
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:t
ces
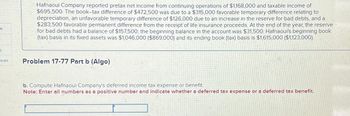
Hafnaoui Company reported pretax net income from continuing operations of $1,168,000 and taxable income of
$695,500. The book-tax difference of $472,500 was due to a $315,000 favorable temporary difference relating to
depreciation, an unfavorable temporary difference of $126,000 due to an increase in the reserve for bad debts, and a
$283,500 favorable permanent difference from the receipt of life insurance proceeds. At the end of the year, the reserve
for bad debts had a balance of $157,500; the beginning balance in the account was $31,500. Hafnaoui's beginning book
(tax) basis in its fixed assets was $1,046,000 ($869,000) and its ending book (tax) basis is $1,615,000 ($1,123,000).
Problem 17-77 Part b (Algo)
b. Compute Hafnaoui Company's deferred income tax expense or benefit.
Note: Enter all numbers as a positive number and indicate whether a deferred tax expense or a deferred tax benefit.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Livia Company’s pretax income was $72,000. To compute taxable income, the following information is provided: Excess of estimated bad debts over write-offs $26,000 Penalty for late filing of income taxes 21,000 Excess of tax depreciation over accounting depreciation 36,000 Tax rate 20% What is the current portion of income tax? $12,400 $6200 $16,600 $22,600arrow_forwardam.115.arrow_forwardSol Limited. reported earnings of $510,000 in 20X8. The company has $91,000 of depreciation expense this year, and claimed CCA of $142,000. The tax rate was 25%. At the end of 20X7, there was a $122,000 loss carryforward that was not recorded because use was considered less than probable. The company also reported a deferred tax liability of $71,000 caused by capital assets with a net book value of $1,310,000 and UCC of $1,010,000. The tax rate had been 20% in 20X7. Required:What is the amount of income tax expense in 20X8? Prepare the income tax entry or entries. - Record the entry income tax expense. - Record the entry loss carryforward.arrow_forward
- Munabhaiarrow_forwardFor its first year of operations, Tringali Corporation's reconciliation of pretax accounting income to taxable income is as follows: Pretax accounting income $ 300,000 Permanent difference (15,000 ) 285,000 Temporary difference-depreciation (20,000 ) Taxable income $ 265,000 Tringali's tax rate is 25%. Assume that no estimated taxes have been paid. What should Tringali report as its deferred income tax liability as of the end of its first year of operations?arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Hafnaoui Company reported pretax net income from continuing operations of $903,500 and taxable income of $712,500. The book-tax difference of $191,000 was due to a $242,000 favorable temporary difference relating to depreciation, an unfavorable temporary difference of $117,000 due to an increase in the reserve for bad debts, and a $66,000 favorable permanent difference from the receipt of life insurance proceeds. b. Compute Hafnaoui Company's deferred income tax expense or (benefit). Note: Enter all numbers as a positive number and indicate whether a deferred tax expense or a deferred tax benefit. X Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Deferred income tax expense $ 712,500arrow_forward
- Book income of $1,900,000 Included in the computation were favorable temporary differences of $230,000, unfavorable temporary differences of $226,000 and favorable permanent differences of $168,000. What is the company's deferred income tax expense or benefit?arrow_forwardHafnaoui Company reported pretax net income from continuing operations of $912,000 and taxable income of $587,500. The book–tax difference of $352,500 was due to a $235,000 favorable temporary difference relating to depreciation, an unfavorable temporary difference of $94,000 due to an increase in the reserve for bad debts, and a $211,500 favorable permanent difference from the receipt of life insurance proceeds. At the end of the year, the reserve for bad debts had a balance of $117,500; the beginning balance in the account was $23,500. Hafnaoui's beginning book (tax) basis in its fixed assets was $1,014,000 ($821,000) and its ending book (tax) basis is $1,535,000 ($1,107,000). a. Compute Hafnaoui Company's current income tax expense. b. Compute Hafnaoui Company's deferred income tax expense or benefit. c. Compute Hafnaoui Company's effective tax rate. d. Provide a reconciliation of Hafnaoui Company's effective tax rate with its hypothetical tax rate of 21 percent.arrow_forwardGrand Corporation reported pretax book income of $612,000. Tax depreciation exceeded book depreciation by $408,000. In addition, the company received $306,000 of tax-exempt municipal bond interest. The company's prior-year tax return showed taxable income of $51,000. Compute the company's current income tax expense or benefit. (Leave no answer blank. Enter N/A or zero.) 이 Current income tax Deferred income tax N/A expense $arrow_forward
- During the current year, Dale Corporation sold a segment of its business at a gain of $315,000.Until it was sold, the segment had a current period operating loss of $112,500. The company had$1,275,000 from continuing operations for the current year.Prepare the lower part of the income statement, beginning with the $1,275,000 income fromcontinuing operations. Follow tax allocation procedures, assuming that all changes in incomeare subject to a 20% income tax rate. Disregard earnings per share disclosures. (Round all calculations to nearest dollar amount.)arrow_forwardAt the end of the year, a deductible temporary difference of $40 million has been recognised due to the difference between the carrying amount of a liability account for estimated expenses and its tax base. Taxable income is $50 million. No temporary differences existed at the beginning of the year, and the tax rate is 35%. Required: a. Prepare the journal entry(s) to record income taxes during the period. b.How much will income tax expense be shown in the income statement? c.arrow_forward77. Hafnaoui Company reported pretax net income from continuing operations of $800,000 and taxable income of $500,000. The book-tax difference of $300,000 was due to a $200,000 favorable temporary difference relating to depreciation, an unfavorable temporary difference of $80,000 due to an increase in the reserve for bad debts, and a $180,000 favorable permanent difference from the receipt of life insurance proceeds. At the end of the year, the reserve for bad debts had a balance of $100,000; the beginning balance in the account was $20,000. Hafnaoui's beginning book (tax) basis in its fixed assets was $1,000,000 ($800,000) and its ending book (tax) basis is $1,500,000 ($1,100,000). a) Compute Hafnaoui Company's current income tax expense. b) Compute Hafnaoui Company's deferred income tax expense or (benefit). c) Compute Hafnaoui Company's effective tax rate. d) Provide a reconciliation of Hafnaoui Company's effective tax rate with its hypothetical tax rate of 21 percent.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education