
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Given a 6.5 x 2.5 x 1.5 cm solid block of wood and a bandsaw with miter sled (see image below), sketch the operations required to create the object shown right. Minimize glue joints on surfaces visible in this view. The miter sled can be rotated on a vertical axis to create angled cuts. Assume a 0.25 cm blade thickness.
Use pictorial sketches to describe the process. Then prepare a multiview of both the initial block and the final result showing all the cut lines and labeling each piece. Identify unused off-cuts.
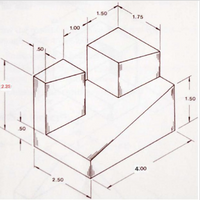
Transcribed Image Text:1.50
1.75
1.00
.50
2.25
1.50
50
4:00
2.50
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Explain the importance of standards and the principles of free hand in sketching in engineering drawing. 2. Explain the uses of the following drawing instruments: • French curve • Compass • Protractorarrow_forwardThe Sleeve Bearing Problem A machinist had pressed a new prelubricated, porous sintered bronze bearing in an electric motor. The rotor shaft would not fit into the searing. Measuring the bore, the machinist discovered that it was a few thousandths of an inch undersized. He removed it, put it in a lathe, and bored out the excess material. The bearing was pressed in again, the motor assembled, and put into use. A few days later the motor was back in the shop with the bearing burned out. What had happened to this prelubricated, sintered bearing to cause the failure.arrow_forwardI need a solution within 15 minutesarrow_forward
- (a) A turning operation is performed on a 660 mm cylindrical part of a certain alloy. The work material has a length of 140 mm as shown in Figure Q3-1. The finished (produced) part is shown in Figure Q3-2 which has an overall length of 100 mm. The remaining part of the raw material length is kept as a gripped part on the turning machine chuck. The cutting data is shown in Table Q3(a). Apply engineering calculations on the given metal cutting operations, Table Q3(a) Depth of cut Feed 2.5mm 0.15mm/rev Cutting Speed Rake angle The chip thickness after cut Shear strength 40m/min 50 0.17mm 280 MPa (i) Shear force. (ii) Coefficient of friction. e (iii) Cutting force. (iv) Time required to cut the part (v) Rate of material removal. 50mm $60mm -20mm 60 mm 140 mm 40 mm Figure Q3-1 Figure Q3-2 4 1 + DRG Ans Realm ? Ran x10*arrow_forwardA cup of internal diameter 80 mm and height 45 mm is to be drawn from a sheet metal 2 mm thick. Four blank sizes are available for the operation. You want to ensure the blank is large enough to make the required cup height while minimizing the material waste. Calculate the starting blank diameter for this operation?arrow_forwardASSIGNMENT-2 Sheet metal tapered wall tray Objective: To perform cutting and forming processes on a sheet metal to produce a tapered wall tray with dimensions of 50 X 40, 70cm Length, and 25cm hight at the end side with handle holes diameter 20mm, and spot welding at both sides. 25 50 handle hole diameter 70 20mm Instructions • List all the tools used in practice regarding Marking-Out Tools (name, sketches, objective and application). • List all the tools used in practice regarding Sheet Metal Work (name, sketches, objective and application). • Show practically how to transfer a specific drawing, measurements, and shape onto a sheet of metal. Write down the steps to produce a tapered wall tray with dimensions of 50 x 40, 70cm Length, and 25cm hight at the end side, as it mentioned in the figure above, using a sheet metal thickness of 1mm. • Mention the tool used for each step. • Show the practical diagrams, sketches for each step. • Anyone copying will be given zero. Notice That: A…arrow_forward
- A shaft of 0.5 m in length and 100cm in diameter is to be machined. What operation will you utilize on lathe to bring the specimen of size 50 cm diameter and 0.25 m length?arrow_forwardCalculate the force needed to cut two metal parts of 10 mm dia and 15 5 points mm dia . if the ultimate shear stress is 100 Mpa or N/mm2, what is the force required? *arrow_forwardBeam loaded as shown in Fig. below. Determine the Following: Reaction support at point B. a. 56KN (Downward Direction) b. 56KN (Upward Direction) c. 35KN (Downward Direction) d. 35KN (Upward Direction) Reaction support at point D. a. 26 KN (Downward Direction) b. 26 KN (Upward Direction) c. 24KN (Downward Direction) d. 24KN (Upward Direction) Shear force equation of section AB. a. -30KN b. 30KN c. -32KN d. 32KN Shear force equation of section CD. a. -24KN b. 24KN c. -28KN d. 28KN Bending moment equation of section BC. a. 26KN(x)+56KN.m b. 26KN(x)-56KN.m c. -26KN(x)+56KN.m d. None of the above. Maximum bending moment of the beam. a. 47KN.m b. 46KN.m c. 48KN.m d. None of the abovearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY