
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
For the following problems use an allowable stress equal to 25 ksi for both
tension and compression. Calculate the volume of the truss.
PART A. Use the beam-truss analogy to design the following truss.
PART B. Perform the structural analysis of the truss and design each member using its
actual internal force. Compare the truss volume to the one of PART A.
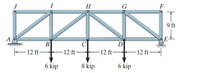
Transcribed Image Text:The image illustrates a truss structure supported at points A and E, with a series of interconnected members labeled from J to F. The truss spans a total length of 48 feet, divided into four 12-foot segments between the joints B, C, D, and E.
**Structure Details:**
- **Support Points:**
- Point A: Fixed support on the left.
- Point E: Roller support on the right.
- **Members and Joints:**
- The members are connected sequentially at the joints indicated by letters J, I, H, G, and F.
- **Forces:**
- A downward force of 6 kips is applied at joint B.
- A downward force of 8 kips is applied at joint C.
- A downward force of 6 kips is applied at joint D.
- **Height:**
- The vertical distance from joint F to joint J is 9 feet.
The truss is designed to evenly distribute loads across the structure, which is crucial in civil engineering applications to ensure stability and safety. Understanding the distribution of forces and the support system helps in analyzing the structural integrity of bridges, roofs, and similar constructions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The two vertical steel [E = 200 GPa] rods that support rigid bar ABCD are initially free of stress. Rod (1) has an area of A1 = 410 mm2 and a length of L1 = 3.2 m. Rod (2) has an area of A2 = 355 mm2 and a length of L2 = 1.3 m. Assume dimensions of a = 3.4 m, b = 1.2 m, and c = 1.5 m. After a load of P = 50 kN is applied to the rigid bar at D, determine: (a) the normal stresses in rods (1) and (2) (b) the magnitude of the downward deflection of the rigid bar at D. y,v (2) L2 a B C D x,u Rigid bar |(1) Answer: (a) o1 = i MPa 02 = i MPa (b) VD = i mmarrow_forwardPlease help on the 3 questions in the photoarrow_forwardB 900 N Determine the force in each 1.2 m member of the truss and A D indicate whether the members 0.9m 1.5m are in tension or 2700 N compression.arrow_forward
- truss. need asaparrow_forwardProblem 2: Determine the forces in all diagonal and horizontal members of the truss shown below using the method of sections. Determine the force in all vertical members using the method of joints. Hint, the structure is symmetric. The distributed load is transferred to the truss from the roof purlins. State whether the members are tension or compression. Summarize your results on a sketch of the truss. 2.5 k/ft H M K 12 ft A G B C D F 6 @ 12 ft = 72 ftarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning