any friction betweenthe masses and the surface. Derive the equations of motion of the systems.arrow_forward
- A 1.5 kg mass is attached to a 1.6 m long rigid rod of negligible mass that is anchored to the ceiling. The mass is pulled back to an initial angle of 45°and released with an initial speed of 3.0 m/s. Note: The mass is initially moving down not up! 2. L m (a) [Hint: The height of the mass above its lowest point is L(1 – cos 0).] How fast is the mass moving at the bottoms of its swing, when 0 = 0°?arrow_forwardProblem 2. F Consider the Mass-Spring-Damper system shown in Fig. 2 (left), where m is the mass of the cart, k is the spring constant, and b is the damper constant. The input of the system is u(t), which represents the external force acting on the cart. The displacement of the cart is denoted as x(t). = x(t). 1) (10 points) Consider the velocity (t) as the output of the system, i.e., y(t) Assuming the zero initial conditions, write the transfer function G(s) from the input u(t) to the output y(t). 2) (15 points) If a proportional controller is used to control the system, then the block diagram of the closed-loop system is given by Fig. 2 (right). Assume that m = 1 kg, b = 4 N.s/m, and k = 3N/m. Sketch the Bode plot of G(s) for K = 1. 3) (15 points) Sketch the Nyquist plot based on the Bode plot. Determine the range of K for which the system is stable. Consider both positive and negative values of K. b x(t) J u(t) m R K G(s) Y Figure 2: Mass-Spring-Damper system in Problem 2.arrow_forward3: A 24 lb weight stretches a spring 6 feet. The weight hangs vertically from the spring and a damping force numerically equal to 2√√3 times the instantaneous velocity acts on the system. The weight is released from 3 feet above the equilibrium position with a downward velocity of 14 ft/s. (a) Determine the time (in seconds) at which the mass passes through the equilibrium position. (b) Find the time (in seconds) at which the mass attains its extreme displacement from the equilibrium position.arrow_forward
- Fig. P4.6 4.22. Derive the differential equation of motion of the simple vehicle model shown in Fig. P4.7. The vehicle is assumed to travel over the rough surface with a constant vehicle speed v. Obtain also the steady state response of the vehicle. For this system, let m = 10kg, k = 4 x 103 N/m, c = 150N · s/m, i = 2 m, and the amplitude Yo = 0.1 m. Determine the maximum vertical displacement of the mass and the corresponding vehicle speed. Determine also the maximum dynamic force transmitted to the mass at the resonant speed. m 2πη y = Y, sin y Fig. P4.7arrow_forwardFigure 4 shows a trolley of mass 6.12 kg passing through point A with a velocity of 6 m/s. It slides down a rail to point C. From A to C, 250 J of energy is lost due to friction. What is the equation used to find the velocity of the trolley at point C ?arrow_forwardIf the rope on the wall suddenly snaps, what will be the acceleration vector and velocity vectors of these masses at 1=1s after the break? N.B.: the strings are assumed to be massless, flexible and inelastic.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY