
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
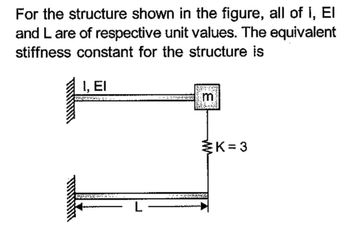
Transcribed Image Text:For the structure shown in the figure, all of 1, El
and L are of respective unit values. The equivalent
stiffness constant for the structure is
1, EI
de Grà
K=3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Triangular wedges stresses.arrow_forward2. From the given figure and data below. Determine the: a. P so that the structure is stable (in equilibrium) b. Draw the FBD of the member BC c. Reaction at A Weight of the member AB and BC = 50kg µ at C= 0.5 1.5 m 3m 1.5 m 30 30° 4, = 0.5arrow_forward1. At a temperature of 5°C, a 3-mm gap exists between the end of polymer bar (1) and support A as shown. Bar (1) is 50 mm wide and 20 mm thick (E = 800 MPa, a = 140 x 10-6/°C). Bar (2) is 75 mm wide and 25 mm thick (E = 2.7 GPa, a = 67 x 106/°C). The supports at A and C are rigid (i.e., fixed). Determine: a) the temperature at which the normal stress in bar (2) will be equal to -3.0 MPa, and b) the lengths of the two polymer bars at this temperature. (1) 3-mm gap 50 mm 500 mm B 75 mm 400 mm (2)arrow_forward
- A load P will be supported by a structure consisting of a rigid bar ABCD, a polymer [E = 2,300 ksi; α = 2.9 × 10-6/°F] bar (1) and an aluminum alloy [E = 10,000 ksi; α = 12.5 × 10-6/°F] bar (2), as shown. Each bar has a cross-sectional area of 2.00 in.2. The bars are unstressed when the structure is assembled at 30°F. After a concentrated load of P = 56 kips is applied and the temperature is increased to 100°F, determine the normal force in bar (1).arrow_forwardThe state of strain of the element has components of €x = 500(106), y = 300(106), Yxy=-200(10-6). Determine the equivalent state of strain on an element at the same point oriented 45° CW with respect to the original element. Eydy! dy Yxy 2 y Yxy 2 -dx- €xdx ·xarrow_forwardAn initially rectangular element of a material is deformed into the shape shown in the figure. Find the: a. Normal strain in the x- direction b. Normal strain in the y- direction c. Total shear strain -Draw and label the diagram correctly, No diagram in the solution will be marked wrong. -Shortcut solution will be marked wrong.- Direction of the assumption of the equilibrium equation must be shown, no direction will be marked wrong.arrow_forward
- A load P will be supported by a structure consisting of a rigid bar ABCD, a polymer [E = 2,300 ksi; a = 2.9 × 10-6/°F] bar (1) and an aluminum alloy [E = 10,000 ksi; a = 12.5 × 10-6/°F] bar (2), as shown. Each bar has a cross-sectional area of 2.00 in.². The bars are unstressed when the structure is assembled at 30°F. After a concentrated load of P = 69 kips is applied and the temperature is increased to 100°F, determine the normal force in bar (1). 6 ft 2.5 ft 07.01 kips 5.63 kips 8.39 kips 9.29 kips 6.66 kips (1) B 3 ft C 8 ft 1.5 ftarrow_forwardThe state of stress on an element is as shown in the figure. If E=2×10 N/mm² and Poisson's ratio = 0.3, the magnitude of the stress o for no strain in BC is 80 N/mm² G B C 80 N/mm²arrow_forwardTwo polymer bars are connected to a rigid plate at B, as shown. Bar (1) has a cross-sectional area of 1.21 in.? and an elastic modulus of 2350 ksi. Bar (2) has a cross-sectional area of 1.032 in.? and an elastic modulus of 4100 ksi. Assume L1=20 in., L2=49 in., Q=7.1 kips, P=2.9 kips, and R=12.9 kips. Determine the horizontal deflection of end C relative to end A. P (1) (2) C В L1 L2 Answer: uc/A in. %3Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning