
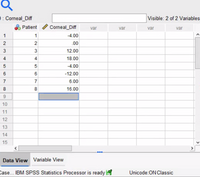
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the United States, N. Ehlers measured the difference in corneal thickness (in microns) between the two eyes of eight patients. Each patient had one eye that had glaucoma and one eye that was normal. The difference was measured as the corneal thickness of normal eye – corneal thickness of eye with Glaucoma. Corneal thickness is important because it can mask an accurate reading of eye pressure. Use ? = .05.
Hypothesis:
H0: μd=0Ha: μd≠0
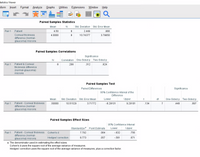
Using output
Test statistics :
t=0.134P value=0.897
Degrees of freedom (df):
df=7
Level of significance:
α=0.05
Decision:
P value > 0.05 thus we fails to reject null hypothesis.
Question
a)Write a report summarizing your findings. When writing the
report consider that medical staff estimate that a difference of 4.5 microns or more could impact on their ability to interpret eye pressure correctly.
b) Define for the hypothesis stated in part b) what a type 1 error and type 2 error would
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- A vending machine says there is at least 12 ounces in a coffee cup it dispense.you want to prove the machine is defective. Identify the parametersarrow_forwardthe critical value of chi-square is what when degrees of freedom equal 4 and a equals .05.?arrow_forwardThe accompanying data on y=mortar dry density (lb/ft^3) versus x=mortar air content (%) for a sample of mortar specimens. Number of mortar specimensn =17, the error sum of square is SSE = 43.44 the sample mean of mortar air content is X = 47.36 and Find the value of SE B,). a) SE B=17.592 b) SE B=16.286 c) SE B 11.248 d) SE B=10.248arrow_forward
- An article published by the American Meteorological Society, gives a rating system used to classify Nor'easter storms that frequently hit New England which often cause havoc near the ocean. A severe storm has an average peak wave height of μ=16.4μ feet for waves near the shore. Suppose that a Nor'easter is in progress at the severe storm class rating. Peak wave heights are usually measured from land off piers. Suppose that a reading of 32 waves showed an average wave height of x¯=14.3 feet. Previous reports of severe storms indicate that σ=3.5 feet. Does this information suggest that the storm is decreasing below the severe rating? Use α=0.01 to test the claim.What is the level of significance? State the null and alternate hypotheses. H0:H0:? p σ μ χ Select an answer < = ≠ > H1:H1:? μ p χ σ Select an answer ≠ > = <arrow_forwardWhich scale of measurement is used in terms used for classifying participants into groups the increasing temperature of hot peppers a ruler in centimeters height.arrow_forwardI need help solving this problem in R. The size of the left upper chamber of the heart is one measure of cardiovascular health. When the upper left chamber is enlarged, the risk of heart problems is increased. The paper ("Left atrial size increases with body mass index in children")[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19147240] (International Journal of Cardiology [2009]) described a study in which the left atrial size was measured for a large number of children age 5 to 15 years. Based on this data, the authors concluded that for healthy children, the left atrial diameter was approximately normally distributed with a mean of 26.4 mm and a standard deviation of 4.2 mm. i) Use `plotDist` to draw the probability density function of the left atrial diameter. ii) Generate 50 sample measurements of the left atrial diameters and plot the measurements using a histogram. iii) Approximately what proportion of healthy children have left atrial diameters less than 23.5 mm?arrow_forward
- A researcher is looking at a new marketing campaign for a product. After 200 people watched the marketing campaign about 60 percent liked the product. Prior to the marketing campaign the product was liked by about 50 percent of people. What are the chi-square test degrees of freedom for this research description?arrow_forwardTo compare the effectiveness of competing fertilizers on increasing radish size, researchers randomly divided 20 radish seeds of the same type into two groups of 10 and planted them. To one of the groups, they applied Fertilizer A, and to the other, they applied Fertilizer B. Then the researchers measured the radii of the radishes grown from the seeds in the two groups. The mean radius of the Fertilizer A group was 0.52 inches smaller than the mean radius of the Fertilizer B group. The researchers wanted to determine if this difference was due to the type of fertilizer or simply due to more seeds that produced smaller radishes being randomly assigned to the Fertilizer A group. To test if a difference of the means (A - B) of -0.52 inches or less could be due to chance, the researchers used a computer simulation to shuffle and randomly reassign the radishes to the two fertilizer groups. The difference between the two group means was then calculated and plotted on a dot plot. They…arrow_forwardHow would you figure this out!arrow_forward
- If the coefficient of determination between two independent variables is 0.33, what is the VIF? VIF= (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardSuppose the lengths of human pregnancies are normally distributed with u = 266 days and o = 16 days.arrow_forwardOverproduction of uric acid in the body can be an indication of cell breakdown. This may be an advance indication of illness such as gout, leukemia, or lymphoma.f Over a period of months, an adult male patient has taken seven blood tests for uric acid. The concentration was x = 5.35 mg/dl. The distribution of uric acid in healthy adult males can be assumed to be normal, with o = 1.77 mg/dl. (a) Find a 95% confidence interval for the population mean concentration of uric acid in this patient's blood. What is the margin of error? (Round your answers to two decimal places.) lower limit upper limit margin of error (b) What conditions are necessary for your calculations? (Select all that apply.) O o is unknown O normal distribution of uric acid O n is large Oo is known O uniform distribution of uric acid (c) Interpret your results in the context of this problem. O The probability that this interval contains the true average uric acid level for this patient is 0.05. O The probability that…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





