
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Propose a mechanism to account for the product of the following reactions. Please show the structures of the intermediates and using curved arrows to indicate electron flow in each step. Rearrangements occur.
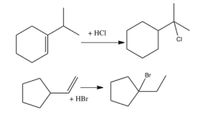
Transcribed Image Text:### Alkene Halogenation Reactions
This image illustrates two alkene halogenation reactions, showing how alkenes react with hydrochloric acid (HCl) and hydrobromic acid (HBr) to form haloalkanes.
#### Reaction 1: Alkene with HCl
- **Reactants**: A cyclic alkene with a methyl group attached reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl).
- **Product**: The chlorine atom from HCl adds to the tertiary carbon (carbon with the most substituents) in the alkene, forming a chlorine-substituted cyclohexane derivative.
#### Reaction 2: Alkene with HBr
- **Reactants**: A cyclopentene group with a propyl side chain reacts with hydrobromic acid (HBr).
- **Product**: The bromine atom from HBr adds to the secondary carbon of the alkene, generating a bromine-substituted cyclopentane derivative.
These reactions demonstrate the Markovnikov's Rule, where the hydrogen atom from the acid more often bonds to the carbon atom with the greater number of hydrogen atoms 'originally', while the halide (Cl or Br) bonds to the more substituted carbon. This is due to carbocation stability, leading to the regioselectivity observed.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Synthesize the following from benzene.arrow_forwardWhich alkene product would you expect to be the major product under kinetic conditions? Under thermodynamic conditions? The given pictures are the reactions in which we have to determine which alkene product we expect would be the major product under kinetic and thermodynamic conditions.arrow_forwardRank the following alkenes in order of increasing rate of hydrogenation. 11 OI<|||< IV < II <|| < |||arrow_forward
- The following reaction can produce two products. The first of thes contains ONE double bond. What is the structure of this material?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Follow the arrows and draw the intermediate and product in this reaction. Include all lone pairs. Ignore stereochemistry. Ignore inorganic byproducts. :O: H3C-MgBr Draw Intermediate H3O+ Draw Product Draw Tetrahedral Intermediate :0: CH3 H3C-MgBr Qarrow_forward3) Draw the structures of the major organic product(s) for the following reactions. HI in CH₂Cl₂ 3 excess Cl₂ in H₂O H₂SO4 in H₂O (Two products) Br-Cl in THF 1) BH3 2) alkaline H₂O₂ OSO4 + HOOHarrow_forward
- Provide stepwise synthesis show all reagents need and intermediates formed along the wayarrow_forwardPlease explain step byarrow_forwardWhen 2-iodo-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane is heated in acetic acid, CH3COOH, a mixture of substitution and elimination products is obtained. Provide structures for all possible products, writing [not drawing] the name of the mechanism by which each one is formed.arrow_forward
- 6) 25pts. Draw the structure of the major alkene product (or products) formed by treatment of each of the following haloalkanes with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Assume the mechanism is E2 elimination. t-BuO K t-BUOH Br CH3 Eto Na F ETOH CH2CH3 CI H- Eto Na -CH2CH3 ELOH H- ČH3 Br Eto Na ELOH CH3 CI, H Eto Na CH2CH3 H3C H D ELOHarrow_forward• Same reagents as acid-catalyzed dehydration, except starting with a instead of an alcohol. • Same as the general mechanism hydrohalogenation, except with . Remember that EVERY acid-cat. mechanism begins with General Reaction: EXAMPLE: Provide H₂O H₂SO4 EXAMPLE: Provide the mechanism for the following addition reaction. H₂O H₂SO4 OH WH H₂O H₂SO4 as the nucleophile and ends with do PRACTICE: Provide the mechanism and predict the product of the following reaction. MAXOarrow_forwardA common alkene starting material is shown below. Predict the major product for each reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY