
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
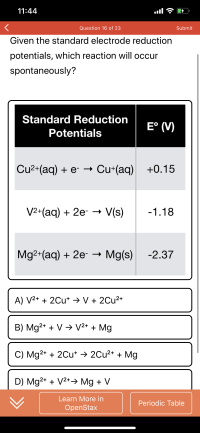
Transcribed Image Text:Given the standard electrode reduction
potentials, which reaction will occur
spontaneously?
Standard Reduction
E° (V)
Potentials
Cu2+(aq) + e- → Cu+(aq) +0.15
V2+(aq) + 2e- V(s)
-1.18
Mg2+(aq) + 2e- → Mg(s)
-2.37
A) V2+ + 2Cu* → V + 2Cu2+
B) Mg2+ + V > V²* + Mg
C) Mg2+ + 2Cu* → 2Cu2* + Mg
D) Mg2+ + V2*→ Mg + V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two half-reactions are shown with their standard cell potentials. If a galvanic cell is constructed using them, which electrode would be the anode, and what would the cell potential be? Cd2* (aq) + 2e – Cd(s); E=-0.40 V Cr3+ (aq) + 3e → Cr(s); E=-0.74 V Oa. Cadmium, -0.34 V Ob. None of the other options Oc. Cadmium, -1.14 V Od. Chromium, -1.14 V Oe. Chromium, 0.34 Varrow_forwardGiven the standard electrode reduction potentials, which reaction will occur spontaneously?arrow_forwardUsing standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 6CI (aq)+2Cr0 (aq)+8H,0 (1) → 3Cl, (g)+2Cr(OH), (s) + 10OH (aq)arrow_forward
- Calculate the standard cell potential (E°cell) of a galvanic cell made of lead and cadmium. Then determine the non-standard cell potential (Ecell) if the molarity of the cadmium solution was 0.20 M, and the molarity of the lead solution was 0.10 M. The temperature of the cell is 300 K. Cd2+(aq) + 2e– → Cd(s) E° = –0.403 V Pb2+(aq) + 2e– → Pb(s) E° = –0.126 V E°cell = ______________ Ecell = ______________arrow_forwardThe cell potential of the following cell at 25°C is 0.475 V: Zn|Zn?t (1.0 M) || H* (test solution) H2 (1.0 atm)|Pt What is the pH of the test solution? The standard reduction potential for Zn+ is –0.76 V. (Enter your answer to two significant figures.) pH =arrow_forwardCalculate the equilibrium constant, K, for the reaction shown at 25 °C. Fe+(aq)+B(s) + 6 H, O(1) → Fe(s) + H,BO,(s) + 3 H,O*(aq) The balanced reduction half-reactions for the equation and their respective standard reduction potential values (E") are Fe3+ (aq) + 3 e- → Fe(s) H,BO, (s) + 3 H,0*(aq) + 3 e- – B(s) + 6 H, O(1) E' = -0.04 V E' = -0.8698 V K =arrow_forward
- Calculate Eu for the following cell: Pt(s) | H₂(g) | H *(aq) || Pb2+ (aq) | PbSO4(s) | Pb(s) given the following standard reduction potentials. 2 H(aq) + 2e →→ H₂(g) PbSO4(s) + 2e →→ Pb(s) + SO42 (aq) O a. -0.712 V O b. +0.356 V O c. -0.356 V O d. +0.712 V O e. -0.178 V E° = 0.000 V E = -0.356 Varrow_forwardConsider the electrolysis reactions cathode anode whose standard reduction potentials can be found in this table. Calculate the voltage needed to drive the net reaction if the current is negligible. Ecell = Cu²+ (aq, 0.177 M) +2e=Cu(s) H₂O(1) ⇒ 10₂(g, 1 bar) + 2 H+ (aq, 0.195 M) + 2 e¯ The cell has a resistance of 66.0 and a current of 7.17 mA when the cathode overpotential is 0.231 V and the anode overpotential is 0.050 V. Calculate the voltage needed to overcome these effects and drive the net reaction. Ecell = V Varrow_forwardCalculate the cell potential for the reaction as written at 25.00 °C, given that [Mg? +] = 0.788 M and [Fe² +] = 0.0200 M. Use the standard reduction potentials in this table. Mg(s) + Fe2+(aq) = Mg2+(aq) + Fe(s) E = Varrow_forward
- Consider the following reduction potentials. Ag*(aq) + e → Ag(s) E° = + 0.80 V Sn2*(aq) + 2 e -→Sn(s) E° = - 0.14 V Mg2 (aq) + 2 e - → Mg(s) E° = - 2.37 V a.) Calculate the cell potential at standard conditions (E°cell) for a voltaic cell of Mg2+/Mg and Ag*/Ag, in Volts. E° cell = v b.) Calculate Ecel in V at 298 K if [Mg2*] = 0.100 M and [Ag*] = 0.100 M. %3D Ecell = Varrow_forwardThe cell potential for a voltaic cell composed of zinc and copper is 1.0 V under standard conditions. Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) => Cu(S) + Zn2+(aq) What is the cell potential when one of the following deviations from standard conditions are made? A) [Zn2+] = 0.25 M; [Cu2+] = 0.25 M B) [Zn2+] = 0.25 M; [Cu2+] = 0.50 M C) [Zn2+] = 0.75 M; [Cu2+] = 0.75 M D) [Zn2+] = 0.75 M; [Cu2+] = 0.25 M E) [Zn2+] = 0.25 M; [Cu2+] = 0.75 Marrow_forwardConsider the following standard reduction potentials: Zn2*(aq) + 2 e → Zn(s) E° = -0.76 V Mg2*(aq) + 2 e → Mg(s) E° = -2.37 V Ag*(aq) + e → Ag(s) E° = +0.80 V Which is the strongest oxidizing agent? Mg2*(aq) Zn2*(aq) Ag*(aq) 5:08 PM 90°F Partly sunny P Type here to search 8/6/2021arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY