
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
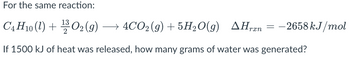
Transcribed Image Text:For the same reaction:
▲Hræn
C4H10 (1) + O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 5H₂O(g) AHran = −2658 kJ/mol
13
If 1500 kJ of heat was released, how many grams of water was generated?
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- When 1.42 g of iron reacts with 1.80 g of chlorine, 3.22 g of iron(II) chloride (FeCl2, molar mass = 126.75 g/mol) and 6.8 kJ of heat is produced. What is the enthalpy change for the reaction when 1 mole of iron(II) chloride is produced? round to sig figsarrow_forwardIn an industrial process to produce ammonia (NH3); nitrogen, N2, reacts with hydrogen, H2, the enthalpy change (∆H) is – 46 kJ/mol. Write a correctly balanced equation for this reaction. Would this reaction absorb heat or give out heat to the environment?arrow_forwardWhat is the enthalpy change for the first reaction? Fe2O3(s) → 2Fe(s) + 3/2O2(g) ΔH = 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) ΔH = -1,652 kJarrow_forward
- In a coffee cup calorimeter, 40.0 mL of 0.33 M nitric acid (HNO3) and 40.0 mL of 0.33 M potassium hydroxide (KOH) are mixed to observe the heat released during the neutralization reaction. Based on the data in the table, what is the enthalpy of the neutralization reaction between HNO3 and KOH? Initial temperature in the calorimeter (°C) Final temperature in the calorimeter (°C) Final mass of the neutralized solution (g) Calorimeter constant (J/C)) 21.3 23.5 79.74 4.57arrow_forwardWhat is the enthalpy change when 2.00 mol of oxygen (O2) react? C12H22O11(s) + 12 O2(g) → 12 CO2(g) + 11 H2O(l) ΔH = -5644 kJarrow_forwardThe reaction between HCl and NaOH is represented below. When equal volumes of 1.00 M NaOH and 1.00 M HCl are mixed, 57.1 kJ of heat is released. What would A H be if 2.00 M HCI and 2.00 M NaOH is used instead of 1.00 M? HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H₂O(l) AH = -57.1 kJ/mol... (A) - 28.6 kJ B-85.7 kJ (c) -57.1 kJ D - 114 kJarrow_forward
- The flame in a torch used to cut metal is produced by burning acetylene (C2H2)(26.04 g/mol) in pure oxygen. Assuming the combustion of 1 mole of acetylene releases 1251 kJ of heat, what mass of acetylene is needed to cut through a piece of steel if the process requires 22.5 × 104 kJ of heat? 2 C2H2(g) + 5 O2(g) → 4 CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) ΔH = –2502 kJarrow_forwardWhen 3.8 g A are reacted with 8.5 g D, according to the balanced chemical equation below, 33 kJ of energy are released. Please calculate the enthalpy for this reaction when 3 moles of G are produced. 2A + 3D = 2Z + 3G given molar masses: A = 141.8 g/mole D = 63.996 g/ mole Z = 4.032 g/ mole G = 56.028 g/ molearrow_forwardcan you please solve part c and darrow_forward
- Consider the following chemical reaction which produces nitric oxide from its constituent elements: N2 (g) + O2(g) → 2 NO (g) AH = 182.6 kJ/mol If nitrogen and oxygen were mixed and allowed to react under constant pressure conditions, which of the following statements must be true? Select as many answers as applicable however points will be deducted for incorrect guesses. ΔΗ = q This is an endothermic reaction The temperature of the surroundings would decrease The temperature of the surroundings would increase AH = AUarrow_forwardThe enthalpy of formation of H2O(l) is -285.8 kJ/mol. What is the enthalpy change if 1.62 g H2(g) reacts with 9.21 g O2(g) to form H2O(l)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY